This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Master, Doctor Do Xuan Chien - Head of Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Ha Long International General Hospital.Goiter is also known as thyroid goiter, classified into 3 groups: benign, cancerous and thyroid endocrine dysfunction (increase or decrease in thyroid hormone.
)
1. Is goiter dangerous?
Benign thyroid tumors, if large in size, will cause difficulty swallowing or swallowing, difficulty breathing (due to insertion into the trachea, esophagus) or protrusion in front of the neck, causing cosmetic loss. Malignant thyroid tumor is a cancer that invades surrounding organs, especially the laryngeal laryngeal nerve, causing hoarseness or when the tumor metastasizes, it will damage the liver, lungs, bones, brain... Thyroid gland with endocrine dysfunction such as: Hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism will affect many organs in the body such as: Exhaustion, weight loss or gain, chest palpitations, insomnia, hair loss, trembling hands , sweat. However, many other diseases also cause these abnormalities, requiring a doctor's visit to confirm the disease.
2. Symptoms of malignant goiter
Most thyroid tumors are benign, but about 5% are malignant (thyroid cancer). The doctor will examine, ultrasound, blood test, aspiration cytology ... to determine the type of goiter. In particular, when a new malignant goiter begins, it will not cause any abnormalities, but can only be detected through ultrasound examination or incidentally when taking CT, MRI, PET scans of the neck because of other diseases. Symptoms will appear when the tumor progresses:
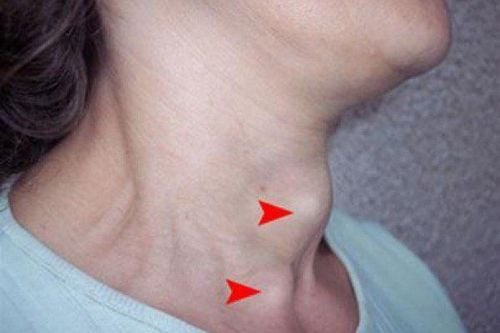
Appears a tumor in the neck: It is necessary to monitor the condition of the tumor, we can recognize that when swallowing, a benign tumor will move up and down, while a malignant tumor Will not move when swallowed. Hoarseness: The voice turns hoarse because the laryngeal nerves control the muscles that open and close the vocal cords, located behind the thyroid gland. As the condition worsens, thyroid tumors can spread and severely damage the sound box. Check for thyroid nodules with firm, well-defined margins, rough or smooth surface, and movement with swallowing rhythm. There are cervical lymph nodes, small, soft, mobile lymph nodes, appearing on the same side as the tumor. Symptoms of late thyroid cancer The tumor is large, hard, fixed in front of the neck. Severe hoarseness, difficulty in breathing Difficulty swallowing, difficulty swallowing, pain due to tumor compression The skin in the neck area is dark, dark, even ulcerated, bleeding When the ultrasound clearly shows thyroid tumors, cancer is detected. clear thyroid.
3. How to cure goiter There are many treatment methods for goiter. Depending on the medical condition, the doctor will appoint 1 of the following 3 methods:
Radioactive iodine The patient will take radioactive iodine, then Then iodine will follow the blood to the thyroid gland to destroy cells. This method is effective for about 90% of treatment cases, of which 50-60% of patients reduce tumor size after 12-18 months. This method can cause an underactive thyroid, but this is rare.
Take medicine If the patient has hypothyroidism, the doctor will prescribe thyroid hormone replacement medicine. These medications slow the release of thyroid-stimulating hormone from the pituitary gland, helping to shrink the goiter.
If the cause is thyroiditis, the doctor will prescribe aspirin or corticosteroids to treat it.
Note that sometimes these drugs can cause some side effects such as chest pain, sweating, headache, heart palpitations...
Surgery If the tumor is large, uncomfortable, difficult If breathing or swallowing is difficult, the doctor will recommend surgery. The doctor will choose one of the methods of lobectomy, total thyroidectomy, total thyroidectomy, and isthmusectomy. In addition, in some cases, needle aspiration can be used to drain fluid in the case of a water-filled goiter (called a thyroid cyst).
4. Should a benign goiter be operated on?
Most goiters are benign and require almost no surgery. Only in cases of absolute necessity are there indications to resort to surgical methods. Cases of benign goiter requiring surgery include:
Benign tumor causing compression, difficulty breathing, difficulty swallowing or loss of aesthetics Suspicion of cancer Thyroid dysfunction hyperthyroidism. Surgery is not required in case of small benign tumor and is not required when the benign tumor is large but does not cause difficulty in breathing or swallowing. When the tumor is benign, small, and does not cause discomfort, it usually does not require any treatment and is monitored by periodic re-examination every 1-2 years. Seek medical attention immediately if there are changes in the neck area or abnormalities in the body.
5. When is thyroid surgery required?
Malignant thyroid nodule (cancerous): diagnosis of malignancy by biopsy. Nodular goiter with biopsy findings of non-malignant but suspected malignancy (cytological or ultrasonographic). Nodular goiter with a direct family history of thyroid (K) cancer. The goiter is large enough to cause compression, causing symptoms for the patient. Symptoms are caused by goiter, not patients with sore throat, cervical spine pain, reflux...
6. Complications that may occur during thyroid surgery
Bleeding in the neck, possibly causing a hemangioma Infection Voice change (hoarseness) due to damage to the recurrent laryngeal nerve, this damage can be caused by inflammation, by thyroid tissue, by lack of blood supply, recover within 6 months. If more than 6 months have not recovered, it is very likely that permanent damage. Hypoparathyroidism causes symptoms of hypocalcemia (numbness of face, mouth, extremities, muscle contractions...). In particular, hypocalcemia is caused by damage to the 4 parathyroid glands (function of regulating blood calcium) which can be temporary due to lack of blood supply or permanently due to the removal of 4 parathyroid glands. When hypocalcaemia, the patient should be taken to the hospital immediately for timely treatment by the doctor. Hypothyroidism: is the most common complication, if the thyroid gland is completely or nearly completely removed, permanent hypothyroidism is inevitable (because all thyroid tissue has been lost). With this complication, the patient may need to take thyroid hormone medication for the rest of his life.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.