This is an automatically translated article.
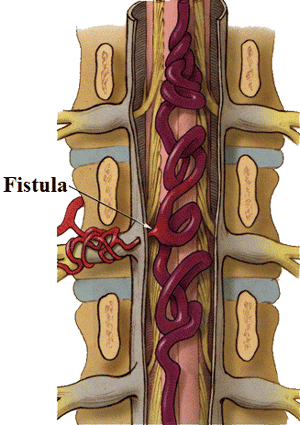
Marrow vascular malformation is a congenital disease, caused by a disorder in the development of blood vessels during the fetal period. The disease can progress silently, without symptoms, but there is a risk of sudden paralysis, or “sudden death”.1. Danger of spinal vascular malformations
Medullary vascular malformations can progress silently, without symptoms for a long time, until the blood vessels are too dilated, pressing on the spinal cord and nerves or may rupture. cause spinal cord bleeding.
If the malformed mass is located in the cervical spinal cord, the patient may experience numbness and weakness in the arms and legs, which can then lead to paralysis of the limbs, stop breathing and lead to death, if not treated promptly.
Deformity mass located in the thoracic or lumbar spinal cord will cause symptoms of slow weakness in the legs followed by muscle atrophy in both legs. The patient could not walk, then became paralyzed in both legs, and could not urinate. Patients usually have no or very little pain. However, in the case of a ruptured malformation, pain and paralysis often occur suddenly and rapidly.
2. Diagnosis of spinal vascular malformations
Currently, the Vinmec hospital system usually performs two diagnostic tests, including:
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): This test will use a magnetic field and frequency waves to create detailed images of the spinal cord. . MRI is capable of detecting an aneurysm that is the result of abnormally connected blood vessels along with a vascular malformation. Angiography: This test is often used to detect the location and characteristics of the malformation of the blood vessel. A catheter is inserted into the femoral artery and guided to the spinal cord, and contrast is injected into the spinal blood vessels to make them visible on radiographs.
Chẩn đoán bệnh dị dạng mạch máu tủy sống
3. Treatment of spinal vascular malformations
Treatment of spinal vascular malformations involves a combination of methods to relieve symptoms as well as reduce the risk of complications. Treatment options will often depend on the size, location, and blood flow of the deformity, your neurological exam, and your general health.
The goals of treatment for spinal vascular malformations are to reduce the risk of bleeding and to stop or prevent progression of symptoms.
Digitalization of spinal cord malformations and nodes is a technique for treating spinal vascular malformations applied at Vinmec international general hospital:
Cervical region: Selective catheterization of the second vertebral artery side, body armor, neck and shoulder, then pump the drug. The dorsal and apical spinal cord: Insert a 4 - 5F catheter to each intercostal artery for injector imaging. Find the artery of Adamkiewicz, usually split across the level of the T7-T9 thoracic vertebrae, the incidence of many left T9 sites. Inject the contrast agent through the machine with a volume of 6ml, speed of 2ml/s, pressure of 300 PSI. Recording and taking series of films focusing on the skull in an upright position, can take more inclined or oblique films when there is an injury. Arteriovenous malformation plug
Insert a 1.3-1.4 F microcatheter into the feeding pedicle to the malformation below the lead 0.08-0.11” Methods NBCA Glue Collation : Mix NBCA with Lipiodol depending on the degree of catheterization: If the flux is large, the phase is solid, if the flux is low, the phase is diluted. Inject a mixture of NBCA and Lipiodol through the microcatheter into the fovea. When there is reflux, immediately withdraw the microcatheter. Button with Onyx: Use a separate microcatheter or do not reach the malformation. The DMSO pump fills the microcatheter void. Pump slowly Onyx. When there is reflux, stop for 2 minutes, then pump again. If a non-separable microcatheter is used, reflux is not allowed to exceed 2 cm. If a separate microcatheter is used, the reflux position should not exceed the Marker position that breaks the cord. Metal spiral plug: When the catheter is direct, release the metal coil to block the catheter. After the scan is satisfactory, remove the catheter and catheter and apply manual pressure directly on the puncture site for about 15 minutes. minutes to stop bleeding, then apply pressure for 8 hours. Neurology - Department of Examination and Internal Medicine - Vinmec International General Hospital is the address for treating cerebrovascular malformations with many outstanding advantages such as: There are many different specialties, a team of rich doctors experience in specialized fields, modern equipment system..
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.