This is an automatically translated article.
Heavy menstrual bleeding can be a warning sign of a dangerous gynecological condition affecting health. In fact, there are many risk factors for this condition. Therefore, women need to pay attention to monitor and observe abnormal signs to go to gynecological examination soon and intervene when necessary.1. What are the signs of heavy menstrual bleeding?
It is difficult to pinpoint exactly what heavy menstrual bleeding is because they are different for every woman. It is possible that this condition is normal in some people but it may be abnormal in others. Most women will lose less than 80ml per menstrual cycle, about 50-80ml on average. Accordingly, heavy menstrual bleeding was defined as the loss of 80ml or more of blood in each menstrual period, or menstruation lasting more than 7 days, or both of these factors co-occurring.Usually it is not necessary to measure menstrual blood volume. Most women know how much bleeding is normal during their period and can tell when there is excessive bleeding.
Some simple signs to help you recognize heavy menstrual bleeding are:
You have to change your tampon every hour or every 2 hours. Have a blood clot larger than 2.5cm (about the size of a dime). Heavy menstrual bleeding on your clothes or bedding. It is necessary to use 2 types of cleaning products together. Even so, you may sometimes feel like you're bleeding more, but the total amount of blood lost in a period is usually about 60 milliliters (about 2.7 ounces). With such a bleeding rate, it takes about four hours for a regular tampon or pad to fully absorb. But these are just averages: more menstrual flow on some days than on others.
Doctors consider a woman to have heavy periods if the woman regularly loses more than 80 ml of blood during a menstrual period. That much blood loss may or may not affect your health, depending on your general fitness and other individual factors.
Kinh nguyệt ra nhiều có thể gây ảnh hưởng đến sức khỏe do mất máu nhiều
2. What causes heavy menstrual bleeding?
Some women have heavy menstrual bleeding right from the start of their period. However, in most cases, periods only begin to become heavier later, such as after childbirth or after using an IUD, hormonal changes, such as during periods. Menopause, may also play a role in the condition.The most common cause of heavy periods is the uterus not being able to contract properly. Uterine contractions usually help to shed the lining of the uterus and ensure that the bleeding doesn't last too long.
The muscles of the uterus are prevented from contracting properly if larger benign tumors such as fibroids or polyps get in the way. Polyps develop in the lining of the uterus, while fibroids develop in its muscular layer. In addition, the IUD can also interfere with the muscles of the uterus.
Intrauterine scar tissue is also a common cause of heavy periods and inflammation in the uterus or fallopian tubes. These scar tissue may be present from birth, or they may be caused by surgery or severe endometriosis. Malignant tumors such as uterine cancer or cervical cancer are rarely the cause of heavy periods.
In rare cases, other medical conditions such as hormonal disorders, blood clotting disorders, or problems affecting the heart, kidneys, thyroid or liver can also cause heavy periods.
In some cases no obvious cause can be found. About half of women experience heavy menstrual bleeding, with no underlying cause found. But there are a number of conditions and some treatments that can cause heavy bleeding. In addition, certain conditions of the uterus and ovaries can cause menstrual periods to be prolonged and heavy, including:
Fibroids: noncancerous growths in or around the uterus and May cause prolonged menstruation or dysmenorrhea. Endometriosis: The endometrium is found outside the uterus, such as in the ovaries and fallopian tubes. Adenomas: when tissue from the lining of the uterus becomes attached to the wall of the uterus, this can also cause menstrual pain. Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID): This is an infection of the upper genital tract (uterus, fallopian tubes, or ovaries) that can cause symptoms such as pelvic or abdominal pain and bleeding after sex. sex or between periods, vaginal discharge and fever. Uterine polyps: noncancerous growths in the lining of the uterus or cervix (cervix) Uterine cancer: the most common symptom is irregular bleeding, especially after menopause. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): is a common condition that affects the way the ovaries work. It causes irregular periods and can cause heavy bleeding when it starts again.
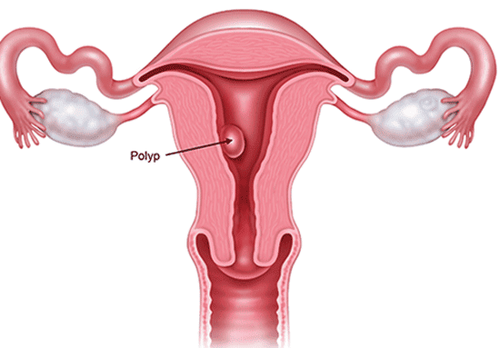
Polyp tử cung: là một nguyên nhân khiến kinh nguyệt ra nhiều
Blood clotting disorders, such as Von Willebrand's disease Hypothyroidism: the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones, causing fatigue, weight gain and feelings of depression . Diabetes Medical treatments that can sometimes cause heavy periods include:
Intrauterine device (IUD) to prevent pregnancy : this can make your period heavier within a few days. The first 3 to 6 months after the ring is placed. Anticoagulants are commonly used to prevent blood clots. Certain drugs used for chemotherapy. Some herbal supplements can affect your hormones and possibly affect your period - such as ginseng, ginkgo and soy MORE: What is menorrhagia? Does menorrhagia warn of any disease?
