This is an automatically translated article.
Our skin ages due to various causes such as sun, harsh weather and bad habits. But there are many things we can do to help keep our skin soft and fresh and slow down the rate at which it ages.
1. Age and skin
The degree of aging of the skin will depend on many factors: lifestyle, diet, genetics and other personal habits. For example, smoking can generate free radicals, and these free radicals damage cells, leading to premature wrinkles.
The main factors that contribute to wrinkled, mottled skin include the natural aging process, sun exposure, pollution, and loss of the subcutaneous support layer (fatty tissue between skin and muscle). Other factors that contribute to skin aging include stress, gravity, daily facial movements, obesity, and even sleeping positions.
As we age, the following changes occur naturally:
Skin becomes harder. Skin develops benign tumor-like lesions. The skin becomes saggy. The loss of elastic tissue (elastin) in the skin with age causes the skin to hang loosely. Skin becomes more transparent. This is due to the thinning of the epidermis (surface layer of the skin). Skin becomes more fragile. The skin becomes more prone to bruising because of thinner blood vessel walls. Subcutaneous changes also become evident as we age, including:
Loss of subcutaneous fat in the cheeks, temples, chin, nose and eye area can lead to loose skin, sunken eyes. Bone loss, mainly around the mouth and chin, can become apparent after age 60 and causes peeling skin around the mouth. Loss of cartilage in the nose causes sagging of the nose and makes the bony structures in the nose visible.

Theo thời gian, làn da của bạn sẽ dần lão hóa và có nhiều nếp nhăn
2. The sun and your skin
Exposure to sunlight is the biggest culprit for aging skin.
Over time, the sun's ultraviolet (UV) rays damage certain fibers in the skin, called elastin. The breakdown of elastin fibers causes the skin to sag, reducing its tension and losing its ability to contract after a skin tightening. The skin also bruises easily, breaks easily, and takes longer to heal. So while sun damage may not show up when you're young, it does show up as you age.
Nothing can completely reverse sun damage, although sometimes the skin can repair itself. Lasers can also help reverse some damage. So it's never too late to start protecting yourself from the sun and skin cancer. You can delay skin aging-related changes by avoiding the sun, covering up, wearing a hat, and making it a habit to use sunscreen.
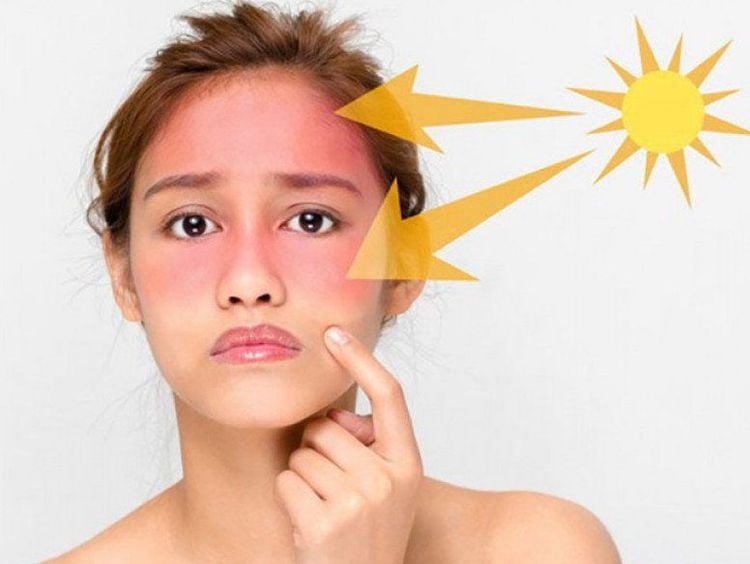

Ánh nắng mặt trời làm tăng mức độ lão hóa của làn da
3. Effects of aging on skin
As you age, you are at increased risk of skin damage because your skin becomes thinner, more susceptible to damage, and the skin loses its protective fatty layer. You may also experience decreased sensations such as touch, pressure, vibration, heat, and cold.
Rubbing on the skin can cause tearing of the skin. Fragile blood vessels, bruising, purpura, and hematomas can form after minor trauma.
Pressure ulcers can be caused by skin changes, fat loss, decreased activity, poor nutrition, and disease. The sores are most visible on the outer surface of the forearm, but they can occur anywhere on the body.
Wound healing can be up to 4 times slower than when you were younger, which contributes to pressure sores and infections. Diabetes, blood vessel changes, reduced immunity and other factors also affect the body's healing process.
Skin disorders are very common in older people and more than 90% of all elderly people have some type of skin disorder. Skin disorders can be caused by a variety of conditions, including:
Vascular disease, such as hardening of the arteries, diabetes, heart disease, liver disease, nutritional deficiencies, obesity, response to medications, stress
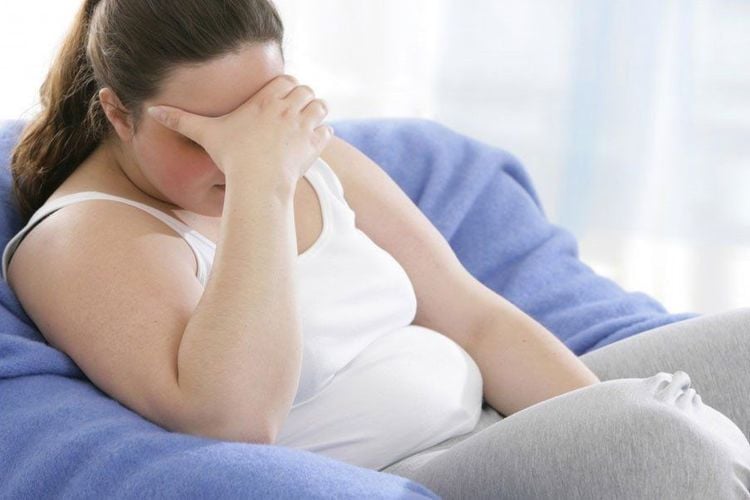

Béo phì có thể làm tăng nguy cơ mắc rối loạn da
Other causes of skin changes:
Allergies to plants and other substances Climate Clothing Exposure to industrial and household chemicals Indoor heating Sunlight can cause:
Loss of elasticity (elastosis) Keratoacanthoma Age spots Skin thickening Sun exposure is also directly linked to skin cancer, including basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma . Reference source: webmd.com; medlineplus.gov