This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Bui Tien Dat - Emergency Medicine - Cardiology - Emergency Resuscitation Department - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.Cardiovascular collapse is an extremely dangerous condition that can cause permanent disability or sudden death in a short time. Understanding cardiovascular collapse and the risk of sudden death will help prevent disease more effectively.
1. Cardiovascular collapse and sudden death
Cardiovascular collapse is a term for inadequate cerebral blood flow to maintain the awake state of the brain due to acute cardiac and/or peripheral vascular dysfunction.
In the heart, there is an internal electrical system that controls the heartbeat, heart failure occurs when the heart's electrical system works abnormally, the heart rhythm is disturbed, the heart suddenly stops working for a period of time. but can also stop beating completely, this is an extremely critical condition, the patient is at high risk of disability due to lack of oxygen transport to the brain causing permanent brain damage or the risk of sudden death.
2. Causes of cardiovascular collapse
There are many causes leading to cardiovascular collapse, the most common of which are ventricular fibrillation and atrial fibrillation, especially in patients with acute or chronic coronary atherosclerosis.
Ventricular fibrillation : is a condition in which the heart chambers (two upper atria and two lower ventricles) contract to an uncontrollable rate, fluttering in vain instead of pumping blood. Ventricular fibrillation causes significant changes in heart rate, sudden drop in blood pressure, and in some cases cut off blood supply to vital organs, causing sudden death. Atrial fibrillation: The sinus node is the master node of the heart, it is a collection of differentiated cardiac muscle cells capable of emitting regular electrical impulses, these impulses will be transmitted to the heart cells, commanding the heart beats rhythmically. When the impulse does not come from the sinus node but from other locations in the two atrial chambers leading to continuous atrial muscle stimulation, the ventricles cannot pump blood effectively to the body, a condition called is atrial fibrillation. Subjects at high risk of heart attack are:
People with a history of cardiovascular diseases such as acute and chronic coronary atherosclerosis, myocardial hypertrophy, dilated cardiomyopathy, myocarditis, heart valve, cardiac electrophysiology abnormality,... Having a history of heart attack or a family history of heart attack People who use drugs or stimulants People with an unbalanced diet, potassium levels and low magnesium Smokers, alcoholics, obese People with high blood pressure, diabetes, blood cholesterol Gender and age: Men have a higher rate of cardiovascular collapse leading to sudden death than women. It usually occurs in men over 45 years old and women over 55 years old.
3. Symptoms of heart failure
When having a heart attack, patients often experience the following symptoms:
Falling suddenly Stop breathing Chest pain, dizziness, fainting, Shortness of breath, Pain in the arms, neck pain, back pain, lower jaw pain, upper back pain taste, sweat.
4. What to do to save people with heart failure?
If you think you or someone else is showing symptoms of heart failure, immediately call 911 or a loved one to take them to the nearest medical facility. Brain damage or death can happen in as little as four to six minutes.
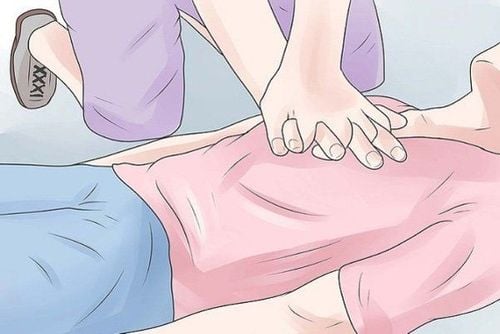
Brain cells are the most special cells in the body, when damaged, they cannot regenerate and compensate like other cells. The maximum tolerance for hypoxia of the brain under normal conditions is 5 minutes. This time period is called the clinical death phase, the re-supply of brain blood and oxygen must be carried out during this stage to save the patient. When a patient with a heart attack has lost consciousness and stopped breathing, while waiting for an ambulance, the following basic emergency steps can be taken to increase the patient's chances of survival:
Clearing the way Breathing: Place patient supine on firm ground, head and neck maximally flexed, face turned to one side. The first-aider opens the patient's mouth with his hand and cleans the sputum and foreign objects with his hand. Blow the patient: mouth-to-mouth or mouth-to-nose blowing can be used, however mouth-to-mouth is usually more effective. Place one hand on the patient's forehead, press the patient's head back, and use the index finger and thumb to catch the patient's nose. The fingers of the second hand lift the patient's lower jaw while opening the patient's mouth. The rescuer takes a deep breath and presses tightly against the victim's mouth and mouth, blowing all the stored air through the patient's mouth. The blowing frequency should be 10-12 times/minute, if done correctly, after each blow, the patient's chest will expand. Extrathoracic chest compressions: choose an appropriate position on one side of the patient, one hand is placed on the center 1⁄2 below the sternum, the other hand is placed on top of the front hand, fingers alternate in the same direction, Apply pressure perpendicular to the patient's chest so that the sternum sinks 4-5cm, then lift your hand to perform the second compression, the frequency is at least 100 times/minute. Two movements of chest compressions and breaths are performed alternately according to the cycle of cardiopulmonary resuscitation. A CPR cycle consists of 30 chest compressions followed by 2 breaths.
If you often have symptoms such as chest pain, headache, dizziness, irregular heartbeat, shortness of breath, wheezing, fainting, ... go to medical facilities to be checked by a doctor. check the risk of cardiovascular disease. In addition, create for yourself good habits in eating and living, not smoking, drinking alcohol, having a balanced, nutritious diet, being physically active, etc. to prevent danger. life-threatening cardiovascular collapse.
To protect heart health in general and detect early signs of heart attack and stroke, customers can sign up for Cardiovascular Screening Package - Basic Cardiovascular Examination of Vinmec International General Hospital. The examination package helps to detect cardiovascular problems at the earliest through tests and modern imaging methods. The package is for all ages, genders and is especially essential for people with risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
Master. Doctor. Bui Tien Dat received intensive training in the field of cardiology and cardiovascular emergency resuscitation at Hanoi Medical University and Bach Mai Hospital. The doctor has more than 12 years of experience in the field of emergency and cardiovascular resuscitation and is currently a doctor at the Emergency Department of Vinmec Hai Phong International Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.