This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Dr. Ngo Dac Thanh Huy - Cardiologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.Atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter are both conditions with abnormal heart rhythms. It occurs when there is a problem with the electrical signals and pathways in the heart, causing the heart to beat irregularly. However, the distinction between atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter is clearly important, given the implications for treatment and long-term prognosis of the patient.
1. What is atrial fibrillation and flutter?
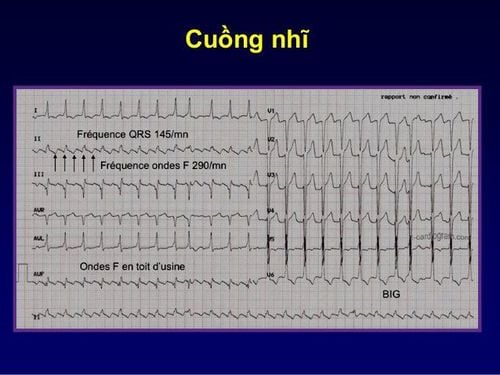
Atrial flutter is a type of atrial tachycardia that leads to arrhythmias. In it, the atria have atrial flutter, sending out a signal that causes the heart to beat too fast at the rate of the tachycardia. The electrocardiogram shows that the ventricular contractions in atrial flutter are usually regular. This has been demonstrated under electrophysiological investigation, the mechanism of atrial flutter is the large size re-entry loops.
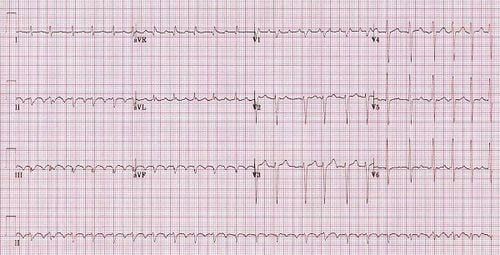
Atrial fibrillation is another type of atrial tachycardia, although in some cases it has been shown to be closely related to atrial flutter. However, the arrhythmia that occurs in atrial fibrillation is often much more chaotic and leads to erratic bradycardia, causing the patient to feel nervous and uncomfortable in the left chest. This difference from atrial flutter is due to the fact that in atrial fibrillation, the electrical investigation shows that the two atrial chambers receive disorganized electrical signals and transmit these signals indiscriminately down the ventricles instead of by the loops. back in like in a madness. Re-entry loops in atrial fibrillation, if present, are less common and of small size, so interventional control will not be highly effective.
In clinical practice, the physician will distinguish these two diagnoses mainly by the electrocardiogram. The ECG pattern of contraction waves from the two atria in atrial fibrillation is an irregular rolling pattern while in atrial flutter it is chipped and the ventricular rhythm may be regular.
On the other hand, although both conditions increase the risk of thrombosis and stroke, it is clearly important to distinguish between atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter, because of its implications for treatment and prognosis. long-term quality of the patient. The heart rate, the patient's symptoms in these two conditions, and the reduction in the risk of blood clots can all be managed with medication (such as warfarin or a newer anticoagulant. Atrial flutter always requires early diagnosis of atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter in order to properly treat and reduce the risk of stroke with the striking difference that atrial flutter can be completely resolved with ablation during fibrillation. Atrial fibrillation can only be treated mainly by medical treatment.
2. Do people with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter feel any different?
In fact, there are many patients who are only diagnosed with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter when complications of cerebral infarction have occurred, so they are hospitalized. Some other patients were found to be due to a general physical examination or to a doctor for another medical condition but had an electrocardiogram.
Only a very small number of patients with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter go to the doctor because of simple arrhythmia symptoms. And the difference in symptoms between atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter is often vague and nonspecific.