3. Heavy menstrual bleeding, when to see a doctor?
You should see a gynecologist if:You are concerned about your bleeding Your periods are heavier than usual You also have other symptoms, such as menstrual pain or bleeding between periods Your period The specialist will start by asking you about your heavy periods, any changes to your period, and any other symptoms you have such as bleeding between periods or menstrual pain .
All women with heavy menstrual bleeding should have a blood test to check for iron deficiency anemia. Your doctor may also recommend a physical exam or other tests to try to figure out what's causing your heavy periods. Other tests may include:
Blood tests Ultrasound Hysteroscopy: a small laparoscope with a light and camera on the end is passed into the uterus through the vagina to examine the inside of the uterus.
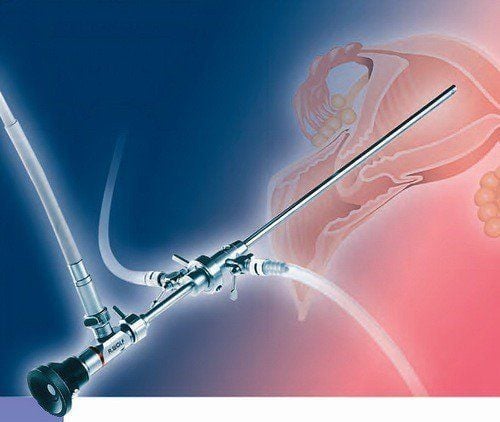
Nội soi tử cung có thể được chỉ định để chẩn đoán tình trạng kinh nguyệt ra nhiều
4. Treatment of heavy menstruation, prolonged menstrual cycle
There are different treatment options for heavy menstrual bleeding. The choice of treatment will depend on your symptoms, general health, the underlying cause of heavy menstrual bleeding, and whether you want to have children now and in the future...Accordingly, You should discuss the benefits and risks of different treatments with your doctor, including any impact on future fertility from some treatments.
4.1. Intrauterine system (IUS)
The levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system (IUS) is a small plastic device that your doctor inserts into your uterus. It slowly secretes a hormone called a progestogen.This device prevents the lining of the uterus from growing rapidly and is also a contraceptive. However, this method does not affect your ability to get pregnant after you stop using it.
Possible side effects of IUS use include:
Irregular bleeding that can last for more than 6 months Breast enlargement Acne Stopping or missing periods IUS is usually the preferred first-line treatment for women Women experience heavy menstrual bleeding, but it can take at least 6 periods for you to start seeing results.
4.2. Tranexamic Acid
You may be prescribed tranexamic acid tablets if the IUS method is not appropriate or you are awaiting further testing or other treatment. Tranexamic acid tablets work by helping the blood in your uterus to clot. Tranexamic acid tablets are usually taken 3 times a day for up to 4 days. You start taking the pill as soon as your period starts.Tranexamic acid tablets are not a form of birth control and they do not affect your ability to get pregnant. If necessary, tranexamic acid can be combined with a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID).
Possible side effects from using tranexamic acid include:
Diarrhea Feeling unwell Being sick

Thuốc Axit tranexamic có thể gây nên tình trạng tiêu chảy
4.3. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may also be used to treat heavy menstrual bleeding if an IUS is not appropriate or if you are awaiting further testing or other treatment. It is taken in pill form from the start or just before menstruation, until heavy bleeding stops. NSAID medications used to treat heavy menstrual bleeding include:Ibuprofen Mefenamic acid Naproxen Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs work by reducing the body's production of a hormone-like substance called prostaglandin, which is involved to prolonged menstruation. At the same time, the drug can also help relieve menstrual pain. However, these drugs are not a form of contraception.
You can keep taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for a while if they make your bleeding less severe and don't cause significant side effects. Make sure that you do not take more than the recommended daily dose indicated on the package.
4.4. Combined oral contraceptive pill
Combination birth control pills can be used to treat heavy periods, because they contain the hormones estrogen and progestogen.The benefit of using combined oral contraceptives as a treatment for heavy menstrual bleeding is that they provide a more reversible form of contraception than the IUS. They are also beneficial in regulating the menstrual cycle and reducing menstrual pain.
Combination birth control pills work by stopping the ovaries from releasing an egg each month. However, for maximum effectiveness, you must use it correctly. Common side effects of combined oral contraceptives include:
Mood swings Feeling nauseous Headache Headache Chest tightness
Nữ giới nên uống tránh thai kết hợp để điều trị kinh nguyệt ra nhiều, chu kỳ kinh kéo dài
4.5. Cyclic Progestogens
If other treatments don't improve, you may be given a medication called a cyclic progestogen. It is taken in pill form for part of your menstrual cycle. Your doctor will advise you on how to take the pill and it is not an effective form of birth control and can have unpleasant side effects, including breast tenderness and bleeding between periods.4.6. Endometrial ablation
Endometrial ablation involves thinning, removing, or destroying the lining of the uterus. It can either shorten your period or stop it, depending on how much lining you have left.Various techniques can be used for endometrial ablation, including:
Endometrial ablation using heat: an electrical source, radio waves, or a laser are used to destroy it. Endometrial destruction through the vagina and cervix Endometrial ablation: High levels of ultrasound energy from outside the body are used to destroy fibroids without causing damage to healthy uterine lining These techniques can be performed under local or general anesthesia. The process is fairly quick and you can usually go home the same day. In fact, you may experience menstrual-like vaginal bleeding for a few days after an endometrial ablation. Some women may bleed for 3 or 4 weeks. In addition, you may also experience abdominal cramps, like menstrual cramps, for a day or 2 after the procedure. They can be treated with pain relievers, such as paracetamol or ibuprofen.
