This is an automatically translated article.
The article is expertly consulted by a Doctor of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Da Nang International General Hospital.Acute pancreatitis is a relatively common gastrointestinal disease in the community. The most common causes are acute gallstone pancreatitis and acute alcoholic pancreatitis. The disease often progresses acutely with severe severity, but how dangerous acute pancreatitis is, not everyone knows. Here are the complications of acute pancreatitis we need to pay close attention to.
1. Collection of fluid around the pancreas
When the pancreas is acutely inflamed, the pancreatic parenchyma is damaged. The pancreatic cells are no longer structurally secure, so they burst, releasing the cytoplasm containing pancreatic enzymes, causing fluid to accumulate around the pancreas. This is the earliest sign on ultrasound that helps to suspect the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis in the situation where the patient is admitted to the hospital because of epigastric pain with severe vomiting.If the degree of inflammation is localized or rapidly intervened, the complication of fluid accumulation is merely around the pancreatic tissue and will be absorbed slowly. If the degree of inflammation is severe or delayed, the inflammatory fluid spreading around will be favorable conditions for necrosis or intra-abdominal infection.
2. Pancreatic pseudocyst
Pancreatic pseudocyst is a complication occurring in the second or third week after the onset of acute pancreatitis. Pancreatic enzymes are released instead of spreading around, the inflammatory response stimulates the creation of fibrous tissue to localize pancreatic juice, limiting the spread of damage to surrounding tissue.These cysts may spontaneously degenerate or open to the pancreatic duct, then disappear over the next several weeks. However, if the cyst is too large and contains a lot of fluid, the survival time may be longer. At this time, the patient needs to be intervened with early drainage because this is a factor that promotes infection and abscess.
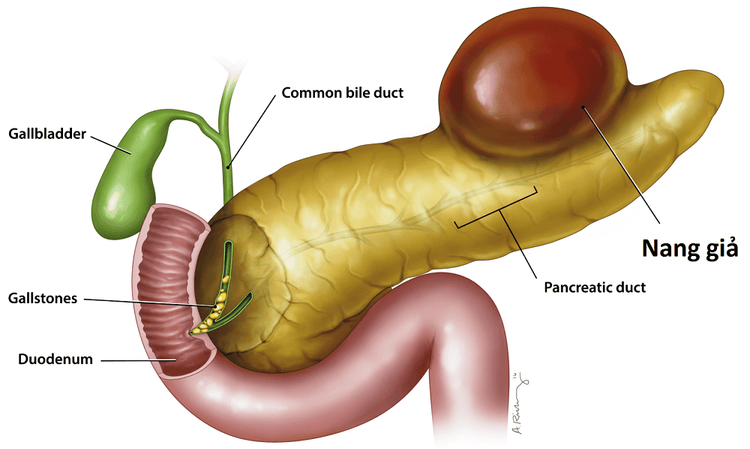
Nang giả tụy là biến chứng xảy ra vào tuần thứ hai hoặc thứ ba sau khởi phát viêm tụy cấp
3. Pancreatic necrosis
The pancreas is a gland that is both endocrine and exocrine. The exocrine function of the pancreas is to produce and supply digestive enzymes to the small intestine, which help break down food into small sized nutrients for absorption into the bloodstream.Therefore, when pancreatic enzymes are released from the parenchyma, the pancreas itself will also be "digested" by pancreatic enzymes, causing necrosis. The more the pancreatic parenchyma is necrotic, the more pancreatic enzymes are released, creating a vicious cycle and extremely severe disease progression.
4. Cholestasis
The pancreas and the hepatobiliary system share a common duct that carries digestive enzymes into the small intestine. When the pancreatic parenchyma is inflamed, the edema will cause obstruction of the bile ducts, blocking the bile.Bile is secreted by liver cells and is not consumed, causing stagnation, damaging the liver as well as creating conditions for bacteria to easily invade and cause disease.
5. Abdominal infections
This is the result of the release and stagnation of pancreatic juice in the abdomen, following the complications mentioned above. This complication usually occurs around the end of the first week or the beginning of the second week after the onset of acute pancreatitis.Persistent inflammation turns to an abscess. The accumulation of inflammation can be anywhere in the abdomen, such as around the pancreas, under the liver, under the diaphragm, in the sac... If not treated promptly with the appropriate course of antibiotics, the abscess will burst. out, pus and bacteria spread to the abdomen, leading to peritonitis and easy septic shock and toxicity.
6. Bleeding
Pancreatic enzymes are released and enter the bloodstream as a toxin. Blood vessel walls are damaged and bleeding occurs everywhere.This complication, if it occurs, usually appears very early, within a few days of pancreatitis. The state of blood cells as well as plasma extravasation everywhere easily causes circulatory collapse, high prognosis of death.
7. Thrombosis
Biến chứng huyết khối có thể xảy ra khi bị viêm tụy cấp
8. Multi-organ failure
Because pancreatic enzymes, when released out of the parenchyma, will trigger a "waterfall" that activates the inflammatory response process in the body, causing damage to the organs. Patients easily fall into acute respiratory failure due to pulmonary edema, circulatory collapse due to acute heart failure, toxic accumulation due to acute renal failure ... and multi-organ failure, including nervous system, hematology.As a result, it will quickly lead to shock and life-threatening if it is not detected early and does not have timely treatment facilities.
9. Exacerbation of medical diseases
Acute pancreatitis is also considered an acute-onset event of medical comorbidities despite being well controlled. Important medical diseases can be coronary artery disease, chronic heart failure, chronic lung disease, chronic kidney failure ...At this time, the patient is not only affected by complications of acute pancreatitis but also affected by the episode. level of internal diseases. The progression of the disease becomes more severe than that of a person without a history, the treatment problem will be more difficult.
10. Chronic pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis will result in a patient with recurrent acute pancreatitis. The most common cause of this condition is acute alcoholic pancreatitis. Not only that, in subjects with alcohol abuse, the risk of multiple acute pancreatitis is very high on the background of chronic inflammation of the pancreatic parenchyma.At that time, these patients also have to face complications of chronic pancreatitis such as prolonged digestive disorders, leading to exhaustion due to malnutrition, diabetes due to pancreatic damage and even pancreatic cancer.
In short, the pancreas is a small organ, with a silent mission and hidden in the abdomen. However, when acute inflammation, this organ causes serious complications, easily affecting life if not treated promptly.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.