This is an automatically translated article.
Professional consultation article by Doctor of Obstetrics and Gynecology Department, Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
Uterine bleeding in women usually only occurs during menstruation. However, it is possible that because of a certain gynecological disorder, the bleeding becomes unusual compared to usual. When there is abnormal vaginal bleeding, women need to go to the doctor immediately for timely diagnosis, testing and treatment.
1. What is abnormal uterine bleeding?
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding (AUB) is a term describing an abnormal condition of the menstrual cycle in terms of the time of menstruation, the duration of menstruation, the amount of blood loss during menstruation... is the most common gynecological cause, accounting for one-third of all visits to the doctor.
2. Causes of abnormal uterine bleeding
2.1 Gynecological inflammation Cervicitis, endometritis, and pelvic inflammatory disease are some of the reasons for abnormal uterine bleeding. This usually occurs after sexual intercourse. If not treated early, the disease can potentially affect a woman's reproductive function.
Gynecological diseases such as: Uterine fibroids, cervical polyps, cervical cancer also cause abnormal vaginal bleeding. Possible accompanying symptoms are pain in the lower abdomen, urinary disorders, menstrual disorders,...
2.2 Hormonal disorders Imbalance between estrogen and progesterone hormones is the reason for bleeding in the reproductive organs. abnormal sex. To be sure, women should have an endocrine exam, ultrasound evaluation of the lining of the uterus to check.
Women going through menopause can have regular but shorter menstrual cycles. If menstrual cycles are shortened but irregular, other causes should be evaluated.
2.3 Due to Abortion, Miscarriage, or Ectopic Pregnancy After an abortion or miscarriage, women will experience vaginal bleeding for a few days to 1-2 weeks depending on the gestational age at the time of the abortion or the miscarriage. Similar to the case of postpartum, if abnormal bleeding lasts for a long time, has a lot of blood or has a bad smell, maybe even a fever, there is a risk of infection, stillbirth, retained placenta or some other serious problems after birth. abortion.
If bleeding during pregnancy, women need to go to the hospital immediately for examination. Fresh bleeding in the intimate area during pregnancy can be a sign of an ectopic pregnancy, stillbirth, threatened miscarriage, placenta previa... Abnormal bleeding during pregnancy is an extremely dangerous sign. .
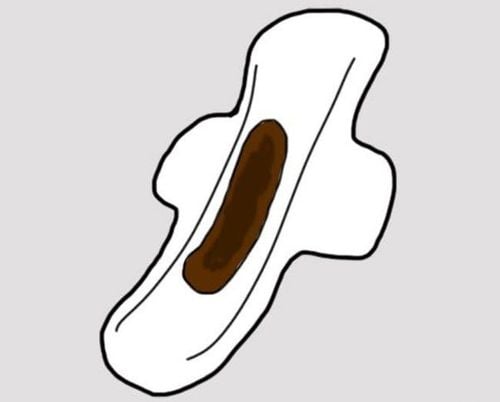
2.4 Postpartum Postpartum After giving birth, a small amount of blood is left over called a puerperal discharge. The discharge usually disappears after 3-4 weeks of birth, the amount of blood usually decreases, gradually changing from bright red to brown, light pink. If the bleeding lasts longer than the postpartum period, the blood clots or the amount suddenly increases, you need to see a doctor immediately.
Nếu máu hậu sản có bất thường thì bệnh nhân cần đi khám ngay
2.5 Taking birth control pills The use of birth control pills not following the doctor's prescription, taking them irregularly and during an emergency period are also some of the reasons that cause abnormal uterine bleeding. When you see this phenomenon, the first thing you should do is go to a gynecological clinic for advice and quick treatment.
2.6 Due to physical diseases Congenital or acquired uterine vascular abnormalities: This disease causes prolonged menstrual periods and heavy bleeding. This abnormality usually occurs after a previous invasive procedure. Thyroid disease: It is one of the common causes of prolonged and heavy menstrual bleeding, but it is not a common cause. Ovulation disorders: Characteristic of this condition is that the patient has not had a period for many months, then there is bleeding or heavy bleeding. Polycystic ovary syndrome and some endocrine disorders can cause abnormal uterine bleeding due to ovulation disorders. Defects in intrauterine cesarean section scarring, cervical stenosis, and Asherman's syndrome that reduce menstrual blood volume are also causes of abnormal uterine bleeding. In addition, people with primary ovarian failure, diabetes, thrombocytopenia, hepatitis, dengue fever, lymphedema, stress, stress due to work pressure, life can also cause disorders. period .