The common clinical symptoms of these two types of arrhythmia are:
Palpitations, the patient feels his heart pounding Fatigue Loss of breath Blurred vision, dizziness Feeling like fainting Severe symptoms Worsening of atrial fibrillation or flutter may include the following:
Shortness of breath Chest pain or heaviness in the chest Sweating Fainting or loss of consciousness

3. Are the causes and risk factors for atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter different?
To date, the cause of atrial fibrillation or flutter is not well understood. However, many doctors and healthcare professionals agree that the risk factors for these two arrhythmias are essentially the same, including:
Hypertension Diabetes Diabetes Heart failure Obesity Any serious acute or chronic heart disease such as valvular disease, cardiomyopathy and/or ischemic state
Advanced age Recent cardiac surgery Lung disease Chronic Sleep Apnea Syndrome Hyperthyroidism Excessive alcohol consumption or continuous use of hard alcohol
4. Is there a distinction in the treatment of atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter?
In general, because the two types of arrhythmias present in the same way and the risk of complications is the same, the treatment is mostly similar. Although drug selection and dosage may vary depending on the patient's condition and comorbidities, the classes of drugs that have been shown to be effective for the treatment of atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter as recommended are the following: antiarrhythmic drugs, ventricular rate control drugs, and anticoagulants to prevent blood clots.
In addition, for atrial flutter alone, through electrophysiological examination, a large re-entry loop may be considered, the patient may be considered for intervention including electrocardiographic surgery on the heart, ablation (cutting the aneurysm). radiofrequency re-entry, laser ablation, cryosurgery) on the pathological atrial tissue. Since then, the atrial tissue after the intervention will limit the generation of electrical impulses or abnormal conduction pathways, the heart rate is commanded by a rhythmic drive with a regular physiological frequency.
At the same time, although atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter are difficult to prevent because there are many underlying causes that cannot be changed such as old age, people can still actively prevent disease by avoiding diseases manage risk with simple daily activities:
Regular physical activity Consume a heart-healthy diet, low in salt, saturated fat, trans fat and cholesterol Avoid excessive alcohol and caffeine Don't smoke Maintain a healthy weight Good treatment of risk factors, underlying diseases such as high blood pressure, sleep apnea syndrome, hyperthyroidism, diabetes and any heart disease, especially especially angina attacks, valvular heart disease or heart failure.

5. What is the prognosis for a patient with atrial fibrillation or flutter?
Prognosis and median life expectancy for patients with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter are dependent on different underlying conditions. Individuals with multiple comorbidities and poor response to medications have a worse prognosis and a higher risk of arrhythmia complications.
In most cases, patients with atrial flutter alone may have a partially better prognosis than patients with atrial fibrillation. This is thanks to today's radiofrequency ablation techniques that achieve high conversion efficiency with very low recurrence rates. As a result, the cardiovascular function of patients with atrial flutter can return to normal, just need to be checked periodically after the intervention without having to take long-term drugs.
However, if not well controlled, both types of arrhythmias have the potential to become serious. Although some have suggested that atrial flutter is less dangerous than atrial fibrillation because there is less risk of embolism due to clot formation in the lower chambers of the heart, once an ischemic event occurs, the brain is Most often, the sequelae are permanent.
In summary, atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter are both quite common heart rhythm disorders, both causing the heart to beat faster than normal and the patient feeling palpitations and palpitations. The biggest and most significant difference between atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter is that most cases of atrial flutter can be cured with radiofrequency ablation while atrial fibrillation is mainly treated with antipsychotic drugs. rhythm. Understanding this will help better control the patient, limiting complications due to arrhythmias in the long run.
Patients with atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter need to see a cardiologist immediately because the disease has a very dangerous risk of leading to a stroke.
Proactive disease prevention as well as improving cardiovascular health is an effective measure to prevent disease progression. When visiting Vinmec International General Hospital, customers will be clinically examined by a doctor and perform some diagnostic tests:
Diagnosis by electrocardiogram is a routine test. Can be detected by mobile devices that monitor heart rate over long periods of time such as Holter electrocardiogram. Event recorder: Monitor ECG several weeks, months,... Echocardiography: Detect structural heart disease causing atrial fibrillation. Blood tests: Thyroid disease or other causes of atrial fibrillation,... Exercise testing, chest X-ray: Help your doctor interpret signs and symptoms.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.