This is an automatically translated article.
The article was expertly consulted by MSc Nguyen Ngoc Khanh - Head of Department of Gastroenterology - Urology - Robotic Surgery & Pediatric Surgery, Vinmec Times City International Hospital.1. What are gallstones? Gallbladder stone location
The gallbladder is a small pear-shaped sac located under the right liver that stores and concentrates bile. Bile secreted by the liver is stored in the gallbladder and then excreted into the intestines to digest fats.Solid gallstones are formed by cholesterol, bile salts and calcium, the size of the stone ranges from a few millimeters to several centimeters. Quantity can be from 1 to hundreds of tablets.
2. Causes of Gallbladder Stones
Usually due to metabolism, when there is too much excess cholesterol in the bile, the crystals form from which gallstones are formed.3. Who is at risk for gallstones?
Gallstones can affect anyone, younger people are less likely to get them. The following people belong to the high-risk group:
Fat people: Because stones are related to excess cholesterol in the blood. Women taking birth control pills that contain estrogen. People with inflammatory bowel diseases such as Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis.
4. Symptoms of Gallbladder Stones
Most patients have no symptoms, gallstones are discovered incidentally during ultrasound examination of other diseases.Some symptoms such as:
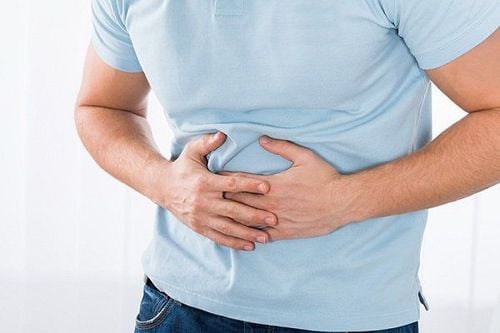
Dull abdominal pain under the right flank, through the back, up the right shoulder. Severe cramping pain is rare, often associated with stones blocking the cystic duct, acute cholecystitis requires the patient to be hospitalized for medication, monitoring and possibly emergency surgical intervention if too much. Progressive inflammation leads to gallbladder necrosis.

5. How are gallstones diagnosed?
Ultrasound, tomography is an effective means for diagnosing gallstones. Blood tests help determine liver function, blood cholesterol status.
6. How to treat gallstones?
6.1. Gallbladder stone conditions
Gallstones larger than 1cm without symptoms:
May not need treatment. Because in fact stones are often discovered incidentally and the person carrying the stone has lived with the stone for many years without symptoms. And the complication of this stone is usually mild: cholecystitis.
Women of childbearing age
According to Ths.Bs Nguyen Ngoc Khanh with a special case: Women of childbearing age with gallstones should undergo active surgical intervention before pregnancy to prevent cysts. Inflammation of the gallbladder during pregnancy makes the treatment very complicated, especially if cholecystectomy is required at this stage.
Small stone 2-3mm
Small stone 2-3mm is more dangerous than large stone 1-2cm because it can cause very serious complications even death is acute necrotizing pancreatitis. Therefore, when the patient discovers that there are small gallstones of 2-3 mm, he should proactively consult a surgical hospital to request surgery even though the stones have not caused any symptoms.
Stones cause painful symptoms, fever intermittently
At this time, it should be treated with surgery.
6.2 Methods of treatment of gallstones
Treatment of "litholytic" drugs as advertised by many drug companies has very limited effects, mainly effective in preventing stone formation in high-risk people: gastrectomy, slimming,...
Lithotripsy: No Used to treat gallstones. It is ineffective and causes complications.
The current gold standard treatment for gallstones is laparoscopic cholecystectomy. It can be conventional laparoscopic surgery with 3-4 small skin incisions 0.5-1cm on the abdominal wall to insert the instrument or SILS surgery with an incision through the navel so that no scars are visible after surgery.
The average surgical time for a gallbladder stone case is 15-30 minutes, the hospital stay after surgery is 1-2 days.
In surgical treatment, surgery when the gallbladder is not inflamed is much easier than when the gallbladder has been inflamed many times.
7. When cholecystitis, what to do?
You need to be hospitalized for treatment, where doctors will make a diagnosis and consider treatment in the following order:
Confirmed diagnosis. Diagnosis of severity. Determine the level of risk for common bile duct stones. Select a method of treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.