This is an automatically translated article.
The article was consulted with Specialist Doctor I Huynh Kim Long - Emergency Resuscitation Doctor - Emergency Resuscitation Department - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.Coughing up blood in large quantities can cause suffocation, blood loss leading to death. Therefore, people who cough up blood need to be treated promptly. Based on the symptoms of the disease and related factors, the doctor will give emergency indications appropriate to the patient's condition.
1. What is hemoptysis?
Hemoptysis is a condition in which blood is flushed out of the mouth by the act of coughing, i.e. blood from the airways (trachea, bronchi, lungs). It is a warning symptom of acute pulmonary or systemic disease.Severe hemoptysis is an emergency because the patient is at risk of blood loss, suffocation leading to death. The amount of blood coughed up > 100 - 600 ml/24 hours is considered severe hemoptysis.
2. Diagnosis of hemoptysis
Clinical examination: The doctor observes the characteristics of the coughed blood: Fresh blood, fresh out of the box, may be accompanied by foam; Auscultation of the lungs with crackles or crackles Subclinical: Chest X-ray examination shows tuberculosis lesions, bronchiectasis, pulmonary infarction or lung tumor. In addition, some other tests may be ordered including CT scan, bronchoscopy, etc.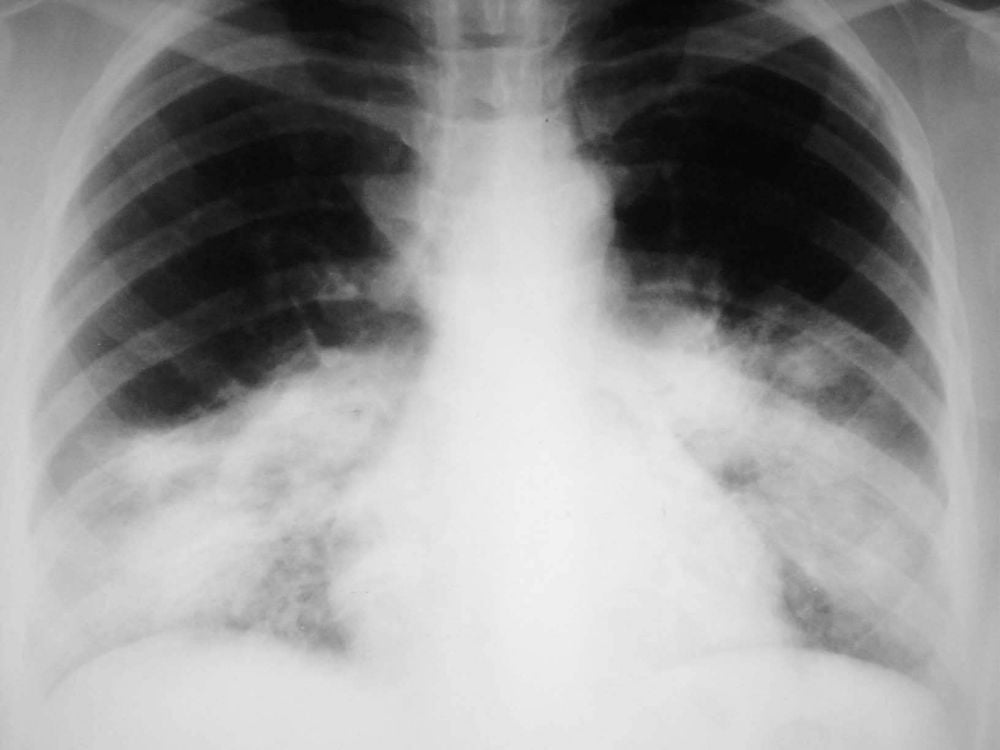
3. First aid for patients coughing up blood
Severe hemoptysis, which accounts for <5% of cases of hemoptysis, is an emergency indication requiring immediate examination and treatment. The life-threatening factor is suffocation, not blood loss. Therefore, bleeding rate is the most important prognostic factor.Emergency treatment of coughing up blood is indicated individually in each case based on the bleeding rate, bleeding location, and the patient's condition. Medical treatment is indicated in cases such as chronic pneumonia, cystic fibrosis, bilateral FQ dilatation to preserve lung function.
First, it is necessary to control the airway, provide O2 and locate the bleeding site. Most deaths are due to asphyxia and hypoxemia due to blood flow to other areas of the lungs. To control hemoptysis, consultation with specialists in anesthesiology, thoracic surgery and radiology is required.
Give extra O2 by giving the patient oxygen. Give the patient a cough suppressant containing codeine if bleeding slows or stops completely. Instruct the patient in a semi-recumbent or side-lying position, maintain the position and conduct a chest x-ray.
If the bleeding continues to be intense, the doctor should continue to recommend additional diagnostic tests and treatment. FQ endoscopy is the key to locating the site of bleeding and treatment should be instituted without delay.
There are 2 options, hard or soft FQ bronchoscope. The advantage of rigid FQ endoscope is better ability to aspirate blood and clot; better visualization of the main airway; easier ventilation and airway control.
However, this procedure needs to be done in the operating room. In milder cases of hemoptysis, FQ endoscopy with a flexible bronchoscope can be performed at the hospital bed or in the intensive care unit. This method allows better visualization of the superior lobe and accessory lobe.

The effectiveness of coronary artery bypass grafting in controlling hemoptysis in the short term is 90%, with late recurrence after 1 year occurring in > 10-20% of patients. These patients need to have the procedure done again. This is a very useful technique for the control of hemoptysis, but it is not applicable to patients with hemoptysis who are indicated for surgery due to the high recurrence rate.
Coughing up blood in large quantities can cause respiratory failure, blood loss leading to death. Therefore, people who cough up blood need to be treated promptly. Based on the symptoms of the disease and related factors, the doctor will give emergency indications appropriate to the patient's condition.
Vinmec International General Hospital has a team of doctors and emergency nurses at the Department who are professionally trained, able to receive and urgently handle severe cases.
Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities and medical equipment combined with a team of respiratory and vascular specialists with many years of experience in medical treatment combined with advanced techniques. Hemostasis by bronchoscopy, surgery, bronchial artery embolization (with modern DSA system).
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.