This is an automatically translated article.
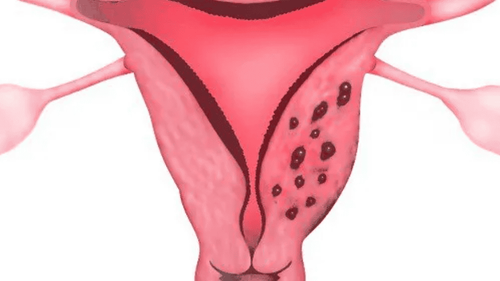
Tubal fluid retention is a gynecological disease in women of reproductive age, which can lead to infertility if not detected and treated early.
1. Causes of tubal stasis
According to doctors, obstetricians have many causes of tubal fluid retention in women. When the exact cause of the disease is known, the treatment will be more appropriate and effective. Specifically, some common causes of tubal stasis can be mentioned:
Women have a history of or are suffering from diseases related to the genital organs such as: Vaginitis, pelvic inflammatory disease due to infection. Chlamydia , salpingitis, tubal adhesions, endometriosis Unhealthy, unsafe sex Not cleaning the private area properly, clean before and after sex or during menstruation Women have a history of genital surgery, especially fallopian tube surgery Female with sexually transmitted diseases, ruptured appendicitis ...

Có nhiều nguyên nhân dẫn đến ứ dịch vòi trứng ở nữ giới
2. Symptoms of tubal stasis
Tubal stasis is quite difficult to detect, the symptoms of the disease are often confused with other gynecological diseases. However, women need to pay attention to the following symptoms to go to the doctor to detect the disease as soon as possible:
Pain in the lower abdomen or pain throughout the abdomen, possibly with vaginal discharge Dull abdominal pain, or Severe pain in the lower abdomen, sometimes the whole abdomen. pain worsens near menstrual period Excessive menstrual flow Difficulty in getting pregnant Some other symptoms such as digestive disorders, vaginal discharge a lot, or pain after sex... Symptoms say The above does not completely confirm that you have tubal fluid retention. However, if you have the above symptoms, you need to see an obstetrician and gynecologist, have tests as prescribed by your doctor to have an accurate conclusion about your health status and have appropriate treatment orientation.
3. Diagnosis of tubal stasis
Based on the above symptoms of tubal stasis, the doctor will prescribe appropriate diagnostic methods for tubal stasis. In which:
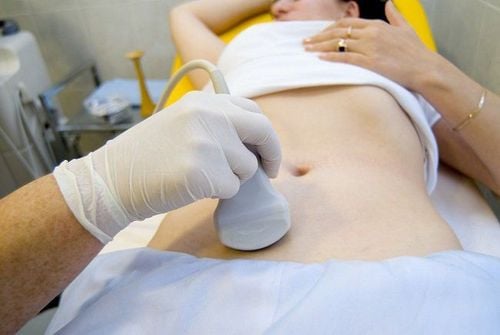
Ultrasound pump water of the uterus by putting physiological saline and sterile gas through the cervix to easily observe the reproductive organs to detect abnormalities or blockages here. Ultrasound helps to detect tubal fluid retention.
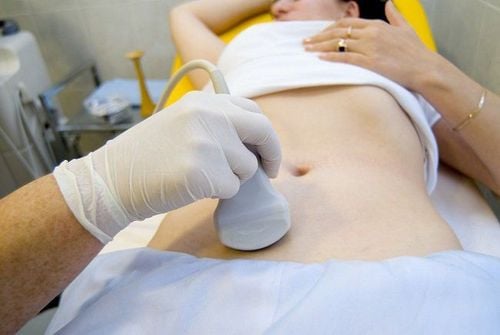
Siêu âm giúp phát hiện và chẩn đoán ứ dịch vòi trứng
X-ray of the uterus and fallopian tubes to diagnose tubal obstruction by inserting contrast and the patient's vagina and cervix before performing the x-ray. Endoscopy helps doctors see organs, directly remove stagnant fluid and other lesions. At the same time, it helps to quantify other pelvic lesions that may be the cause of infertility such as endometriosis.
4. Treatment of tubal stasis
Women after concluding that they have tubal stasis, depending on the situation, there will be different appropriate and timely treatment indications. The specialist will advise and treat the patient with appropriate methods.
4.1 Tubalectomy The most common treatment for tubal stasis today is surgical removal of the affected fallopian tube. With this method, the fallopian tube is cut to its full length.
This method is often not recommended by doctors because surgery can damage blood vessels that feed the ovaries, affect egg quality, and reduce the possibility of pregnancy. Surgery also helps to remove scar tissue or other adhesions that can affect fertility.
If tubal fluid retention is caused by endometriosis, your doctor may remove abnormal growths of endometrial tissue.
If pelvic inflammatory disease is the cause of tubal fluid retention, the patient can be treated with antibiotics.

Bệnh nhân có thể tự điều trị bằng kháng sinh nếu ứ dịch vòi trứng do viêm
4.2 Sclerotherapy Another effective method of treating tubal stasis is sclerotherapy. The patient will have the fluid in the ovaries aspirated with a needle, and then injected with special drugs to prevent the fluid from accumulating. This is a treatment that helps women recover faster than surgery, and has less complications, but according to doctors, with this treatment, the possibility of recurrence is also high.
4.3 Laparoscopy Laparoscopic surgery to unblock fallopian tubes, fallopian tubes: The doctor conducts tubal catheterization under the guidance of laparoscope, which helps to remove debris and separate adhesions in the lumen of the fallopian tubes. egg. Laparoscopic surgery to remove adhesions of fallopian tubes and fallopian tubes: Applied to cases where the fallopian tubes are attached due to inflammation, easily leading to ectopic pregnancy, the patient needs to undergo dilation and removal of the fallopian tubes. , the fallopian tube to make sure sperm and egg can flow normally without getting stuck. After surgery to unblock and remove the fallopian tubes, the patient should leave it alone for 3 months, if not, then plan for infertility treatment. To limit the risk of complications causing infertility in women, women need to have regular obstetric and gynecological examinations at hospitals and specialized medical facilities. Especially when there are unusual signs and symptoms.
At Vinmec International General Hospital, Vinmec Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, customers are examined and treated for tubal stasis and other obstetrics and gynecological diseases by a team of experienced and highly qualified specialists and obstetricians and gynecologists. . Please contact Vinmec at the nationwide system here for advice, appointment to schedule an appointment for effective, appropriate and timely treatment of tubal stasis.
MORE
Vaginal infections are the leading cause of blocked fallopian tubes Learn what are fallopian tubes? How many centimeters long is the fallopian tube? X-ray of the uterus and fallopian tubes (HSG scan) in which case?