3. Diagnose the cause of the disease
3.1 Clinical examination Determine the location of uterine bleeding: cervix, vagina, vulva, perineum, ureter, anus. Identify abnormalities in the genital tract: tumors, tears, foreign bodies, ulcers... Abnormalities of the uterus: if the uterus is enlarged, it may be due to uterine fibroids, endometriosis in the uterine muscle. or malignancy of the uterus. If the uterus is poorly mobile, it may be due to endometriosis. The uterus is enlarged and painful due to endometriosis in the myometrium. Bleeding status: Determine the bleeding with a small amount or a lot, with blood clots, blood from inside the cervix or outside the vagina. 3.2 Pregnancy test or quantification of -hCG to confirm or rule out pregnancy. Hematology: Assess the state of blood loss. Assess thyroid function; prolactin quantification test; quantitative testing of androgen levels in the blood; estrogen quantification test. Test for FSH and LH secreted by the pituitary gland: If premature ovarian failure is suspected, FSH should be measured. If hypothalamic dysfunction is suspected, FSH and LH should be measured as well as estrogen/progestin testing. Blood clotting tests: this is a common cause in women of reproductive age. About 15-24% of women with menorrhagia may have clotting abnormalities. In the case of heavy and prolonged bleeding at the beginning of menstruation, the patient should be suspected of having a coagulopathy, these patients often have signs such as easy bruising or prolonged bleeding in the mucosa. At the same time, the doctor can examine and rule out other causes of bleeding from the cervix; endometrial biopsy (if necessary); transvaginal ultrasound unless contraindicated (unrelated patient); MRI and CT-scan to monitor metastatic status of malignancy or cases where ultrasound does not provide enough information; hysteroscopy to help diagnose and treat lesions in the uterine lining.
Bệnh nhân cần thực hiện một số xét nghiệm để giúp chẩn đoán bệnh
4. Treatment of abnormal uterine bleeding
The process of treating vaginal bleeding requires the cooperation of the patient. The doctor will prescribe an appropriate treatment method:
4.1 Using drugs Once the cause of abnormal uterine bleeding is identified, the patient will be prescribed medication. What medication to take and in what dose depends on the treating doctor. The treatment drugs used may include the following effects:
Hormonal birth control, menstrual cycle regulation. Stop the menstrual cycle and reduce the size of uterine fibroids. Treatment of severe vaginal bleeding. Anti-inflammatory, control bleeding, relieve menstrual pain. Treat infection if present. If you have a bleeding disorder, medications that help with blood clotting may be included. 4.2 Surgery In cases where medication cannot solve the problem, surgery may be required. Your choice of surgery depends on your bleeding, your age, and your decision about whether or not you want to have more children.
Surgical methods used to treat abnormal uterine bleeding include:
Removal of the lining of the uterus: Helps stop bleeding or significantly reduces it. However, the possibility of pregnancy also disappears after the procedure. Serious complications include severe, life-threatening bleeding. If having this surgery, it's best to use long-term contraception until after menopause. Uterine artery embolization: Used to treat uterine fibroids. This surgery helps to block blood vessels to the uterus, thereby limiting blood supply to the fibroid. Another treatment that doesn't affect the uterus is surgical removal of the fibroids. Hysterectomy: Use when all other treatments have failed. Hysterectomy is also surgery to treat endometrial cancer. After the uterus is removed, the woman will no longer be able to menstruate, nor will she be able to get pregnant. Patients who see signs of uterine bleeding should go to the doctor early to determine the most accurate cause and condition, thereby taking appropriate treatment measures, avoiding complications of reproductive health that may affect the patient's health. influence the motherhood of women.
Vinmec International General Hospital is a leading medical facility in the examination, diagnosis and treatment of obstetric and gynecological diseases. With outstanding medical expertise, modern and high-tech invested facilities, especially a civilized and polite medical examination space, confidentiality of personal information for customers is always focused. ... all will help women feel secure when taking care of their health here.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.