This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Le Hong Lien - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.1. When was ultrasound invented?
Ultrasound was first used for clinical purposes in 1956 in Glasgow. Obstetrician Ian Donald and engineer Tom Brown have developed the first prototype systems based on an instrument used to detect industrial flaws on ships.By the end of the 20th century, ultrasound imaging had become routine in maternity clinics around the developed world. Technology has undergone extensive development over the past 20 years.
2. How does ultrasound work?
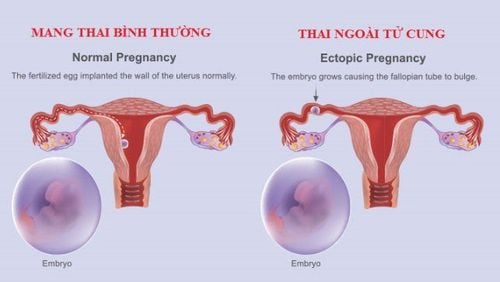
Ultrasound imaging consists of "ultrasonic" sound waves that bounce back - above the range of human hearing - at body structures or tissues and detect the echoes.Obstetric ultrasound is used to take pictures of the fetus in the mother's uterus. It is used to confirm pregnancy, to determine the sex and number of fetuses, and to detect fetal anomalies such as microcephaly (abnormally small head), absence of kidneys, and spinal problems.
During the scan, ultrasound waves are aimed at the pregnant woman's abdomen. Based on the angle of the beam and the time it takes for the echo to return, images of body structures inside the fetus can be created.
In the early days of using fetal ultrasound, clinicians can only detect the baby's head.
3. Types of fetal ultrasound
There are basically 7 different types of ultrasound used, the process and principle are the same. Types of fetal ultrasound include:Transducer ultrasound : Specially designed, using a transvaginal imaging transducer. Usually used in the early stages of pregnancy. Standard 2D ultrasound : Ultrasound uses an abdominal transducer to create 2D images of the fetus Morphological fetal ultrasound : Same as 2D ultrasound but at 12 weeks and 22 weeks to detect abnormalities defects due to chromosomal abnormalities and fetal morphology. 3D-4D- HD live ultrasound: Use specially designed transducers and software to create 3-4-5D images of the fetus. Color Doppler ultrasound: Used to measure small changes in the frequency of ultrasound waves on blood vessels to detect abnormalities such as fetal growth retardation, pre-eclampsia, placenta accreta... Fetal echocardiography: Use ultrasound waves to evaluate your baby's heart function and anatomy. This is used to evaluate fetal heart defects.

4. Is ultrasound safe?
One of the main advantages of ultrasound is that it is non-invasive. The procedure has been performed safely on millions of pregnant women. Concerns about its safety have periodically arisen, with research suggesting that these stem from concerns about the technology's role in pregnancy rather than evidence of harm. They can be confident that at the levels currently used for clinical investigation, ultrasound is safe. No damage patterns were found.However, at high power, ultrasonic waves are capable of damaging human tissue. The researchers don't know exactly to what extent this happens, adding that testing the threshold at which it becomes dangerous in humans would be unethical.
Ultrasound should only be performed for clinical reasons. For example, the so-called "linked scan", taken purely for commemorative purposes, unnecessarily exposes the fetus to high-energy sound waves.
5. How does ultrasound affect emotions?
Ultrasound has enjoyed an enthusiastic reception by pregnant women. In addition to revealing the baby's health, the image also provides a keepsake, especially if the baby moves. In fact, some women say they don't feel pregnant until they see an ultrasound picture.Seeing a developing fetus also has a anthropomorphic effect. One study found that doctors helped develop technology and knew moral images of women contemplating abortions.
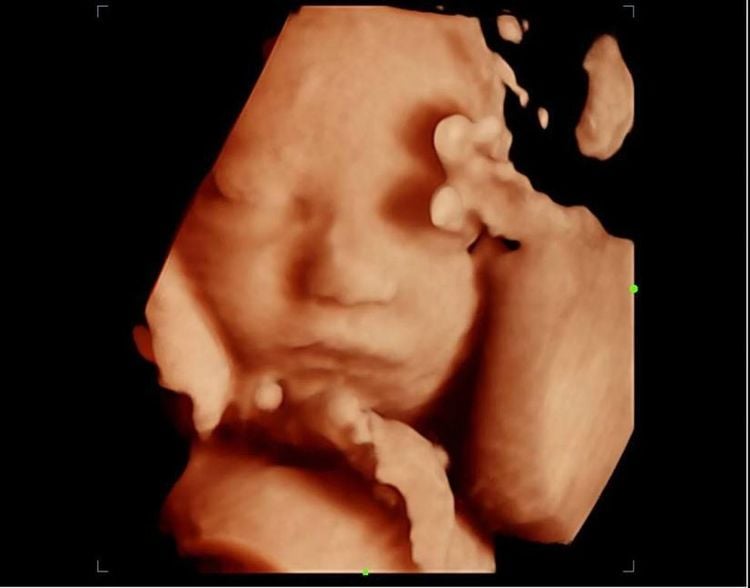
6. Does ultrasound have social significance?
Ultrasound imaging sometimes plays a role in decisions to maintain or terminate a pregnancy. Proponents of abortion take ultrasound images as proof that the fetus is still alive and therefore should not be aborted.On the other hand, ultrasound can be used to diagnose potentially fatal or debilitating abnormalities in the fetus, which may encourage termination of pregnancy.
In some East Asian countries, ultrasound is used to detect the sex of the baby unambiguously so that a fetus with less sex drive (usually female) can be aborted.
However, anecdotal evidence suggests that if pregnant women see pictures of their fetuses - especially of their own - they are less likely to terminate the pregnancy.
Vinmec International General Hospital now has a package of Maternity services, protecting the health of mother and baby during pregnancy - during labor and after birth. When registering for the Maternity Package, pregnant women are examined and monitored for pregnancy by experienced doctors and specialists in Obstetrics and Gynecology, and are able to perform all necessary tests and ultrasounds during pregnancy for monitoring. development of the baby as well as the health of the mother. Experience a "painless birth" and a comprehensive and thoughtful postpartum care program.
Specialist I Le Hong Lien has been an obstetrician-gynecologist at Vinmec Central Park International Hospital since November 2016. Doctor Lien has over 10 years of experience as a radiologist in the Department of Ultrasound at the leading hospital in the field of obstetrics and gynecology in the South - Tu Du Hospital.
Reference source: livescience.com
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.