This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Senior Doctor, Dr. Vu Van Tam - Infectious Internal Medicine Doctor - Department of Medical Examination and Internal Medicine - Vinmec Ha Long International HospitalHeartworm disease is common in countries with hot and humid climates, especially in Southeast Asia. These thread-like worms can stay in the human body for decades and cause many serious consequences.
1. Worms are just what disease?
Heartworm infection is a parasitic disease caused by filariasis. This parasite is transmitted from person to person through mosquito bites and develops into adult worms in the human lymphatic system (hence the name lymphatic filariasis). Lymphatic filariasis causes multiple lesions and causes the tissue system to swell. Elephant's foot edema is a typical sign in the late stage of the disease.2. Causes of filariasis
Adult filariasis and filariasis cannot survive in the natural environment, but only parasitizes in the human body and in the body of the mosquito that transmits the disease.
In our country, hot and humid climate and relatively low socio-cultural level are the main causes of filariasis. Specifically, the education level is not high, the socio-economic conditions are limited, the maintenance of outdated customs and habits, the culture of ponds and cages, unsanitary conditions, many ponds, etc. are all factors. favorable factors for mosquitoes to transmit filariasis to humans.
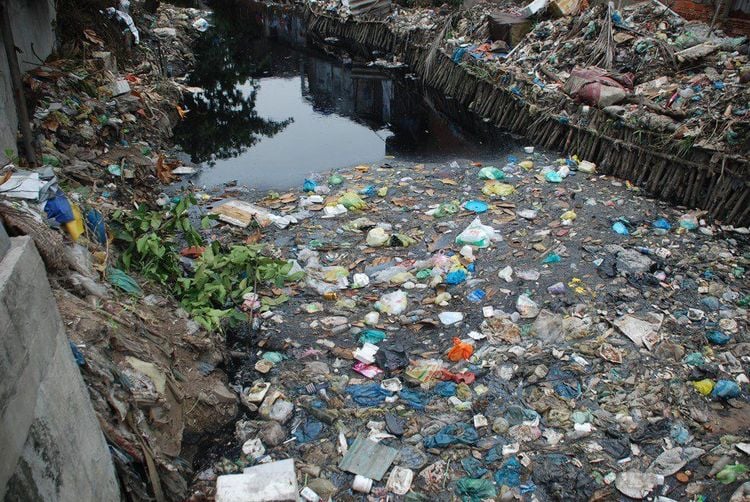

Môi trường đầy rác mất vệ sinh gây ra nhiều dịch bệnh ký sinh trùng.
3. Symptoms of filariasis
3.1. Clinical signs Early stage of the disease: most patients infected with filariasis have no obvious clinical signs. Some cases have symptoms of sudden high fever, the fever recurs intermittently for 3-7 days. Inflammation occurs in the lymph nodes and lymph nodes a few days after the fever. The site of inflammation is swollen, red, painful along the lymphatic system, often appearing on the inner face of the lower extremities, the inguinal lymph node may be enlarged and painful.
Chronic stage of filariasis: the symptoms of worms are more pronounced:
Appearance of elephantiasis. The patient noticed that episodes of edema appeared continuously, the skin gradually became thick and edematous from the bottom up. Most cases of swelling on one leg or one hand, most commonly the whole foot, can spread to the thigh. The patient's skin is increasingly thick and hard, ulcers may appear due to lack of nutrition. Genital inflammation: including epididymitis, orchitis, causing hydrocele. In case of severe disease, the genitals may be swollen like elephant scrotum, elephant breast but not red, painless (so called elephant edema). Elephant edema seriously affects quality of life. The patient's ability to work, daily life, movement, and physiological activities is greatly reduced, greatly affecting aesthetics. Chrysanthemum urine: The phenomenon of cloudy urine like rice water, not settling for a long time, sometimes even mixed with blood. In some cases, the urine has too much chylous, which can be frozen for a long time. 3.2. Symptoms help to identify In the patient's blood, filarial larvae are found. When the patient urinated chylous, urine test showed filariasis larvae. In addition, to diagnose filariasis, the doctor may order ELISA, ultrasound, angiography, lymphatic biopsy to detect adult filariasis.
4. Where do worms live?
To complete a life cycle, filariasis is forced to parasitize on 2 hosts: the main host is a human and the secondary host is a mosquito that transmits the disease. So, in Vietnam, where is the main parasitic worm? In fact, the epidemiology of filariasis is closely related to the mosquito that transmits the disease and the environment in which the mosquito transmits the larvae.
The survival of the mosquito that transmits filariasis depends on appropriate environmental factors, such as geographical conditions, climate and weather. With the climate and geographical position in our country, the mosquitoes that spread the disease mainly live in the plains, midlands, semi-mountains, places with many lakes and aquatic plants such as Japanese duckweed.

Muỗi lây truyền bệnh giun chỉ tại Việt Nam (tên khoa học là Culex quinquefasciatus).
After sucking the blood of an infected person, the filariasis larvae live inside the mosquito, which takes about 12-14 days to develop into adult larvae. At this time, adult filariasis larvae exist in the mosquito's salivary glands, ready to enter the healthy human body as soon as the mosquito sucks blood.
Everyone is susceptible to infection and the human body is the only reservoir for filariasis. The incubation period from the time the patient is infected with the larvae in the blood until the filariasis develops into an adult and then gives birth to a new larva is 6-12 months and most patients do not show any symptoms. any clinical.
The average lifespan of heartworms can be up to decades if left untreated. As for the larvae after birth, if not carried away by the infected mosquito within 10 weeks, the larvae will die in the human body.
5. How to prevent filariasis
Propagating and educating people together to prevent filariasis: focusing on the following main contents:
Heartworm disease is transmitted by mosquitoes, when sick, it is necessary to immediately go to a medical facility for diagnosis and treatment. Prevent filariasis by sleeping under mosquito nets, covering up with regular nets, clearing bushes, clearing drains, throwing away broken pots around the house, choosing light-colored clothes, wearing long pants and tight-sleeved shirts at night to limit disease. prevent mosquito bites. Kill mosquitoes, eliminate the source of disease transmission: coordinate with authorities in launching campaigns to kill mosquitoes. Everyone is susceptible to infection and the human body is the only reservoir for filariasis. Therefore, maintaining personal hygiene and environmental hygiene is the most effective way to prevent filariasis.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.