This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master. BSCK II Phan Thi Minh Huong - Gastroenterologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Da Nang International General Hospital.The liver plays an important role in the storage and metabolism of fats. However, when too much fat accumulates in the liver, it causes fatty liver disease. So how many levels of fatty liver and how dangerous is this disease?
1. Definition of fatty liver
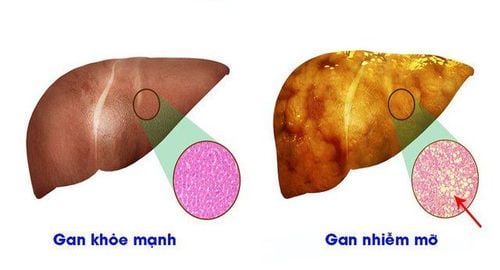
The normal liver weighs about 2,300 grams, is the second largest organ in the body, helping to process nutrients from food and filter out harmful substances. In every 100g of the weight of the liver contains about 5g of lipids, of which 14% are triglycerides, 64% are phospholipids, 8% are cholesterol and 24% are free fatty acids).Fatty liver is defined when the accumulation of fat in the liver exceeds 5% of the weight of the liver or can define fatty liver when observed under the microscope more than 5% of hepatocytes contain particles fat. Most cases of fatty liver are mainly composed of triglycerides, and in a few other cases, the fat is mainly phospholipids.
Fatty liver can be the result of many different diseases and lifestyle habits. From metabolic diseases, nutritional disorders, medication use to alcoholism can all lead to fatty liver.
Rượu là nguyên nhân dẫn đến xơ gan và gan nhiễm mỡ
2. Identify fatty liver
Most patients with fatty liver will not show any symptoms. Most cases are discovered by chance during routine physical examination, some patients are noted to have an enlarged liver, or mild changes in liver enzymesSome cases are discovered by chance through ultrasound General abdomen to screen and check for other diseases. A few are encountered during CT scans to screen for biliary tract diseases.
Manifestations of fatty liver (very low incidence) include fatigue and discomfort in the right upper quadrant or epigastrium. More severe, the patient may appear jaundice, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting.
When fatty liver goes to the stage of loss of liver function or cirrhosis, it shows more clearly such as jaundice, yellow eyes, dark skin, red palms, angioedema, leg edema, ascites, collateral circulation, splenomegaly, hemorrhoids or esophageal varices or severe gastrointestinal bleeding complications.
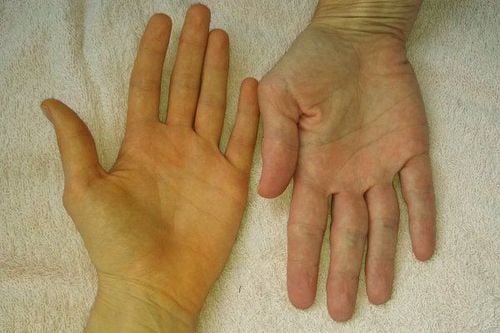
Vàng da là triệu chứng phổ biến của bệnh
3. How many levels of fatty liver?
In the beginning, fatty liver often does not affect health, so patients often do not know they have the disease and do not receive early treatment. However, whether fatty liver is dangerous no longer depends on the degree of fat at the time of disease detection and whether the treatment is correct and timely.Not everyone knows that long-term fatty liver can lead to cirrhosis (20%), impaired liver function. Fatty liver has several levels depending on the severity of the disease and complications:
Fatty liver grade 1: fat percentage accounts for 5 - 10% of the total weight of the liver, this is the first stage of the disease so the symptoms are usually very mild and do not pose a health risk. The thing to do in the treatment of grade 1 fatty liver is to change your diet, increase exercise and follow the doctor's treatment method. Grade 2 fatty liver: is the second stage of the disease, the percentage of fat in grade 2 has reached 10-25% of the weight of the liver. At this time, the fat has spread to the liver and diaphragm tissues, although it is not yet a major health hazard, if not treated promptly, grade 2 fatty liver can progress to grade 3. Level 3 fat: is the final stage of fatty liver disease and is the most dangerous stage, very difficult to treat and recover, possibly even death or increase liver complications such as cirrhosis, cancer liver letter.

Gan nhiễm mỡ kéo dài có thể dẫn đến xơ gan
4. Can fatty liver be treated?
In fact, there is no specific treatment for fatty liver disease. Currently, doctors only focus on treatment on the principle of eliminating or minimizing the cause of the disease.Fatty liver due to overweight and obesity: treatment methods often focus on building a reasonable diet and scientific exercise regime to help lose weight. Fatty liver due to alcoholism: stop drinking alcohol. Fatty liver due to drug use: Immediately stop the drugs that are toxic to the liver and replace the safer drug as prescribed by the doctor. Fatty liver is a consequence of metabolic diseases, especially diabetes: blood sugar control is within the normal range. Fatty liver caused by viral hepatitis: Treatment should be focused on controlling inflammation and limiting adverse events that can lead to cirrhosis.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.