This is an automatically translated article.
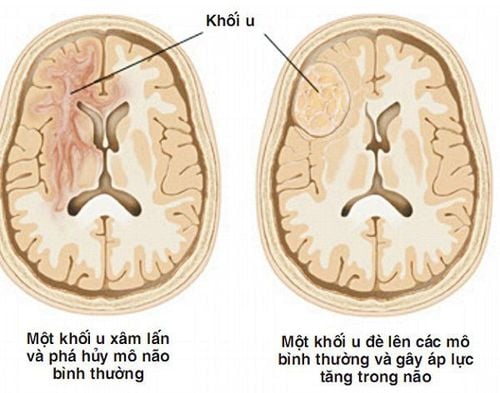
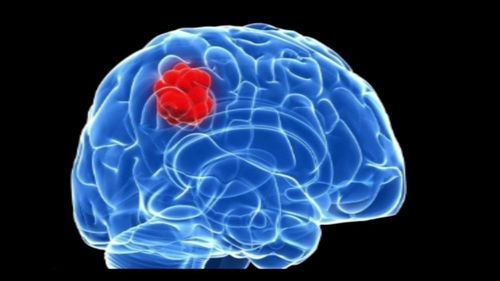
The article was professionally consulted with Master, Doctor Le Hong Duong - Anesthesiologist - Department of General Surgery & Anesthesia - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.Posterior fossa tumor is one of the most common brain tumors in neurosurgery. The method of treatment at this time is mainly surgical resection of the posterior fossa tumor under endotracheal anesthesia. This is the method of general anesthesia commonly applied to most general surgical interventions.
1. What is endotracheal anesthesia for posterior fossa brain tumor?
Endotracheal anesthesia is a method of general anesthesia, actively controlling respiratory function through intubation. Through that, the anesthesiologist and resuscitation specialist will prepare the patient's condition in the best way to be suitable for the surgical process and resuscitation after the posterior fossa brain tumor resection.
Thus, endotracheal anesthesia is completely indicated in cases where the patient has a posterior fossa brain tumor or a cerebellar pontine tumor. However, this procedure is only performed when there are no contraindications such as the patient not agreeing to the surgical intervention or the medical facility conducting it is not fully equipped with the required facilities for anesthesia, recovery. At the same time, one of the prerequisites for this process to be carried out is a team of skilled and experienced neurosurgeons.
2. Preparation steps for endotracheal anesthesia to cut posterior fossa brain tumor
Hình ảnh ống nội khí quản
Step 1: Prepare
Human resources
Doctors, technicians and/or nurses specializing in anesthesiology and resuscitation.
About facilities
100% oxygen supply Anesthesia machine system with artificial respiration control function Life function monitor based on basic ECG parameters, arterial blood pressure, SpO2, EtCO2 , breathing rate, temperature Emergency resuscitation equipment such as defibrillator, viscous aspirator Surgical intubation kit: Laryngoscope, endotracheal tube of various sizes, suction tube, mask (mask), squeeze ball, oropharyngeal cannula, Magill pliers, soft mandrin. Means of prevention of difficult intubation: Cook tube, laryngeal mask, flexible bronchoscope, tracheostomy kit, mouth opener... Local anesthetics such as Lidocaine 10% spray form A quick-acting bronchodilator such as Salbutamol spray About the patient
Have a routine pre-anesthesia visit according to the procedure to detect and prevent risks to the surgery in general
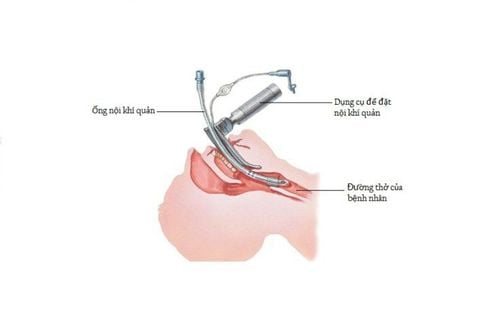
Đánh giá đặt ống nội khí quản
Patients and relatives are consulted about anesthesia and surgical procedures, are explained the benefits and risks for anesthesia and possible perioperative procedures Explain to the patient cooperation, compliance according to the regulations in the pre-operative and pre-anaesthesia preparation procedures, including body hygiene, dressing change and fasting from the night before surgery. Assess difficult intubation and prepare appropriate backup plans Use sedation the night before surgery if the patient is anxious and stressed About administrative procedures:
Medical records as prescribed by the hospital. Ministry of Health Preoperative tests Consent to participate in surgery of patient and relatives Step 2: Steps to perform endotracheal anesthesia to cut posterior fossa brain tumor
Prepare patient:
Arrange patient on operating table in supine position Give 100% oxygen at a flow rate of 3-6 liters/min at least 5 minutes before induction of anesthesia Install a monitor Set up an effective large-needle catheter with aqueous solution Physiological salts flow slowly to keep pills Pre-anesthesia if necessary Initiation of anesthesia:
Sleeping pills: Intravenous anesthetics (propofol, etomidat, thiopental, ketamine...) or volatile anesthetics (sevoflurane...) Painkillers: fentanyl, sufentanil, morphine... Muscle relaxants: succinylcholine, rocuronium, vecuronium...

