This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Pham Thi Yen - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital. Doctor has more than 10 years of experience in examination and treatment in the field of Obstetrics and Gynecology.Hepatitis B and hepatitis C are two very common diseases, but difficult to detect through symptoms, mainly based on laboratory test results. Pregnant women with hepatitis, if not treated promptly, will be at risk of transmitting it to the fetus and causing unfortunate consequences.
1. What are hepatitis B and hepatitis C?
Hepatitis B and hepatitis C are two serious infections that affect the liver, caused by viruses. Both are potentially infectious and carry the risk of serious, long-term complications.Pregnant women with hepatitis not only face the symptoms of hepatitis, but can also pass the virus on to the baby. Many pregnant women don't even know they're infected because the infection sometimes causes no signs or symptoms.
2. How is the hepatitis B virus transmitted?
The hepatitis B virus is transmitted directly through bodily fluids (such as blood, semen, or vaginal fluids) of an infected person. Infection usually occurs during unprotected sex or when sharing needles. For pregnant women with hepatitis B, the baby can be infected at birth. The hepatitis B virus can also be spread if you live with an infected person and share household items that come in contact with bodily fluids, such as toothbrushes or razors. Hepatitis B cannot be spread through casual contact with people or animals. Hepatitis B is not passed on to the baby while the mother is breastfeeding.3. Symptoms of Hepatitis B
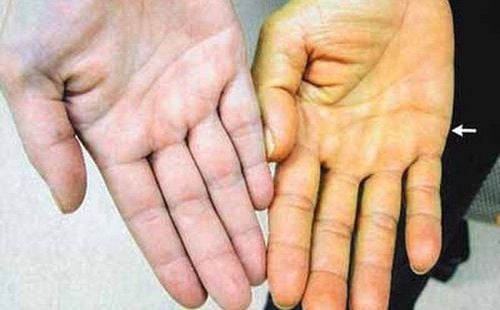
Symptoms of hepatitis B virus infection can be acute or chronic. Acute hepatitis B infection is short-lived for the first 6 months after infection. Common acute symptoms of hepatitis B include:Fatigue Loss of appetite Nausea and vomiting Jaundice (a condition in which the skin and conjunctival area of the eyes become unusually yellow) Abdominal pain Abdominal pain Muscles and joints Pregnant women with hepatitis B often find it difficult to recognize the symptoms because they are so similar to the natural changes in pregnancy. The infection usually clears up completely on its own within a few weeks without treatment. Patients infected with hepatitis B who have recovered from the disease become immune to it, which means they cannot get hepatitis B a second time.
However, a small number of patients, including adults and even children under 5 years of age, infected with hepatitis B never recover. This phenomenon is called chronic hepatitis B infection. These patients always have hepatitis B virus in them for the rest of their lives. They are considered disease carriers. Most cases of chronic hepatitis B do not have any symptoms. However, in rare cases, chronic hepatitis B carriers can lead to serious complications, such as cirrhosis, liver cancer and death.
A mother with hepatitis B can pass it on to her baby and leave many dangerous complications. Specifically, about 90% of pregnant women infected with acute hepatitis B virus will pass the virus on to their babies. For chronic hepatitis B, this rate is about 10% to 20%.
4. Effects of hepatitis B virus on the baby
Being infected with hepatitis B does not affect having a baby. Pregnant women can still give birth vaginally and breastfeed normally if they are infected with the hepatitis B virus.However, hepatitis B is a serious condition for the newborn baby, threatening her later life. they. Infected infants have a high risk (up to 90%) of becoming carriers and transmitting the disease to others. As adults, children who have been infected with the hepatitis B virus since childhood have a 25% increased risk of dying from cirrhosis or liver cancer.
5. Hepatitis B Test
All pregnant women should be tested for hepatitis B. Different blood tests are now available to diagnose hepatitis B virus infection. They will tell you whether the infection is acute or chronic. In addition, you also know whether you have been infected with hepatitis B in the past, are currently immune to the disease and whether you have received the hepatitis B vaccine.If the test results show that you are infected with the hepatitis B virus, you will need to have some additional tests to check your liver function and general health. In addition, your children, family members, your wife (or husband) are also at risk of being infected, and need to be tested and vaccinated in time.
6. Is hepatitis B curable?
There is currently no cure for hepatitis B, but symptoms can be controlled. In addition, vaccines can be used to prevent infection with the hepatitis B virus. People who have been inadvertently exposed to samples from a patient with hepatitis B and have not been vaccinated may receive a medicine called hepatitis B immune globulin (HBIg) along with the vaccine. HBIg contains antibodies against the virus. In some emergency situations, HBIg can provide protection against infection.7. What should pregnant women with hepatitis B do to prevent their children from getting sick?
Within hours of birth, your baby will receive his or her first dose of hepatitis B vaccine combined with a shot of HBIg. Two more doses of the vaccine will be given over the next 6 months. After completing the vaccination series, your baby will minimize the risk of disease. However, the baby still needs to be tested for hepatitis B virus infection.In case the test results show that the baby has been infected with hepatitis B, the doctor will administer special medical care. Your baby needs to be examined regularly and periodically to assess his overall health and liver function.
8. Hepatitis B vaccination for children even if the mother does not have the disease
All babies born should be vaccinated against hepatitis B. Even if a pregnant woman is not infected with the hepatitis B virus, her baby should still receive the first dose of the vaccine before leaving the hospital. If this cannot be done immediately, this dose of vaccine should be given to the baby within 2 months of birth. Subsequent doses are administered sequentially over the next 6-18 months.
9. The spread of hepatitis C . virus
The hepatitis C virus is spread mainly through direct contact with the blood of a patient. The potential for transmission occurs by sharing needles or by sharing utensils that have inadvertently come into contact with blood. A baby can be infected during delivery if a pregnant woman is infected with hepatitis C. The virus can also be spread through unprotected sex, but it's generally rare to be spread this way. Hepatitis C is not spread through casual contact or breastfeeding.10. Signs of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C virus infection presents with signs similar to those with hepatitis B but may also be asymptomatic. Unlike hepatitis B infection, most adults infected with the hepatitis C virus become carriers with rates up to 75%-85%. Most patients have chronic liver problems. In some cases, it will progress to cirrhosis and other serious, life-threatening conditions.11. Pregnant women with hepatitis C affect the health of their children?
Unlike hepatitis B, only about 4% of women infected with the hepatitis C virus will pass it on to their baby. This rate is related to the amount of virus acquired and the likelihood of pregnant women co-infected with HIV.If the mother is infected with the hepatitis C virus, the baby will usually be tested when he is 18 months old. Babies born can still be breastfed.
12. Hepatitis C . Immunization
There is currently no vaccine to protect against hepatitis C. The only way to prevent it from happening is to avoid behaviors that spread the virus and get tested for hepatitis C to detect it. early detection of this disease.Hepatitis C is most common in people born between 1945 - 1965. Therefore, all people in this age group should be tested for hepatitis C to promptly prevent and handle possible complications. .
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: Acog.org