This is an automatically translated article.
Uterine polyps are quite common pathology. The disease can be benign without causing any discomfort to the patient, but in some cases, it can cause uterine bleeding, causing uncomfortable symptoms during menstruation. In particular, ovarian polyps can affect a woman's ability to become pregnant.
1. What are uterine polyps?
Endometrial polyps, also known as endometrial polyps, are small, soft growths in the uterus. Polyps form due to the overgrowth of cells lining the inside of the uterus – the endometrium. Therefore, uterine polyps are also known as endometrial polyps. Usually they have a stalk that connects to the wall of the uterus, with a blood vessel in the middle of this stalk to supply blood to the polyp.The size of polyps can range from a few millimeters (mm) to several centimeters (cm), single or multiple polyps, pedunculated or sessile, and can develop anywhere in the uterine cavity.
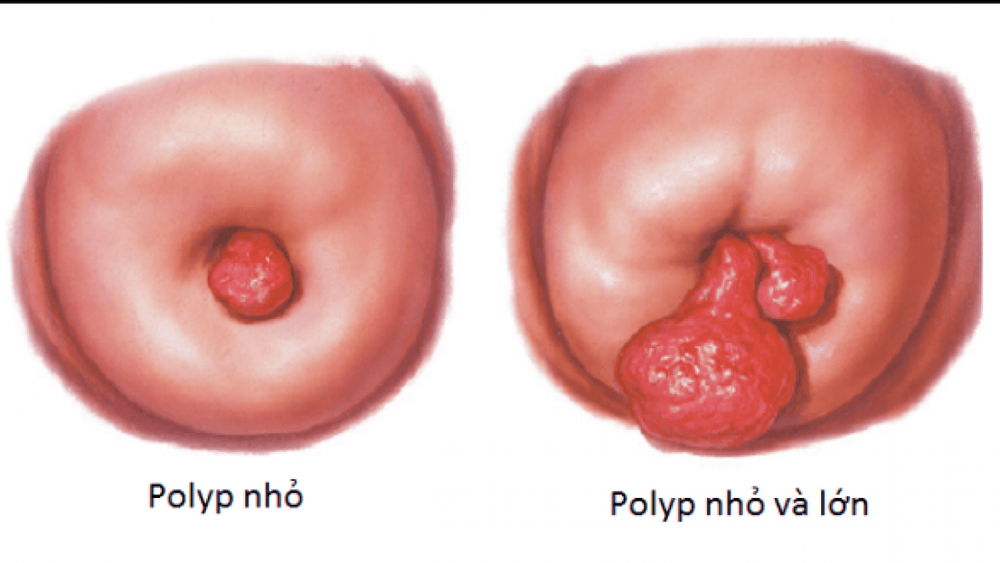
Kích thước polyp lòng tử cung khác nhau ở mỗi người bệnh
2. Are uterine polyps dangerous?
These uterine polyps are mostly benign tumors. Benign cases may not require further treatment.
However, there is still a very small percentage that may be related to cancer later. The risk of developing cancer is higher in perimenopausal or postmenopausal women. Therefore, if there are any abnormal symptoms, it is necessary to follow up according to the instructions of the doctor to rule out the possibility of malignancy.
Uterine polyps can cause infertility. Because polyps take up space in the uterine cavity, the embryo cannot implant. Therefore, patients often find it difficult to get pregnant or are prone to miscarriage.

