This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Master, Doctor Truong Thanh Tam - Pediatrician at the Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.1. Causes of nosebleeds in children
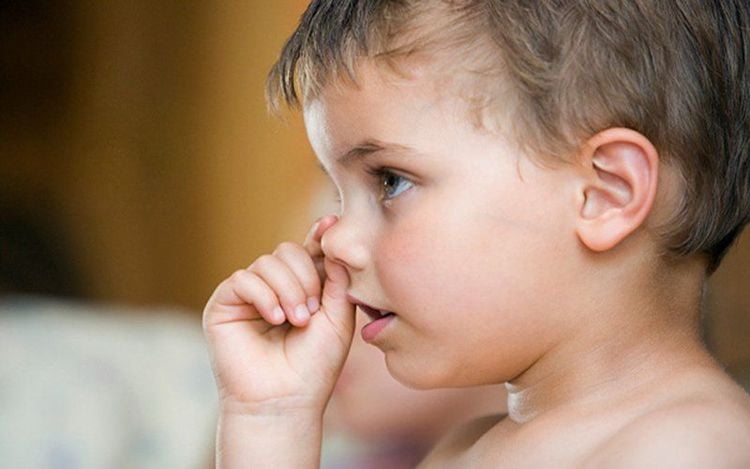
Nosebleeds (also known as nosebleeds) are small blood vessels in the nose that burst and bleed. This is a common phenomenon, appearing more in children 2 - 10 years old. Nosebleeds usually occur on only one side of the nose, rarely both. If there is a lot of bleeding, the blood may flow backwards, down the throat, the child spits up blood, vomits blood or has bloody stools from swallowing nose blood. In case of a lot of blood loss, the child may experience dizziness, fatigue, dizziness, lethargy, and confusion (rarely).Some common causes of nosebleeds in children include:
Impacts, trauma: Children are prone to nosebleeds while playing, hitting hard objects such as tables, chairs or giving foreign objects. , toys into the nose; Weather: In the cold season, the weather is dry, the air humidity is too low, making the mucous membranes of the nasal walls of children less elastic and more sensitive. At this time, even a small impact like a child blowing, sneezing or rubbing their nose can cause a nosebleed on one or both sides. In other cases, when it is hot, the blood vessels in the nose dilate, the child feels itchy and picks his nose, breaking blood vessels in the nose;

2. First aid for nosebleeds in children
Proper first aid at home helps children stop bleeding quickly. Detailed instructions are as follows:Reassurance, encouragement and comfort so that the child does not panic when seeing blood; Have the child sit with his back straight and his head tilted forward to determine which side of the nose is bleeding. Pay attention that the person performing first aid should not tilt the child's head because it will cause bleeding back into the nasal cavity and down the mouth, making the child uncomfortable, choking, coughing, possibly vomiting; Use your thumb and index finger to squeeze the two nostrils of the child into the nasal septum to prevent blood from continuing to flow, let the child breathe through the mouth, hold for about 5-10 minutes. This action helps to squeeze the bleeding point in the nasal septum, stopping the bleeding; You can apply a cold compress, place a cool washcloth on the base of your child's nose and cheeks, or give your child an ice cube to suck on. This helps the blood vessels in the nose to constrict, which slows down the bleeding process. However, this measure only applies if the child agrees to cooperate;
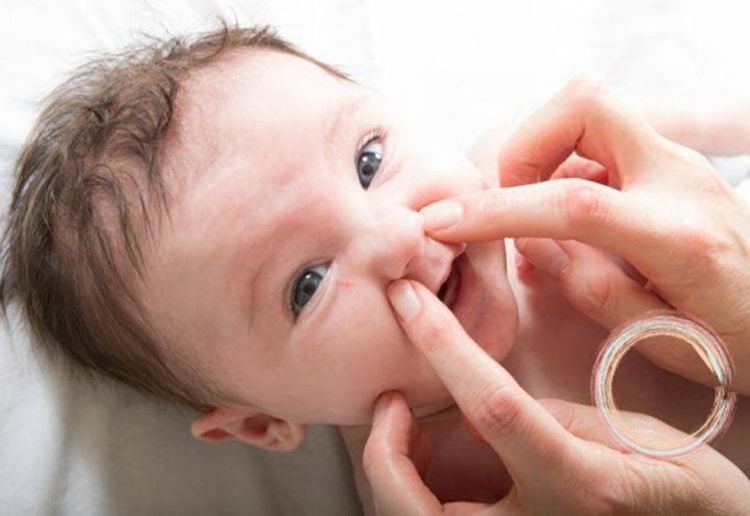

Do not ask the child to blow their nose once the bleeding has stopped, as this may loosen the blood clot in the nose. In case the child has a lot of nosebleeds, blow out before starting to squeeze the nose; Do not let the child tilt his head back because it will be difficult to monitor the amount of bleeding; Similar first aid for nosebleeds can be performed on adults. Take the child immediately to a medical facility specializing in ear - nose - throat if:
First aid measures have been applied for nosebleeds in the child within 20 minutes but the bleeding cannot be stopped; Children with repeated nosebleeds; Nosebleeds due to trauma (falls, collisions); nose bleeds or a lot of blood loss; Children feel weak, dizzy;

Pediatrics department at Vinmec International General Hospital is the address for receiving and examining diseases that infants and young children are susceptible to: viral fever, bacterial fever, otitis media, pneumonia in children, ... With modern equipment, sterile space, minimizing the impact as well as the risk of disease spread. Along with that is the dedication from the doctors with professional experience with pediatric patients, making the examination no longer a concern of the parents.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.