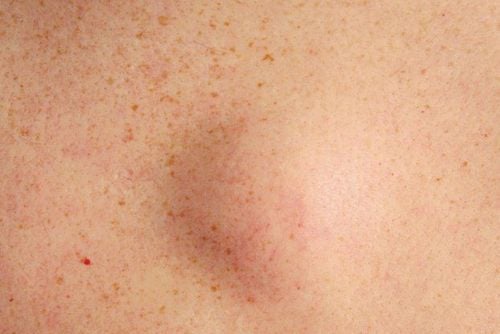
This is an automatically translated article.
The article is written by MSc, BS. Nguyen Le Thao Tram, Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Nha Trang International General HospitalFat necrosis of breast tissue is a benign process, often seen in patients after breast biopsy, breast reconstruction surgery, breast implant removal. This phenomenon does not require deep intervention treatment, in some cases of fat necrosis forming a large mass, the doctor will prescribe intervention depending on the condition of the disease.
1. Overview of breast tissue fat necrosis
Fat necrosis in the breast parenchyma is a pathological process in which an altered localized fat becomes more tender. This is a benign development and is common in women undergoing breast-conserving surgery or undergoing breast tissue interventions.The risk is highest in middle-aged women with loose breast tissue. Onset of fat necrosis is usually quite late, averaging about 10 years after surgery.
Common causes can be direct trauma such as seat belt impact, breast biopsy, implant removal, or breast reconstruction surgery. Clinical practice shows that trauma and surgery are the two most common causes. In addition, necrosis of breast tissue fat can also be seen in a number of other diseases. The most common location is below the areola or around the areola.
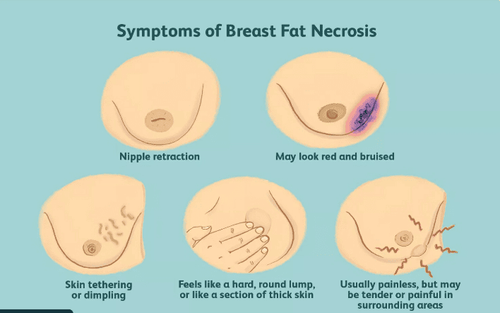
2. Imaging features of breast tissue fat necrosis
2.1. Mammography The image of fat necrosis is quite variable. Initially, it may present as a mass, irregular border dendritic, border is not clear and easily confused with malignancies such as ductal carcinoma in situ. Calcification in fat necrosis is typically peripherally located, which may manifest as "bubble"-like spots in the breast parenchyma with a central radiolucent area.Later, the area of fat necrosis changes to become a well-defined, more evenly bordered mass called "oil cyst". “Oil cysts” may have a very pronounced calcified border at the periphery and the center becomes more uniform with a fatty density.
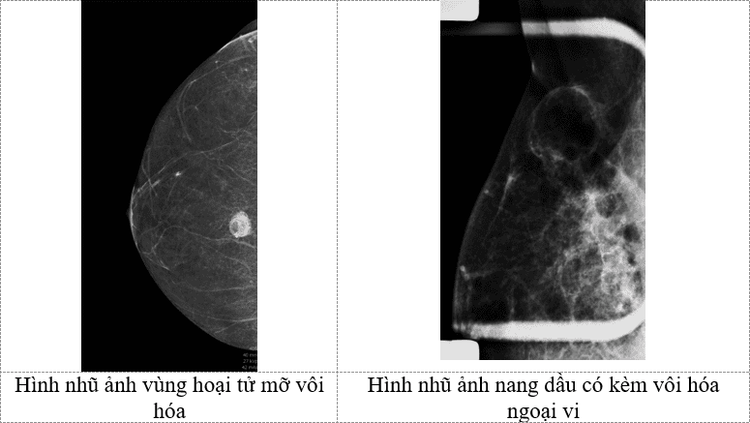
The diagnosis of fat necrosis should be combined with a history of intervention or trauma to the breast parenchyma. This helps radiologists have a more objective view and differentiate fatty necrotic lesions from intraductal cancer.
