This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Specialist Doctor I Le Tuyet Nga - Pediatrician, Pediatric Center - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.Summer weather is hot and humid, which is favorable for viruses to thrive, causing many diseases, including hand, foot and mouth disease. Hand, foot, and mouth disease is a viral disease that spreads quickly, easily outbreaks into an epidemic, the disease is common in children under 5 years old, the peak of the disease is usually from March to May and from August to September. annual. The disease is very dangerous if not detected early and with timely treatment.
1. What is hand, foot and mouth disease?
Hand, foot and mouth disease is mainly caused by Enteroviruses, the most common are Coxsackie A16 and Enterovirus type 71. In particular, Coxsackie A16 virus causes less neurological complications and can resolve on its own within a few days.
In contrast, Enterovirus type 71 (EV71) causes many dangerous complications of encephalitis, meningitis, pneumonia, myocarditis and can lead to death.
In addition to Coxsackie A16 and Enterovirus type 71, some other strains of group A viruses such as Coxsackie A4-A7, A9, A10 or group B Coxsackie viruses (B1-B3, and B5) may also be the cause.
Therefore, parents need to know the early signs of the disease so that they can prevent the disease in time to prevent the spread of the disease, causing damage to the child.
2. Early signs of hand, foot and mouth disease
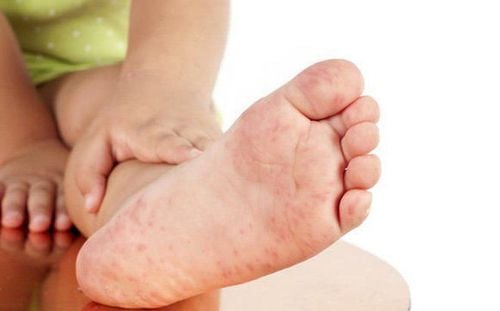
The disease is usually characterized by fever, sore throat, and a blistering rash.
Hand, foot and mouth disease has different signs depending on the stage, specifically:
Incubation period 3 - 6 days.

Người mắc bệnh tay chân miệng có thể xuất hiện triệu chứng sốt kèm theo đau họng và các triệu chứng khác kèm theo
The child has a fever, fatigue, low fever (37.5-38 degrees Celsius) or high fever (38-39 degrees Celsius). Sore throat. Lesions, pain in the teeth and mouth. Lots of saliva. Anorexic. Diarrhea several times a day. The full-blown stage (usually begins 1-2 days after the onset of illness), the child begins to show typical symptoms of the disease such as:
The child has a blister-like rash on the palms, feet, knees , butt. The water balloons are 2 – 10mm in diameter, gray in color, oval in shape. They can grow protruding or hidden under the skin, feel lumpy, painless, and not itchy. Mouth ulcers: in the lining of the cheeks, gums and tongue of the child, blisters of 2-3mm in diameter appear, which are fragile. When broken, they form sores that cause pain when eating and crying. On the buttocks of infants and young children appear sores, blisters. Systemic signs: confusion, delirium, convulsions. In addition to the above typical symptoms, depending on the location, hand, foot and mouth disease also appears additional symptoms such as: Very few blisters interspersed with erythema or only erythema appears. In some cases, only mouth ulcers appear. If the condition is mild, after 7-10 days of home care, the child will fully recover. In case the baby has a high fever (above 39 degrees Celsius) lasting for more than 48 hours with symptoms such as vomiting, trembling hands and feet, convulsions, rapid heartbeat, difficulty breathing, streaked skin, the family needs to take the child to the hospital. right away. After recovering from the disease, the child's body will be immune to the virus that causes the disease. However, according to the results of many studies, children can get hand, foot and mouth disease many times and the next time the illness is caused by different strains of the virus than the previous one.
We must know the route of disease transmission to know how to prevent disease.
The virus that causes hand, foot and mouth disease is capable of spreading very quickly, transmitted directly from person to person through the mouth, through secretions from the nose, mouth, feces or saliva of sick children.
Infected people are likely to shed the virus during the first week (incubation period). However, the infectious period can last for several weeks because the virus is still present in the stool and saliva of the patient.
Hình anh virus Enterovirus 71 - virus gây bệnh tay chân miệng
Ways of transmitting the virus that cause hand, foot and mouth disease:
Children come into direct contact with infected people. Inhalation, swallowing secretions, saliva of sick people when eating together, coughing, sneezing, talking. Direct contact with the fluid of blisters, blisters, feces of the patient. The healthy child holds the toys and touches the objects of the sick child. Spread through the hands of the caregiver. Because the way the disease is transmitted is quite fast, it is easy for hand, foot and mouth disease to break out into a large epidemic. When a child is sick, if there are no timely preventive measures, the children around can also be infected at any time.
3. How to prevent hand, foot and mouth disease
Currently, there is no vaccine to prevent the disease, but parents can reduce the risk of being infected with the viruses that cause hand, foot and mouth disease by the following simple ways:
Wash your hands often with soap before preparing food, drink, for children. Wash your hands immediately after using the restroom, after changing a baby's diaper, and after coming into contact with blisters. Use soap to clean items, disinfect with common detergents. Avoid hugging, kissing, sharing clothes and personal items with infected children. When children are sick, avoid letting them come into contact with crowded places such as kindergartens and schools. Instruct children to cover their mouth and nose when sneezing and coughing. Regarding the daily diet, it is necessary to ensure adequate nutrition, timely rehydration to prevent dehydration and hypoglycemia. For breastfed babies, it is necessary to increase breastfeeding to several times a day. For older children, it is necessary to abstain from foods that can cause pain and damage to the mouth, such as hot, solid foods. Instead, parents should give their children thin, cold, easy-to-digest foods such as diluted porridge, milk, nut milk, bean tea, etc. Or eat yogurt instead. Fruits and vegetables rich in vitamins and minerals are also essential foods for children while treating hand, foot and mouth disease. In addition, parents need to clean the baby's skin to avoid bacterial superinfection by: bathing the child with mild antiseptic water such as green tea leaves, spinach leaves .....
Note the need to regularly monitor the baby to detect early and treat dangerous complications if any. Monitor disease status and get timely medical care. If the child has abnormal symptoms such as high fever, lethargy, loss of consciousness, they need to be hospitalized immediately. Hand, foot and mouth disease is an infectious disease that can be treated at home according to the doctor's protocol. The disease usually goes away on its own after 7-10 days without causing much danger to the child. However, if not detected early and treated promptly, hand, foot and mouth disease can lead to a number of other serious complications. Therefore, parents need to take their children to the doctor as soon as possible when there are abnormal signs.

Trẻ có dấu hiệu bệnh lý tay chân miệng cần được thăm khám bởi các bác sĩ chuyên khoa
Pediatrics department at Vinmec International General Hospital is the address for receiving and examining diseases that infants and young children are susceptible to: viral fever, bacterial fever, otitis media, pneumonia in children, .... With modern equipment, sterile space, minimizing the impact as well as the risk of disease spread. Along with that is the dedication from the doctors with professional experience with pediatric patients, making the examination no longer a concern of the parents.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.