This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Vo Cong Hien - Radiologist - Radiology Department - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital. The doctor has many years of experience in the field of diagnostic imaging.X-ray of the spine is an imaging method widely used in the diagnosis and monitoring of diseases in the spine. The x-ray film shows anatomical images of the spine, thereby knowing the normal and abnormal condition of the spine.
1. X-ray anatomical features of the spine
The normal spine is composed of 7 cervical vertebrae, 12 lumbar vertebrae, 5 lumbar vertebrae, 5 sacral vertebrae and 4 coccyx vertebrae.On each segment, the spine has differences. Some anatomical features that can be seen on X-ray films include physiological curves, vertebrae, synaptic foramen, and joints in the spine.
1.1. Physiological curve
In order to recognize the change of physiological curve, it is necessary to look at the spine radiograph in the inclined position, this is a continuous curve connecting the anterior border of the vertebral body or the posterior border.Neck segment: The curve curves slightly forward. Upper back: Back curve. Lumbar segment: The curve curves slightly forward evenly along the vertebral bodies. Truncated segment: Backward curve. When X-ray of the spine can see the loss of physiological curves in some diseases, combined with other signs to make a diagnosis.
Khi chụp X - quang cột sống có thể thấy được tình trạng mất đường cong sinh lý trong một số bệnh, kết hợp với các dấu hiệu khác đưa ra chẩn đoán bệnh.
1.2. Structure of the vertebrae
Each vertebra has a structure including: vertebral body, vertebral body, vertebral column, spinous process, transverse process, superior and inferior joint process. On X-ray film, it is possible to observe the structural components of the vertebrae.However, at each segment, there are differences in the structure of the vertebral body such as:
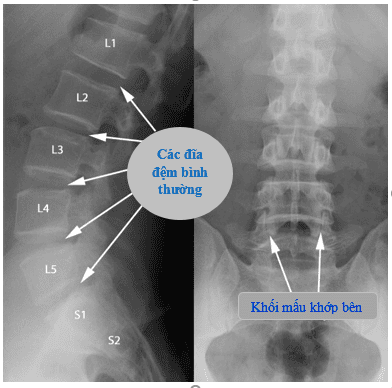
Cervical spine: The vertebral body is small, wide in width, the vertebral body is attached to the side of the vertebral body. The transverse process has a hole to allow the basilar artery to pass and the apex of the spinous process splits into two except for the 7th cervical vertebrae, the 1st cervical vertebra without a vertebral body, and the 2nd cervical vertebra with a small body. Thoracic spine: The spinous process is longer than other segments of the spine with a downward direction, the transverse process has a joint area to match the head of the rib and form the rib joint. Lumbar spine: The vertebral body is the largest compared to other segments of the spine, wide horizontally. Thick vertebrae. The transverse part of the 3rd belt is longest. The spines are rectangular in shape. Sacral vertebrae: There are 5 vertebrae that stick together to form a bone plate and together with the pelvis to form two sacral joints - the pelvis. Vertebral vertebrae: There are 3 - 5 small vertebrae forming the coccyx with a triangular shape. From the anatomical features that can be seen on X-ray films, it is possible to evaluate abnormalities in the structure of the vertebrae.
Từ những đặc điểm giải phẫu có thể thấy được trên phim chụp X - quang cho phép đánh giá những bất thường về cấu tạo của đốt sống.
1.3. Learn about disc slots
On X-ray film, the structure of the disc is not visible because the disc is not contrasted, but the intervertebral disc gap can be seen on both straight and inclined films.The intervertebral disc space is the space between the upper and lower vertebral bodies, which contain the disc. Through the evaluation of the disc space to orient the cases with disc herniation, from which, additional MRI films are indicated for definitive diagnosis.
1.4. Joints in the spine
The vertebral system is made up of the superior and inferior articular processes of two adjacent vertebral bodies. The semicircular joint or Luschka joint is only found in the cervical vertebrae, each cervical vertebra has two semicircular nodes located at the upper outer border of each vertebral body. Usually, the semicircular nodule has a rosette-like appearance and is recognized on radiographs of the cervical spine in the upright position.1.5. Adapter hole
The synaptic foramen, also known as the foramen, is the place where the spinal nerve roots come out. X-ray can detect a narrowing of the synaptic foramen that causes nerve compression.For cervical spine to evaluate the fusion hole, it is necessary to take 3/4 oblique X-ray film. For thoracic and lumbar radiographs, evaluation can be made on lateral radiographs.
1.6. Tube diameter
The diameter of the spinal canal is determined on straight and inclined radiographs by the following limits:Transverse diameter: The distance between the inner margin of the two pedicles on either side of the spine. Anterior–posterior diameter: Distance between the posterior margin of the vertebral body and the anterior margin of the vertebral segment. Anterior and posterior diameters of cervical 1 and 2 cervical canals are wider than those of other cervical canals. The transverse diameter of the spinal canal can widen in the case of myeloma, which is usually only present in young people, especially in the cervical spine. In adults, when the posterior arch is unable to develop further, the myeloma is no longer able to widen the pedicle.
2. X-ray diagnosis of some common spinal diseases
2.1 Congenital spinal deformities Currently, common congenital spinal malformations can be mentioned as:Transitional disorders in the spine: There are 8 cervical vertebrae and 6 lumbar spines. vertebrae or vertebrae remaining 4 vertebrae. Double spine, open waist spine: Double spines are common in lumbar spine 4, 5 and 1, the image is missing or spiny process is split into 2. Open waist is common in lumbar spine 4, 5 and seen above 3⁄4 oblique film. Scoliosis: Seeing the phenomenon of spine misalignment, vertebral body deformity. Humpback: Seen on lateral radiographs, the spine is protruding posteriorly, causing kyphosis. 2.2 Spinal degeneration and trauma Spondylolisthesis is common in people over 40 years of age, with X-ray images such as subchondral thickening, bone spur formation, disc stenosis and graft stenosis. .
As for the situation of spinal trauma, it is common in cases such as:
Fracture of the vertebral body: Seeing the broken line running across the vertebral body, loss of continuity of the vertebral body. Vertebral collapse: The height of the vertebral body is collapsed compared to normal vertebral bodies, increasing contrast. Spondylolisthesis: Can experience sliding forward, backward or sliding to the sides. Orthodontic process fracture of cervical spine 2: Can be detected through radiographs of slanted cervical spine and neck taken in 1, 2 upright positions with open mouth. Posterior arch fractures, transverse processes and spinous processes are less common. 2.3 Ankylosing spondylitis The X-ray image of ankylosing spondylitis is caused by calcification of the anterior longitudinal, interspinous and lateral ligaments of the spine like bamboo or rails. train.
2.4 Tuberculosis of the spine Compared with other diseases, tuberculosis of the spine is the most common condition in the tuberculosis of the joints. The disease is common in thoracic vertebrae 4, 5 and lumbar 1, 2. X-ray images vary according to the stage of the disease.
From the anatomical characteristics of the spine on X-ray films, normal and abnormal signs of the spine can be seen.
In medicine, X-ray of the spine is very important to help doctors accurately diagnose diseases related to the spine. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has applied X-ray techniques in examination and diagnosis of many musculoskeletal diseases.
X-ray technique at Vinmec is performed methodically and according to standard procedures by a team of highly qualified medical professionals, modern machinery system, thus giving accurate results, thereby helping doctors The doctor makes the best diagnosis and treatment for the patient.
Kỹ thuật chụp X-quang tại Vinmec được thực hiện bài bản, đúng chuẩn quy trình bởi đội ngũ y bác sĩ tay nghề chuyên môn cao, hệ thống máy móc hiện đại.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.