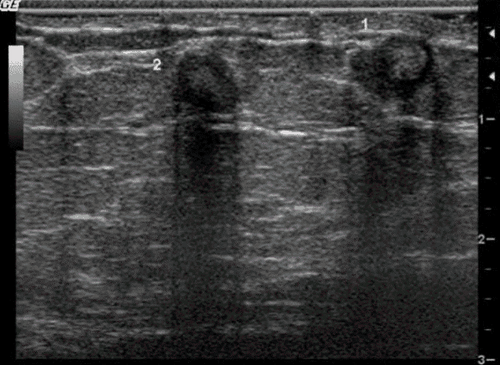
3. Breast Magnetic Resonance
The most common presentation of fat necrosis on magnetic resonance imaging is a round or oval mass, with a signal similar to that of adipose tissue and with a "black hole" signal on some saturation pulses. fat. After injection, the area of fat necrosis may be localized or diffuse, uniformly or heterogeneously. Another form of enhancement is the borderline, which can be difficult to distinguish from a malignancy because the rim can be thick, irregular, and spiny, which is also one of the hallmarks of cancer.4. Progression of breast tissue fat necrosis and differential diagnosis
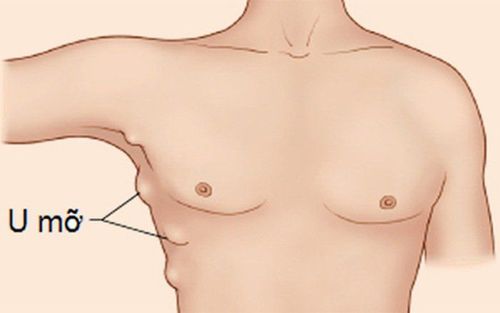
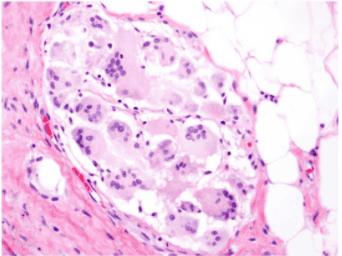
As mentioned above, the localized area of fat necrosis can become an "oil cyst", which is a fat mass surrounded by a surrounding fibrous capsule, at which time the "oil cyst" will be difficult to distinguish from a milk-coated cyst. , intra-mammary lipomas, and especially serous cysts based on ultrasound imaging alone.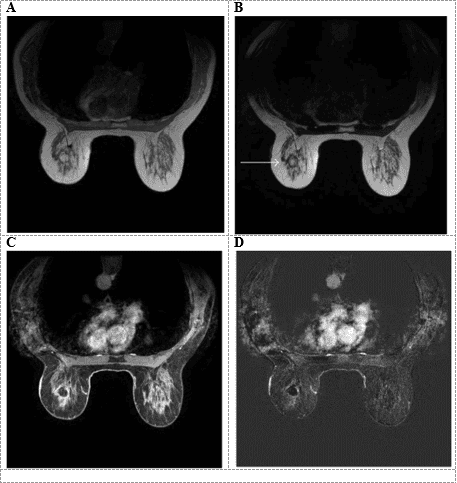
5. Treatment
Most breast tissue fat necrosis requires minimal intervention, and even aspiration of the cyst or biopsy is not a common recommendation because of the benign course of fat necrosis. However, if in the case of fat necrosis forming a large mass, it is possible that the doctors will intervene surgically.To protect your health, you should go to a medical facility for examination and treatment advice. Vinmec International General Hospital is a high-quality medical facility in Vietnam with a team of highly qualified medical professionals, well-trained, domestic and foreign, and experienced.
A system of modern and advanced medical equipment, possessing many of the best machines in the world, helping to detect many difficult and dangerous diseases in a short time, supporting the diagnosis and treatment of doctors the most effective. The hospital space is designed according to 5-star hotel standards, giving patients comfort, friendliness and peace of mind.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: medicalnewstoday.com, radiopaedia.org, hindawi.com