This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Associate Professor, Doctor, Doctor Hoang Dang Mich - Head of Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Department of Medical Examination and Internal Medicine - Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital.Among postpartum thyroid disorders, postpartum hyperthyroidism is common. In particular, hyperthyroidism is more likely to recur and worsen in the postpartum period because at this time, women pay less attention to periodic re-examination and treatment of the disease as prescribed by the doctor.
1. What is hyperthyroidism?
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped endocrine gland, usually located in the front under the neck. The function of the thyroid gland is to synthesize thyroid hormone, which is secreted into the bloodstream and carried to the tissues of the body. Thyroid hormone helps the body use energy, keep warm, and keep the brain, heart, muscles and other organs working properly. Hyperthyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland increases its production of thyroid hormones (including thyroxine and triiodothyronin). In patients with hyperthyroidism, too much thyroxine in the body promotes an abnormally high level of metabolism.Patients often have some typical signs such as difficulty sleeping, irritability, muscle weakness, increased heart rate, heat intolerance, diarrhea, enlarged thyroid gland (goiter) and weight loss.
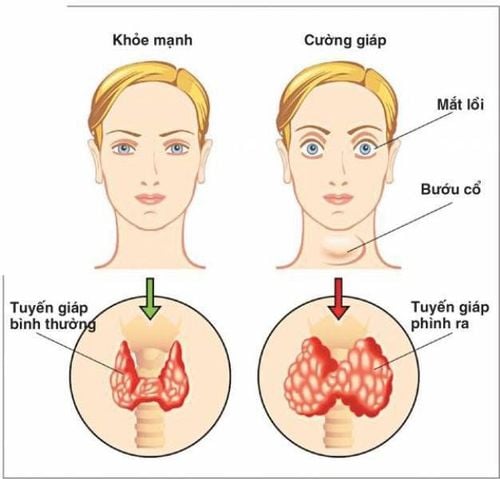
2. The relationship between hyperthyroidism and pregnancy
The cause of hyperthyroidism during pregnancy is mainly Graves' disease (accounting for 80-85% of cases), the prevalence is 1/1,500 pregnant women. In addition, some cases of too high hCG also cause symptoms of hyperthyroidism.Hyperthyroidism can cause preterm labor or preeclampsia. In addition, the mother is also at high risk of heart failure or acute thyrotoxicosis. Basedow's disease may improve in the third trimester of pregnancy or worsen in the postpartum period.
The risks of hyperthyroidism to the fetus are:
Hyperthyroidism is not well controlled, causing the baby to have a congenital heart defect, slow fetal growth, stillbirth, premature birth or possibly birth defects. ; TSI (thyroid hormone too high): Crosses the placenta, can affect the thyroid gland of the fetus and cause hyperthyroidism in the newborn; Synthetic antithyroid drugs Thyrozol and PTU cross the placenta, can affect thyroid function and cause fetal goiter.

3. Treatment options for hyperthyroidism in pregnancy
For pregnant women with mild hyperthyroidism (faint symptoms, slightly increased hormone levels) will be closely monitored without treatment. For severe cases of hyperthyroidism, which requires treatment with synthetic antithyroid drugs, PTU should be selected and thyroid hormone closely monitored monthly, to avoid hypothyroidism for mother and baby.Pregnant women with drug allergies that cannot be treated with synthetic antithyroid drugs can choose surgery. However, thyroidectomy should be carefully considered because of the high risk of complications in anesthesia, adversely affecting the health of both mother and child.
Contraindicated radioactive iodine treatment for pregnant women because radioactive iodine crosses the placenta causing loss of thyroid function of the fetus.
4. Hyperthyroidism is easy to recur and develop after giving birth

Treatment and monitoring time for hyperthyroidism is quite long. The risk of recurrence of hyperthyroidism after childbirth is quite high because at this time, the mother is too busy to pay attention to the periodic health check. There have been many cases of hospitalization with bad condition due to recurrent hyperthyroidism.
Therefore, after giving birth, pregnant women need to pay special attention to strictly following the doctor's advice in periodic re-examination and using prescribed drugs. This prevents hyperthyroidism from getting worse or turning into hypothyroidism due to drug overdose, which seriously affects the health of mother and baby. At the same time, besides medication and follow-up, the mother also needs to pay attention to the lifestyle, rest and eating regime, limit stress, anxiety,...
5. How to prevent thyroid disorders for women after giving birth

To prevent the risk of postpartum thyroid disorders, new-born women should pay attention to the following:
Eat a reasonable diet, add more fruits, grains, lean meat to the diet,. .. This is a healthy food group and good for breast milk; Exercise after giving birth, starting with gentle exercises, then gradually increasing the intensity according to your own health condition; Get enough sleep; People with hyperthyroidism should limit foods high in iodine and dairy products such as sea fish, kelp, sea crab, fish sauce, iodized salt, cheese, butter, ice cream, yogurt,... If you are concerned about hyperthyroidism, especially when you intend to become pregnant or give birth, it is best for the patient to see an endocrinologist at Vinmec Times City International Hospital for examination and accurate advice. best.
Vinmec Times City is the destination of endocrinology examination chosen by many customers because:
Gathering a team of highly qualified, experienced doctors and nurses, wholeheartedly for the patient's health; Comfortable facilities, equipped with modern machinery system, best support for diagnosis and treatment of diseases; Provide comprehensive medical examination, consultation and treatment services;
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.