This is an automatically translated article.
Diarrhea is a common condition in all ages and mostly occurs in mild form, which will go away in 1-2 days. However, the disease can be severe, prolonged and affect the physical health of the patient. In some cases, this condition can be a warning sign of digestive cancer.
1. Diarrhea Overview
After food is put into the body for 2-3 days, it will absorb water and nutrients, then discharge waste from the body. Therefore, the normal person will have a bowel movement about 1-2 times a day and the stool will be moldy, not loose or crushed.
However, if you pass loose stools more than 3 times a day, it will be called diarrhea. This disease is classified into 2 levels respectively as follows:
Acute diarrhea : Occurs when the body is allergic to food or infected with E.coli bacteria, cholera, Rota virus,... Abdominal pain Diarrhea usually lasts less than 14 days. Chronic Diarrhea: A type of diarrhea that lasts more than 14 days, of which there are no 2 consecutive days of diarrhea. The patient's body will be easily weakened, making treatment difficult. The human body has a self-healing function, so diarrhea usually stops at an acute level, does not last long, and is easy to treat. However, there are still some cases of frequent diarrhea that does not go away, even bloody stools. At this point, the patient should see a doctor to determine the exact cause of the disease.
2. When does frequent, smokeless diarrhea warn of gastrointestinal cancer?
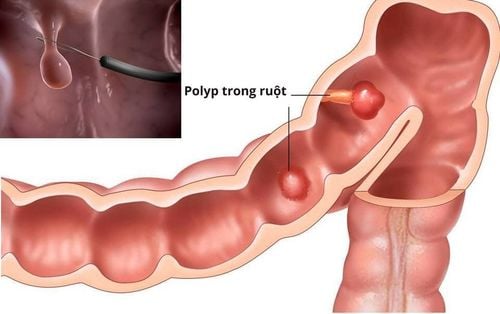
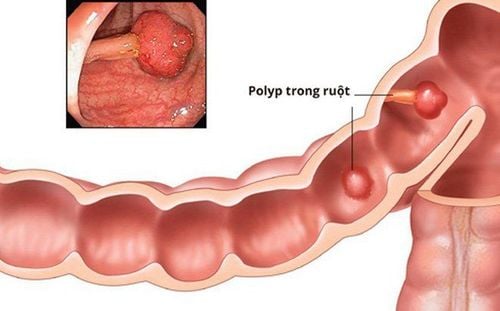
Many people have pain in the lower abdomen for a while, combined with persistent diarrhea, but still subjectively consider it a normal manifestation of the digestive tract. It is not until the stool is loose, with a little bloody mucus, that the digestive cancer is detected at a late stage. The later you go to the doctor, the less likely you are to prolong survival after surgery and more likely to have complications such as: Intestinal obstruction, colon bleeding or distant metastases, etc.
Gastrointestinal cancer is common in humans. middle-aged and elderly people, but in recent years, people under the age of 40 have more and more forms of cancer, some are not even 20 years old and the disease often has no obvious symptoms in the early stages. Most patients are often subjective, only when they see serious digestive disorders such as constipation, flat stools, frequent diarrhea, bloody stools, abdominal pain, weight loss, anemia secondary to chronic blood loss , feel the abdominal mass, ... then go to the hospital specializing in Gastroenterology for examination and diagnosis. Through means such as gastrointestinal endoscopy, CT scan, the doctor will detect the level and condition of the patient, thereby proposing appropriate treatment.

Ung thư tiêu hóa đang ngày càng trẻ hóa.
3. Subjects prone to gastrointestinal cancer
According to research, the following are the subjects who are very susceptible to gastrointestinal cancer and need to pay attention to adjust their living and eating habits:
Obesity, overweight: People with belly fat under the age of 50 are often at risk The risk of bowel cancer is 1.5-2 times higher than that of the general population. Bad eating habits: Bowel cancer is a malignant tumor of the digestive system and is related to eating habits. If your diet is high in fat, fried foods, pickled foods, red meat, low in fiber for a long time, it will weaken bowel function, increasing the risk of bowel cancer. Laziness: Modern life makes many people have the habit of sitting a lot, or refraining from going to the toilet. However, if feces stay in the intestine for too long, it will affect the intestines, harmful substances will be reabsorbed directly causing bowel cancer. Smoking and drinking habits: Heavy smokers are 34% more likely to die from colon cancer than non-smokers. Alcohol is also a harmful substance because it promotes the dilation of the digestive tract, destroys the mucus barrier on the surface of the digestive mucosa, and increases the absorption of carcinogens. Family history of digestive cancer: As with cardiovascular disease, digestive cancer runs in families (about 30%). Therefore, if your parents or siblings have ever had cancer in the digestive tract, go for more proactive screening for polyps and colon cancer than the general population. For digestive cancer in particular and other cancers in general, to have a good prognosis, the thorough treatment of the disease at an early stage is the most important factor. Therefore, gastrointestinal cancer screening is a scientific and effective measure for early detection of gastrointestinal cancer (esophageal cancer, stomach cancer, colon cancer) and giving treatment regimens. best treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference articles: hoangmysaigon.com, msdmanuals.com, suckhoedoisong.vn, medlatec.vn, vietnamnet.vn