This is an automatically translated article.
Hypoglycemia due to hyperinsulinemia in children is a pediatric emergency. The most serious complication of the disease is hypoglycemia with brain damage and can lead to death for the child if not treated promptly.
1. What is hypoglycemia due to hyperinsulinemia in children?
Hypoglycemia in Children (PHHI), also known as childhood hyperinsulinemia, familial hyperinsulinemia, or primary islet cell hyperplasia (nesidioblastosis). The disease is defined as excessive insulin secretion despite low blood sugar. Neonatal hypoglycemia is the leading cause of severe, recurrent hypoglycemia in infants. If not treated properly and promptly, persistent episodes of hypoglycemia in children will cause many permanent damages such as irreversible central nervous system failure, severe neuropsychiatric sequelae, and disability. later ruin the child and even die.
2. Methods of treating hypoglycemia due to hyperinsulinemia
2.1. Principles of treatment of persistent hypoglycemia in infants requires frequent, continuous infusion of sugar or glucose or feeding to maintain a safe blood glucose level. The treatment of hypoglycaemic children in this case requires maintenance of a hypertonic glucose solution intravenously and parenteral delivery. Administer glycemic agents and subtotal pancreatectomy if the pancreatic islet is diffusely involved and eliminate focal lesions. The goal of treating hypoglycemia in children is to maintain the child's blood sugar level above the threshold of 3.8 mmol/l, to avoid brain complications from excessive hypoglycemia. 2.2. Pancreatectomy in hyperinsulinemic children Surgical treatment is indicated if medical therapy is not sustained or an isolated lesion can be identified. The distinction between focal and diffuse lesions is important for selection in surgical intervention. If a focal lesion is found before or during surgery, it can be resected in situ without pancreatectomy. The recommended surgical approach is to take multiple biopsies from different parts of the pancreas. If abnormal beta-cell nuclei are found in all specimens, there is a diffuse lesion, and pancreatectomy is indicated. However, if only one sample contains an abnormal beta cell nucleus, this is a focal lesion. Abnormalities in the biopsy specimen may include a significant increase in size or an irregular shape such as the crescent or ovoid shape of beta cells. In neonatal hypoglycemia, surgery is usually performed within the first 2 months of life. Early complications can be seen after surgery such as bleeding and wound infection. Late complications of surgical treatment include exocrine pancreatic insufficiency and glucose intolerance or diabetes mellitus.
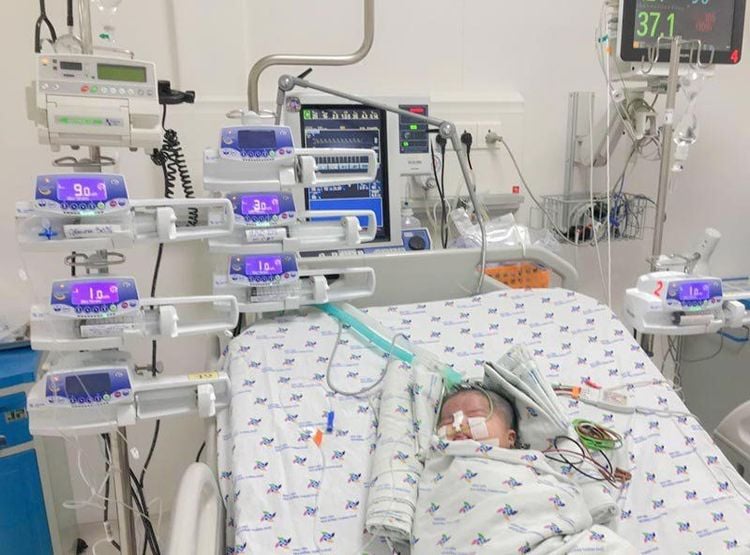
Hạ đường máu ở trẻ sơ sinh cần được chăm sóc và điều trị tích cực
3. Lifestyle and nutrition with hypoglycemia in children
Children need to eat 3 full meals and 3 snacks per day for the purpose of maintaining the serum glucose level at a safe level. Do not let children fast because it will cause blood sugar to drop quickly. Feed children high-protein, high-carbohydrate diets as they provide a prolonged source of glucose to inhibit the continued release of insulin. Always have foods that provide quick sugars such as glucose tablets, glucose gels, fruit juices, hard candies, or sugar with you at all times to prevent hypoglycemia in your child. If the child has persistent vomiting or diarrhea for a long time, parents need to take the initiative to bring the child to the hospital and possibly feed continuously with a nasogastric tube. When children participate in strenuous activities, it is necessary to provide carbohydrates. At home, parents need to have a blood glucose meter and understand how to use it to monitor glucose levels for children.
4. When to take the child to the doctor?
Hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia in children is a rare pediatric emergency. Parents should note that when a newborn baby weighs less (> 4kg) with signs of lethargy, lethargy, poor feeding, respiratory failure, convulsions, etc., it is necessary to quickly take the child to a hospital with a specialist. Department of pediatrics for examination, testing and definitive diagnosis. From there, doctors will come up with appropriate treatment plans, promptly saving the child's life.
Pediatrics department at Vinmec International General Hospital is a prestigious place to receive and examine many diseases with infants and young children, including hypoglycemia in infants. .... With the most modern equipment system, sterile space, minimizing the impact as well as the risk of disease spread. In addition, the dedication from doctors, nurses with professional experience with pediatric patients, helps to best examine and care for children and is no longer a concern of parents.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.