This is an automatically translated article.
The article was consulted professionally with Doctor of Department of Examination & Internal Medicine, Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.The human body has an endocrine system, which secretes hormones and a nervous system that simultaneously regulates the metabolism and physiological functions of the human body. When in a normal state, the hormones keep the body's metabolic balance and physiological function. If for some reason the balance is disrupted, it will lead to endocrine disorders and cause some corresponding clinical manifestations. And one of the causes leading to endocrine disorders is traumatic brain injury.
1. What is a traumatic brain injury?
Traumatic brain injury is sudden brain injury when the head hits something very hard or is hit in the head, or when an object penetrates the skull and enters the brain. Causes include:Falls Motor vehicle accidents Violence, such as gunshot wounds, child abuse or beatings Sports or combat injuries (such as blasting).
2. What is the endocrine system?
The endocrine system consists of glands and organs that produce and release hormones, which are chemicals that help your body function properly by controlling growth, sexual development, and how your body uses it. and energy storage (metabolism), how to cope with illness and more.There are two main systems that regulate bodily functions: the nervous system through the nervous system and the endocrine system through the humoral mechanism. The endocrine system is composed of small, scattered endocrine glands that are not anatomically related but functionally closely related. Besides, it can be said that most organs and cells in the body do endocrine tasks.
Endocrine glands are ductless glands, consisting of two parts: the secretory part forms clusters of cells responsible for synthesizing and releasing hormones, and the rich capillary network surrounds the secretory cells. responsible for receiving hormones into the circulatory system. The main endocrine glands in the body include: hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, pancreas, adrenal and gonads.
Normally, the feedback system of the endocrine glands helps to control the balance of hormones in the blood. If the body has too much or too little of a certain hormone, this system signals the endocrine glands to correct the problem. Hormonal imbalances can occur if the feedback system fails.
3. How does brain injury affect the endocrine system?
Chấn thương não ảnh hưởng đến hệ thống nội tiết như thế nào?
However, traumatic brain injury can damage these two important endocrine glands causing hormone problems. A person with a traumatic brain injury may have hormone problems immediately or months or even years after the injury.
4. What hormone problems are common after traumatic brain injury?
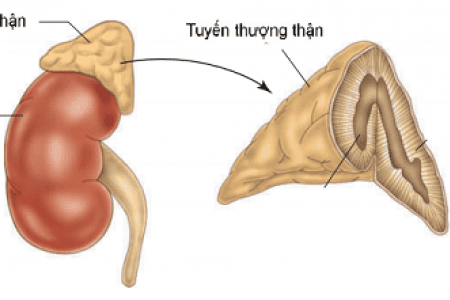
A person with a traumatic brain injury may have one or more problems, depending on the extent and type of injury. Problems that often occur soon after a traumatic brain injury include:Adrenal insufficiency The adrenal glands are small endocrine glands located just above the kidneys. Each gland consists of two parts, the medulla (inner) secretes catecholamine hormones that maintain blood pressure and heart rate, and the cortex (outer) secretes corticosteroid hormones. These hormones are very important for life.
Adrenal insufficiency is a condition in which the adrenal glands produce too little cortisol, leading to disturbances in metabolic processes in the body, fatigue, weight loss, low blood pressure, vomiting and dehydration, which can have a very serious effect. to the patient's health and even death if left untreated.
Diabetes insipidus The most common sign of diabetes insipidus is frequent urination, the urine is thin and pale. Depending on the extent, the amount of urine can range from about 2.5 liters per day if mild diabetes insipidus, if severe, the patient can urinate up to about 15 liters per day, this is often accompanied by the patient taking a lot of urine. many translations.
In addition, the patient often urinates at night, often thirsts for water, especially wants to drink cold water. If left untreated, diabetes insipidus can increase the amount of sodium in the blood, leading to confusion and seizures. There are many causes of diabetes mellitus, including traumatic brain injury that causes the pituitary gland to not produce enough antidiuretic hormone (ADH); leads to frequent urination and extreme thirst.
Hyponatremia Some hormone problems upset the balance of salt and water in the body leading to headaches, fatigue, vomiting, confusion, and seizures.
Possible problems and symptoms like:
Hypothyroidism (not enough thyroid hormone): fatigue, constipation, weight gain, irregular periods, cold intolerance gonads (Hypogonadism): in women stop menstruating and body hair loss; In men, sexual dysfunction, enlarged breasts, loss of body hair and loss of muscle Growth hormone deficiency: in adults there are symptoms of fat gain, muscle and bone loss and decreased energy; in children with growth problems Hyperprolactinemia (too much prolactin): leading to irregular periods, nipple discharge and erectile dysfunction

Sau khi gặp chấn thương não, người bệnh có thể gặp vấn đề đái tháo nhạt
5. How are hormone problems associated with traumatic brain injury diagnosed?
Your doctor will ask about your medical history and perform a physical exam. Blood tests are done to check hormone levels, and an MRI scan is done to check for the pituitary gland and for tumors, cysts, or other problems.6. What is the treatment for hormone-related problems associated with traumatic brain injury?
Usually, the doctor will give the patient a hormone supplement to replace the missing hormones, also known as hormone therapy. Other problems require different treatments, such as treating hyponatremia by cutting back on fluids, giving intravenous saline solutions, and taking other medications, depending on the individual's condition. sick.7. What is the long-term prognosis for hormone problems associated with traumatic brain injury?
Một số vấn đề nội tiết có thể là tạm thời và biến mất trong vòng một năm sau khi chấn thương sọ não
Hormone therapy is a very important part of treatment to restore health, relieve symptoms and improve quality of life and even save lives.
When noticing the above signs and symptoms, the patient needs to go to the doctor for examination and appropriate treatment regimens.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
The article references the source: ncbi.nlm.nih.gov; academic.oup.com; hormones.org