This is an automatically translated article.
Ovarian dermoid cyst is a type of dermoid cyst that is acquired in the ovary. While dermoid cysts can occur anywhere on the body, the ovary is the most concerning because the condition can inadvertently affect a woman's fertility if: are not detected early or even cause many dangerous complications.
1. What is an ovarian dermoid cyst?
The term dermoid cyst is not limited to a specific type of lesion nor is it used within a single medical specialty. Indeed, the term dermoid cyst can be found in dermatology, neurosurgery, pediatrics, general surgery, and gynecology. Accordingly, depending on the location of the dermoid cyst, the patient will be diagnosed according to the respective specialty.
However, in all disciplines, the common feature of dermoid cysts is the presence of a single tumor or sometimes multiple tumors. The tumor is covered with a thick, dermis-like wall, containing many sebaceous glands and nearly all subtypes of the skin. In particular, hair, hair, nails, and a large amount of the fatty coverings all originate in the ectoderm during the embryonic stage.
For ovarian dermoid cyst in particular, ie dermoid cyst formed at the ovary, similar to other locations, this is also a physical ovarian cyst. The cause of ovarian dermoid cyst formation here is believed to be due to the entrapment of skin and skin structures during fetal development.
In general, although there is no information on the frequency of dermoid cysts in general and ovarian cysts in particular, the prevalence of this type of lesion is very rare and has absolutely no or very high risk. low progression to cancer. Even if dermoid cysts are diagnosed early and treated with complete surgical removal, the patient's prognosis will be similar to that of a normal person and without other complications.

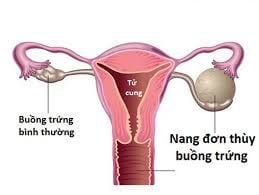
U nang bì buồng trứng là một dạng u nang bì có vị trí mắc phải tại buồng trứng
2. Signs of ovarian dermoid cysts like?
It is difficult to distinguish the signs or symptoms of ovarian dermoid cysts from other gynecological conditions.
If ovarian dermoid cyst is small in size and progresses silently, the patient may not be diagnosed until the doctor is examined because of vague gynecological symptoms as follows:
Infertility Menstrual disorders Pain during intercourse Vaginal bleeding during intercourse Unusual vaginal bleeding Pelvic pain – described as a dull ache or throbbing pain in the lower abdomen on the side of the cyst Abdominal bloating or heaviness in the lower abdomen However, when the patient has sudden and urgent signs as follows, they need to go to the hospital, require immediate medical attention because it is possible that a dermoid cyst is present. Egg complications:
Sudden, severe abdominal or pelvic pain Abdominal pain accompanied by fever or nausea, vomiting Dizziness, lightheadedness, cold skin, floating, rapid breathing and severe weakness
3. How to diagnose ovarian dermoid cyst?
The patient's clinical symptoms are not specific for ovarian dermoid cysts or ovarian cysts in particular, gynecological diseases in general.
Accordingly, the doctor needs to have examinations and appoint specialized tests to diagnose ovarian dermoid cysts as follows:
Abdominal examination: Feel the bulging pelvic fossa, pressing pain or tightness . On the contrary, if the ovarian dermoid cyst is necrotic, hemorrhagic or ruptured, this is an acute surgical abdomen, the patient has signs of resistance to the abdominal wall. Vaginal or anorectal examination for non-sexual women: If the size of the cyst is large, it may be palpable by hand on examination. Ovarian dermoid cyst is a type of organic ovarian cyst, palpable, dense or firm, distinguishing it from functional ovarian cysts, which often contain fluid, so the density is softer. Test blood or urine HCG levels to rule out pregnancy. Transvaginal or abdominal wall ultrasound for women who have not had sex: This method uses ultrasound waves to reconstruct the image and assess the location, size and density of the cyst. ovary. The feature that helps towards ovarian dermoid cyst is often dense, heterogeneous. Computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): These are more advanced imaging tools than ultrasound, with greater sensitivity and specificity in the ability to confirm ovarian dermoid cysts or ovarian cysts. Differential diagnosis with lesions from adjacent organs, especially in patients with previous history. Exploratory endoscopy combined with therapeutic endoscopy: This is an interventional method. By inserting a small laparoscope through the abdominal wall or through the vagina, surgeons can access the tumor and take a local biopsy. Anatomical evidence is the definitive criterion for the diagnosis of ovarian dermoid cyst as well as the assessment of possible malignancy. At this time, the surgeon can also actively dissect the tumor via laparoscopic route or convert it to open surgery if the size of the ovarian dermoid cyst is too large.

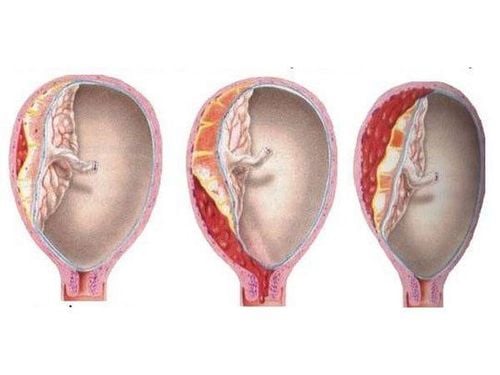
Người bệnh cần được thăm khám và thực hiện các xét nghiệm chuyên biệt để chẩn đoán u nang bì buồng trứng
4. How is ovarian dermoid cyst treated?
Radical surgical excision is the treatment of choice in most cases of ovarian dermoid cysts.
The entrance of surgery can be through endoscopic vaginal, endoscopic fall on the abdominal wall and open surgery if the size of the cyst is large and complicated. In some patients, especially women of childbearing age and planning a pregnancy, surgical manipulations should be performed more carefully than usual, both to preserve ovarian integrity and to maintain the integrity of the ovaries. Limit trauma, easily cause the risk of adhesions when healing scars, increase the possibility of infertility.
On the other hand, the process of dissection of ovarian dermoid cyst needs to be thorough and complete, especially for large tumors, because the fatty component of the cyst may spread to surrounding tissues or adjacent anatomical structures. proximal, especially if the cyst is infected with bacteria. The spread of these substances can cause foreign body reactions and serious complications.
In case of undetected or delayed intervention, ovarian dermoid cyst can cause dangerous complications. Surgical intervention at this time needs to be performed urgently and may not be able to save the ovaries because the ovary has been twisted, causing necrosis or hemorrhage of the cyst, causing massive intra-abdominal bleeding.
In summary, although ovarian dermoid cyst is very rare, when encountered, it is necessary to have a thorough treatment. Because it is a form of organic ovarian cyst, early surgical removal of the tumor will help preserve ovarian function, maintain fertility as well as proactively prevent serious complications due to ovarian dermoid cyst. may cause. Ovarian dermoid cyst is usually a malignant tumor, but it should be detected and treated promptly to avoid the risk of complications affecting reproductive health and the patient's life. Therefore, women should check their health periodically in combination with a reasonable and scientific diet, keeping an optimistic and cheerful spirit to prevent diseases.
Vinmec International General Hospital applies laparoscopic surgery technology using robots capable of overcoming some difficulties in conventional surgery, such as giving clear 3D camera images instead of 2D images, arms Quick and flexible surgery helps to cut and burn quickly and accurately, wide viewing angle overcomes vision difficulties in some areas of the body that are difficult for doctors to see.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.