Thuốc mê bay hơi sevofluran
Conditions for endotracheal intubation:
The patient has slept deeply, has enough muscle relaxation Techniques for oral endotracheal intubation: Open the mouth, insert the laryngoscope to the right of the mouth, move the tongue to the left, push deep lamp, coordinate with the right hand to press the cricoid cartilage to find the epiglottis and glottis. Perform rapid induction of anesthesia and Sellick procedure in case of full stomach (pressing the cricoid cartilage with a weight equivalent to about 20-30 kg as soon as the patient loses consciousness until the intubation is completed). Pass the endotracheal tube gently through the glottis, stopping when the balloon of the endotracheal tube passes 2-3 cm through the vocal cords. Gently withdraw the laryngoscope. Endotracheal balloon pump. Check the correct position of the endotracheal tube with auscultation and EtCO2 results Fix the tube with adhesive tape. Place the canul in the mouth to avoid biting the tube if necessary. Technique for endotracheal intubation: Choose the side of the nasal passage and instill vasoconstrictor drops (naphazoline, otrivine...). Choose an endotracheal tube size smaller than that of the oral route. Insert an endotracheal tube lubricated with lidocaine ointment through the nostrils Open the mouth, insert the laryngoscope into the right side of the mouth, move the tongue to the left, push the lamp deeply, coordinate with the right hand to press the thyroid cartilage to find epiglottis and glottis. Favorable case: insert the endotracheal tube gently through the glottis, stopping when the balloon of the endotracheal tube passes through the vocal cords 2-3 cm. Use Magill pliers to guide the tip of the endotracheal tube into the correct glottis; The assistant pushes the endotracheal tube from the outside in difficult cases. Gently withdraw the laryngoscope. Endotracheal balloon pump. Check the correct position of the endotracheal tube with auscultation and EtCO2 results Fix the tube with adhesive tape. In case of difficult intubation: apply difficult intubation procedure. Perform anesthesia maintenance:
Maintain anesthesia with intravenous or volatile anesthetics, analgesics and muscle relaxants if necessary Control breathing by machine or hand squeeze Monitor during endotracheal anesthesia Monitor depth of anesthesia based on heart rate, blood pressure, sweating, lacrimation (PRST); MAC, BIS and Entropy (if any)... Monitor vital signs: Heart rate, blood pressure, SpO2, EtCO2, body temperature.
Prevent the endotracheal tube from moving, folding, or blocking the tube.
3. Follow-up and post-operative care after endotracheal anesthesia to cut the posterior fossa brain tumor

Theo dõi huyết áp của bệnh nhân để đảm bảo thể trạng người bệnh
Criteria for extubation:
Patient awake, follow orders. Raise the head for more than 5 seconds, TOF > 0.9 if present. Breathe spontaneously, breathing rate within normal limits. Pulse and blood pressure are stable. Body temperature > 350C. There were no complications of anesthesia and surgery. Possible complications and treatment:
Reflux of gastric juice into the airway: Under the residual effect of anesthetic drugs, gastric juice can back up into the airway. Need to aspirate fluid, phlegm in the pharynx and in the endotracheal tube with the patient's head lying down, head tilted to one side. In addition, it is necessary to monitor and prevent postoperative lung infections in these cases.
Hemodynamic disturbances: Side effects on the cardiovascular system due to anesthetics and analgesics may be a factor that hinders surgery. Therefore, it is necessary to detect early signs of low or high blood pressure, arrhythmia on the monitor screen and treat depending on the symptoms and causes to ensure the patient's condition for the surgery to continue. Complications due to intubation: Injury to the lining of the airways, inflammation and swelling of the upper respiratory tract... need to be treated or can be relieved after that.
In summary, endotracheal anesthesia for posterior fossa cystectomy is the classic modality for patient preparation, applicable to most other surgical interventions. However, for the surgery to be successful and to ensure the safety of the patient, the above principles and procedures should be followed as well as the patient's close monitoring during the perioperative period, early detection and treatment. timely response to unexpected situations.
Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit. examination and treatment at the Hospital.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.