This is an automatically translated article.
Chronic glomerulonephritis is a disease with damage to the glomeruli that progresses over many years leading to chronic kidney failure, with the risk of kidney failure complications causing bad consequences for the patient.1. What is chronic glomerulonephritis?
The disease includes conditions of proliferation, edema, exudation and necrosis of hyaline, partial or total fibrosis of the glomeruli. The disease progresses chronically over many years leading to atrophic fibrosis in both kidneys. The disease can progress in stages, after 10-15 years, irreversible chronic kidney failure will appear.Chronic glomerulonephritis is a quite dangerous disease, with this disease, kidney function will be reduced, gradually losing the ability to remove toxic substances from the body and eliminate excess fluids from the body. and causes serious complications such as:
Acute kidney failure causes loss of kidney filtering function, rapid accumulation of toxic substances, in some cases patients need urgent dialysis. Chronic kidney failure is a life-threatening complication of the patient, when kidney function is completely lost, hemodialysis or kidney transplant is required at a very high cost if you want to maintain life. High blood pressure is caused by the accumulation of waste products in the blood. Nephrotic syndrome
Viêm cầu thận mạn là bệnh lý khá nguy hiểm, khi mắc bệnh này chức năng thận sẽ bị suy giảm
2. Recognizing signs of chronic glomerulonephritis
When acute glomerulonephritis occurs for more than 3 months and does not go away due to untreated or inadequately treated, intermittently, it will move to the chronic stage of glomerulonephritis. Symptoms depend on the degree of kidney failure or may not be kidney failure.The function of the kidneys begins to gradually decline, so the symptoms of the disease are very diverse, sometimes due to the accidental urine test during the medical examination for some reason, and the protein and pink color are found. glomerulonephritis, other symptoms are very subtle and do not appear. Most cases of chronic glomerulonephritis have pale, itchy, and edematous skin and mucous membranes.
Edema is the most typical symptom of chronic glomerulonephritis. In the early stages of the disease, there may be discreet swelling, which has not yet affected health, so the patient can still work, work, eat, sleep and live normally, even without knowing he has edema. If the disease begins to worsen, the edema will be very obvious such as facial edema, under the skin around the ankle before the tibia, the sacrum, under the scalp that even the patient can feel and see. Characterized by soft, concave edema on a hard base such as the ankle. In severe disease, edema may present in the form of neck, pleural effusion, or hydrocele. The majority of cases are poor appetite due to anorexia, muscle pain, bone pain, nausea or vomiting (uremia).
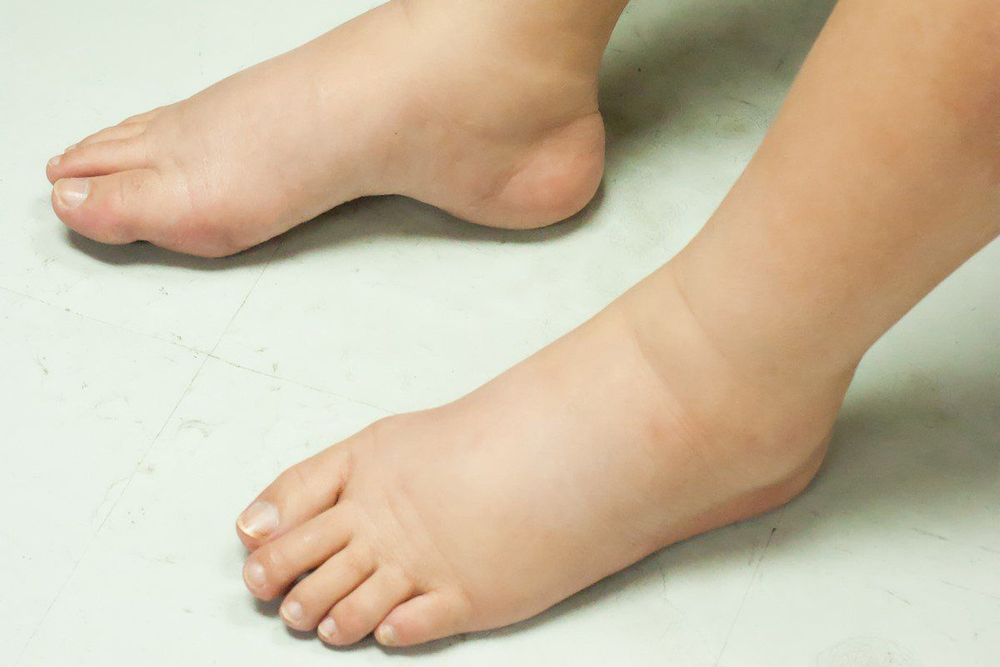
Phù là triệu chứng điển hình nhất của viêm cầu thận mạn.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.