Trong nhiều trường hợp polyp tử cung có thể gây vô sinh
3. Causes and risk factors
This pathology is very rare in adolescence. The majority of cases are thought to be related to increased levels and effects of endogenous or exogenous estrogen.
Currently, the exact cause of why a woman has uterine polyps remains unexplained.
Risk factors thought to be associated with the development of polyps:
Tamoxifen: A drug used to treat breast cancer Obesity: Women with BMI ≥30 have a higher incidence of colon polyps uterus is significantly higher than in other women Some other risk factors are mentioned such as: Hormone replacement therapy in postmenopausal women containing estrogen, Lynch and Cowden syndrome... Hypertension

Béo phì làm tăng nguy cơ mắc polyp lòng tử cung
4. How to diagnose uterine polyps?
Uterine polyps can cause the following symptoms:
Abnormal uterine bleeding. Hemorrhagic nature: usually mid-cycle, oozing; or heavier bleeding during your period (hypermenorrhea). May be accompanied by abdominal pain, anemia. Some cases are asymptomatic, discovered incidentally during fertility testing, or through cervical cytology, uterine biopsy. With suggestive symptoms, the doctor will recommend one or more The following tests are used to diagnose and differentiate from other causes:
Transvaginal ultrasound. Through this image, the doctor will see a polyp with a very obvious stalk or suspicious when the endometrial layer is abnormally thick. Uterine pump ultrasound. This method uses saline to pump into the uterus, stretching the uterine cavity. The ultrasound is then used to reconstruct the image and observe the abnormal structures in the lumen and wall of the uterus. Endometrial biopsy. Your doctor will take one or more of these tissue samples to look for infections or cancer of the uterus. Uterine endoscopy. With this procedure, the doctor inserts a small laparoscope through the vagina and cervix into the uterine cavity. In addition, the doctor can also insert tools to remove polyps during the colonoscopy.
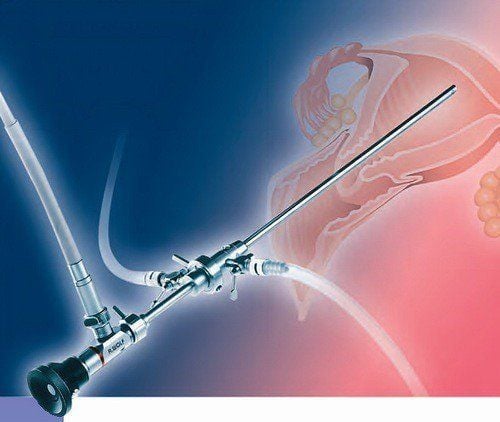
Nội soi buồng tử cung giúp chẩn đoán polyp lòng tử cung
5. Treatment of uterine polyps
5.1 Tracking
About 6.3% of uterine polyps will regress, especially those with polyp size < 10 mm. Therefore, polyps that are small and asymptomatic may not require any treatment. Treatment of small polyps should only be considered when there is an increased risk of endometrial cancer.
5.2 Medical treatment
IUDs contain Levonorgestrel, which can prevent polyp formation, especially in cases where tamoxifen is used.
Use GnRH agonist before performing polypectomy. The effectiveness of this approach was not different from that of polypectomy alone without GnRH agonist therapy.

Bác sĩ sẽ đưa ra phương phap điều trị polyp lòng tử cung phù hợp với người bệnh
5.3 Indications for surgery
Laparoscopic polypectomy is indicated for most cases. The advantage of this method is that it is less invasive, highly effective, and has a short hospital stay. Specify in each specific case.
For premenopausal women
If symptoms are present, polypectomy should be performed regardless of stage. In the absence of symptoms, the indication for polypectomy is primarily related to the assessment of the risk of endometrial hyperplasia or malignancy. In addition, all asymptomatic cases are indicated for polypectomy when: Size > 1.5cm, polyp skin, polyps protruding from the cervix, polyps in infertile cases For postmenopausal women higher risk of malignancy. Therefore, in postmenopausal women with uterine polyps, with or without symptoms, polypectomy is indicated.
In order to help customers detect and treat other gynecological diseases early, Vinmec International Hospital has a basic gynecological examination and screening package, helping customers detect early inflammatory diseases Easy, inexpensive treatment. Screening detects gynecological cancer (cervical cancer) early even when there are no symptoms.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
SEE MORE
What you need to know about cervical polyps Are uterine polyps dangerous? What is uterine polyp? Is it dangerous?