Some women report more severe or longer lasting pain after endometrial ablation. In this case, you should talk to a specialist who can prescribe stronger pain relievers.
It is unlikely that you will be able to get pregnant after an endometrial ablation. But if you have this procedure, you increase your risk of miscarriage or other complications. Therefore, this procedure is not recommended if you still want to have children. Sometimes, endometrial ablation doesn't make periods lighter, or heavy periods may return. If this happens, you may be offered a repeat treatment.
4.7. Uterine artery embolism (UAE)
If heavy menstrual bleeding is caused by fibroids, uterine artery embolization (UAE) may be an option. This involves blocking the blood vessels supplying the fibroids, causing them to shrink.Under X-ray guidance, a small tube is inserted into a large blood vessel in your thigh. Small particles are then injected through the tube to block the arteries that supply blood to the fibroid.
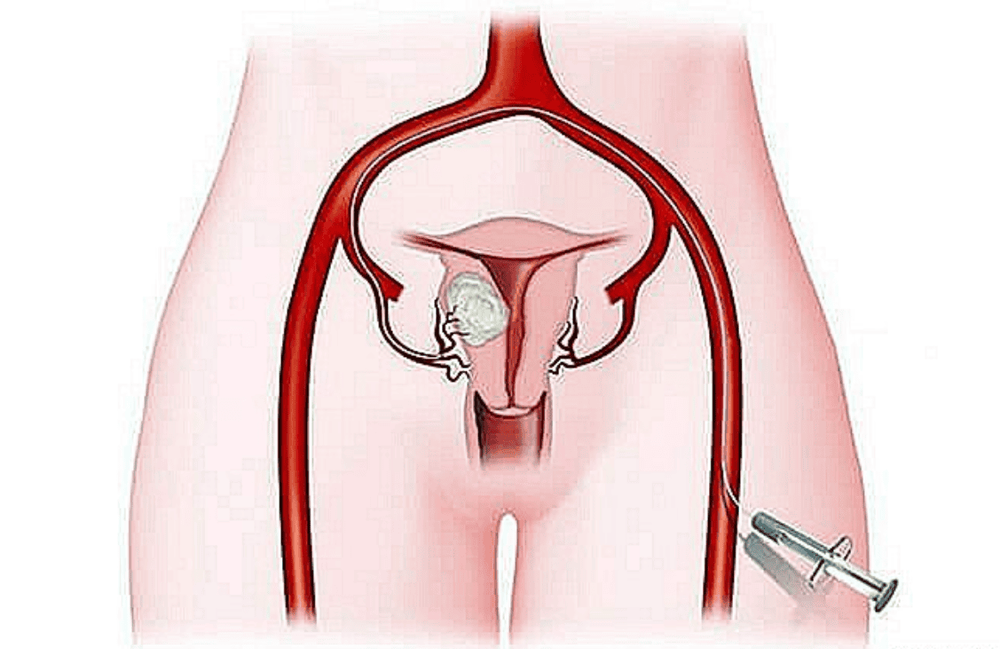
Phương pháp thuyên tắc động mạch tử cung
4.8. Uterine fibroid removal
Fibroid ablation is another treatment option for heavy menstrual bleeding caused by fibroids. It involves surgery to remove fibroids from the wall of your uterus.4.9. Hysterectomy
A hysterectomy will stop menstruation altogether, and this method should only be considered after other options have been tested or discussed. Accordingly, the surgery and recovery time is longer than other types of surgery to treat heavy menstrual bleeding. One big downside is that you won't be able to get pregnant after a hysterectomy.Hysterectomy is only used to treat heavy menstrual bleeding after a thorough discussion with your specialist about the benefits and disadvantages of this procedure.
Many people when they have a lot of menstrual bleeding, they often buy medicine to treat at home. This is not only inefficient, but can also adversely affect health. Heavy menstrual bleeding in each woman has different symptoms, due to different causes. Accordingly, the treatment of the disease and the use of drugs should be based on the examination and identification of the cause. Patients need to go to specialized medical facilities for timely examination and treatment.
Basic gynecological examination and screening package of Vinmec International General Hospital helps to detect inflammatory diseases early for easy and inexpensive treatment. Screening detects gynecological cancer (cervical cancer) early even when there are no symptoms. Accordingly, women with abnormal symptoms such as menorrhagia, vaginal bleeding, prolonged menstruation ... or risk factors should seek early examination to be able to detect the disease accurately and promptly. .
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, .nhs.uk