This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Doctor Tran Quoc Tuan - Head of the ICU - ICU - Emergency Resuscitation Department - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General HospitalAtaxia describes a lack of control of the muscles or lack of coordination in controlling bodily activities. Ataxia can affect various movements, causing difficulty with speech, eye movements, and swallowing.
1. General overview of ataxia of the body
Ataxia is the result of damage to the brain, which is responsible for controlling body coordination. Causes of ataxia can be alcohol and certain drug abuse, stroke, tumours, cerebral palsy, degenerative brain disease, and multiple sclerosis. Inherited defective genes can also cause this condition.Treatment of ataxia must be based on the cause of the disease. Using adaptive devices, such as a walker or cane, can help you maintain autonomy during activity. Physical therapy, acupuncture, and regular aerobics solutions can also help in treating ataxia.

Nghiện rượu bia là nguyên nhân dẫn đến mất điều hòa cơ thể
2. Symptoms of body ataxia
Ataxia can develop over time or come on suddenly. It can cause some signs of neurological disorders such as:Low coordination of muscles and body parts. Unsteady walking and a tendency to stumble. Difficulty with fine motor skills such as eating, writing, or buttoning clothes. Change in voice. Unnatural eye movements. Difficulty swallowing.
3. Causes of body ataxia
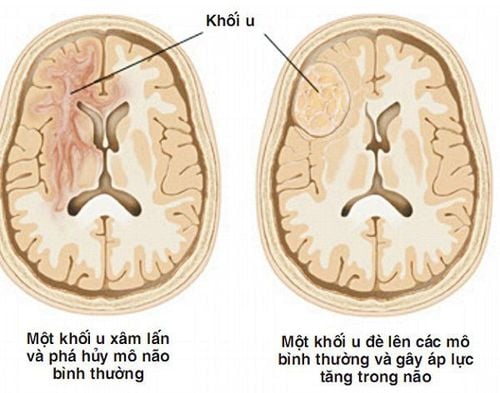
Damage, degeneration or loss of cerebellar neurons leads to ataxia. The cerebellum consists of two folded tissues located at the base of the brain. The right side of the cerebellum controls coordination on the right side of the body; The left side of the cerebellum controls coordination on the left side of the body. Diseases that damage the spinal cord and the peripheral nerves that connect the cerebellum to the muscles can also cause ataxia. Causes of ataxia include:Head trauma. Damage to the brain or spinal cord can cause acute cerebellar ataxia. Stroke. When the blood supply to a part of the brain is interrupted or severely reduced, there is a loss of brain tissue and oxygen leading to brain cells dying. Cerebral palsy . This is a general term for a group of disorders caused by damage to a child's brain during early development including before, during, or shortly after birth. It affects a child's ability to coordinate body movements. Autoimmune disease. Multiple sclerosis, celiac disease, and other autoimmune conditions can cause ataxia. Infection. Ataxia can be a rare complication of chickenpox and other viral infections. It can appear during the healing stages of the infection and last for a few days or weeks. Paraneoplastic syndrome. These are rare degenerative disorders triggered by the immune system's response to cancerous tumors, most commonly from lung, ovarian, breast, or lymphatic cancers. Ataxia can appear months or years before a cancer diagnosis. The appearance and growth of brain tumors, whether malignant or benign, can damage the cerebellum. Toxic reaction. Ataxia is a potential side effect of certain medications such as tranquilizers, benzodiazepines, and some chemotherapy drugs. In addition, alcohol and drug poisoning, heavy metal poisoning such as from lead or mercury, and solvent poisoning such as from paint thinners can also cause ataxia.
Sự xuất hiện và phát triển của khối u trên não kể cả ác tính hay lành tính cũng có thể làm hỏng tiểu não
4. Hereditary ataxia
Some types of ataxia and some conditions that cause ataxia are genetic. If you are born with a defect in a certain gene that produces abnormal proteins. Abnormal proteins interfere with the function of nerve cells, mainly in the cerebellum and spinal cord, causing them to degenerate. As the disease progresses, coordination problems become more limited.The ataxia can be inherited from a dominant gene or a recessive gene from one parent. In cases where neither parent has the disorder, it can be inherited from a family history.
Different gene defects cause different types of ataxia. They all cause poor coordination, but each has different signs and symptoms.
4.1 Autosomal dominant trait ataxia Researchers have identified more than 35 dominant genes causing ataxia. Cerebellar and cerebellar degeneration are common to all types, but the signs and symptoms vary, as does the age of onset depending on the specific gene mutation.
There are seven confirmed types of ataxia 1 through 7. Ataxia 1 and 2 are the most common. Ataxia 1 involves brief episodes of ataxia that can last seconds or minutes. This ataxia is triggered by stress, startle, or sudden movement and is often associated with muscle twitching. Ataxia 2, which typically lasts 30 minutes to six hours, is also triggered by stress. Symptoms may include dizziness, fatigue, and muscle weakness. In some cases, symptoms will subside. Perineal ataxia does not shorten life expectancy and symptoms may respond to medication.
4.2 Autosomal recessive trait ataxia Friedreich's ataxia is a common genetic ataxia associated with damage to the cerebellum, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. Peripheral nerves carry signals from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles. In most cases, signs and symptoms appear before age 25. The rate of disease progression varies, the first sign being difficulty walking and often progressing to the arm. Muscles weaken over time and cause deformity, especially in the feet, legs, and lower arms.
Other signs and symptoms may develop as the disease progresses such as slurred speech, rapid eye movements, nystagmus, scoliosis, hearing loss, heart disease. Early treatment of heart problems can improve quality of life and maintain patient survival.
Ataxia - vasodilatation This is a rare and common childhood disease that causes degeneration in the brain and other body systems. The disease also causes immune system breakdown, increasing susceptibility to other diseases, including infections and tumors. Slow motor skill development, poor balance, and slurred speech are the first signs of the disease. Recurrent sinusitis and respiratory infections are common.
Children with vasodilating ataxia have an increased risk of cancer, especially leukemia or lymphoma. Most people with the disease are wheelchair bound and may die before the age of 30 from cancer or lung disease
Congenital cerebellar degeneration. This type of ataxia results from damage to the cerebellum present at birth. Wilson's disease. Copper builds up in the brain, liver, and other organs, which can cause neurological problems, including ataxia. Identifying this disorder and starting treatment early will slow its progression.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Articles refer to the source: mayoclinic.org