This is an automatically translated article.
Menorrhagia, heavy bleeding is one of the abnormal manifestations occurring mainly in women of reproductive age. Causes of menorrhagia are quite diverse, often divided into two main groups including functional causes and physical causes.
Menorrhagia occurs in many different gynecological diseases, but one thing in common is that they bring many troubles to women. The diagnosis of menorrhagia should be directed toward finding the cause and possible complications. Treatment of menorrhagia should be carried out immediately after the diagnosis and strictly adhere to the recommended treatment regimen to achieve high efficiency for the patient.
1. Overview of menorrhagia
Menorrhagia, heavy bleeding are two of the many types of abnormal uterine bleeding reported clinically. This is suggestive of many different gynecological diseases. Menorrhagia is defined as bleeding from the endometrium that occurs periodically, usually matches the menstrual cycle, and occurs for more than 7 days with variable blood volume. In contrast, heavy bleeding is a term that refers to uterine bleeding that occurs irregularly. In haemorrhage, the amount of blood recorded usually lasts more than a week, can be more, less or moderate depending on the specific case.
On average, about 11% to 13% of women experience heavy bleeding at least once in their life, more common in women of reproductive age 35 to 40 years old. Menorrhagia occurs in many different pathological contexts. Causes of menorrhagia can be divided into two main groups, including:
Functional causes: this group of causes refers to physiological changes according to different ages of a woman that can lead to menorrhagia, bleeding. Ovulation disorders are the cause of abnormal uterine bleeding in girls during puberty. In contrast, in perimenopausal women, anovulatory cycles are thought to be the cause of menorrhagia after no suitable pathological cause can be found.

U xơ tử cung là một nguyên nhân gây rong kinh
Physical causes: this group of causes is common in women of reproductive age, related to obstetric and gynecological diseases. Uterine fibroids, uterine polyps or endometrial hyperplasia are common gynecological diseases that cause menorrhagia. Women during pregnancy may experience abnormal uterine bleeding due to ectopic pregnancy, fetal movement, threatened miscarriage, intrauterine cessation of pregnancy, or abnormalities related to trophoblastics. Other systemic medical conditions have also been reported to cause uterine bleeding, such as coagulopathy, autoimmune thrombocytopenia, chronic kidney disease, impaired liver function, or thyroid disease. Besides, heavy menstrual bleeding can also be an unwanted side effect when a woman uses drugs such as aspirin, heparin, estrogen...
2. Diagnosis of menorrhagia
Diagnosis of menorrhagia not only stops at determining abnormal uterine bleeding, but also needs to orient to find the cause of the disease. The diagnosis of menorrhagia in order to achieve good results requires a combination of clinical and paraclinical factors.
2.1 Clinical
Factors related to the medical history such as bleeding time, blood volume, frequency of symptoms, and periodicity need to be exploited and recorded to distinguish between the two concepts of menorrhagia. and bleeding. Menorrhagia occurs periodically in girls during puberty due to functional causes related to ovulatory dysfunction. An obstetric and gynecological history should also be taken to look for individual risk factors, including previous gynecological conditions, sexual habits, and other medications used.
The clinical examination process should be done in an overview and in detail, not only focusing on menorrhagia and heavy bleeding. A number of abnormalities in other organs may be suggestive of the underlying cause such as hepatocellular dysfunction, thyroid disease, kidney disease or general coagulation disorders. . Rectal or vaginal gynecological examination can help detect physical lesions such as tumors in the genital tract.

Khám phụ khoa giúp người bệnh xác định các yếu tố nguy cơ gây rong kinh
2.2 Subclinical
Laboratory facilities and tests are intended to determine the severity or complications that menorrhagia may bring and to help diagnose the cause of the disease. Complete blood count and coagulation function is one of the routine tests in most cases of women coming to the clinic because of heavy menstrual bleeding. Women of childbearing age need to be ordered to have more quantitative b-hCG blood test to know if they are pregnant or not.
In addition, a number of other tests are also ordered to perform together, including quantitative sex hormones, cervical smear, cervical smear test and curettage biopsy. pathology. Imaging diagnostic tools used in the diagnosis of menorrhagia include abdominal or vaginal gynecological ultrasound, hysteroscopy, and pelvic magnetic resonance imaging.
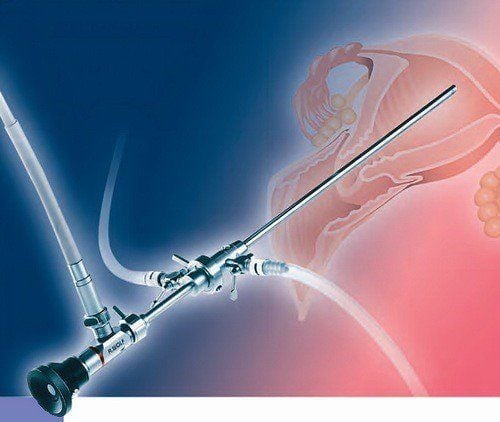
Phụ nữ rong kinh được chỉ định nội soi buồng tử cung
3. Treatment of menorrhagia
The main goals when treating menorrhagia and heavy bleeding include stopping abnormal uterine bleeding, finding the underlying cause and treating complications, and improving the patient's health status. The specific treatment regimen in each case is different, but they all stick to the above goals.
Bleeding from the endometrium can be treated with hormonal drugs, hemostatic drugs or curettage. In particular, uterine curettage is often indicated in pre-menopausal women because it both helps patients to stop bleeding quickly and obtain endometrial specimens for pathology to find the cause. core.
Besides, patients also need supportive treatment and support in cases of heavy menorrhagia causing anemia complications. Blood and blood products may be indicated if anemia is severe. Supplementing with adequate nutrients, including iron, is also a good measure to help improve the patient's health condition.

Bổ sung sắt là một phần quan trọng trong liệu pháp điều trị rong kinh
In order to help customers detect and treat gynecological diseases early, Vinmec International General Hospital has a package of basic gynecological examination and screening, helping customers detect early infectious diseases and help treat Easy, inexpensive treatment. Screening detects gynecological cancer (cervical cancer) early even when there are no symptoms.
Basic gynecological examination and screening package for female customers, has no age limit and may have the following symptoms:
Abnormal vaginal bleeding Having menstrual problems: irregular menstrual cycle, irregular menstrual cycle Irregular vaginal discharge (smell, different color) Vaginal pain and itching Female clients have several risk factors such as poor personal hygiene, Unsafe sex, abortion,... Female customers have other symptoms such as: Abnormal vaginal discharge, itching, pain in the private area, abnormal vaginal bleeding.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.