The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Le Van Quang - Ear, Nose Throat Doctor - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital. BSCKI. Le Van Quang is an expert in the field of ENT with 15 years of experience.
Both pharyngeal cancer and purulent tonsillitis share some similar symptoms, such as difficulty swallowing, sore throat, or swelling in the neck. These overlaps can cause confusion between the two conditions. Let’s explore the specific symptoms of each condition and how to distinguish between them.
1. What is Purulent Tonsillitis?
Tonsillitis occurs in two forms: acute and hypertrophic tonsillitis. If left untreated, it can progress into chronic tonsillitis. One form of chronic tonsillitis is acute purulent tonsillitis.
Causes of Acute Purulent Tonsillitis:
- The tonsils, located at the crossroads of the respiratory and digestive tracts, are prone to accumulating bacteria and viruses, leading to infection.
- The interconnectedness of the ear, nose, and throat means that infections in the ear or nose can easily spread to the throat, causing purulent tonsillitis.
- Delayed or improper treatment of acute purulent tonsillitis can exacerbate the condition, resulting in chronic purulent tonsillitis.
- Environmental factors like changing weather and pollution can weaken the immune system, making the tonsils more vulnerable to damage and infection.
- Poor lifestyle habits such as frequent alcohol consumption, smoking, drinking cold beverages, consuming spicy food, and inadequate oral hygiene can also contribute to the onset of purulent tonsillitis.
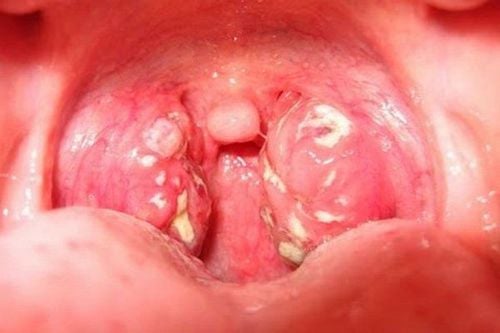
2. Differentiating Acute Purulent Tonsillitis and pharyngeal Cancer
2.1. Acute Purulent Tonsillitis
This condition is a localized complication of untreated or improperly managed acute tonsillitis. Some hallmark symptoms include:
- Pus formation between and around the tonsils.
- A sensation of obstruction in the throat with sharp pain.
- Pain radiating to the ear, painful swallowing, or inability to swallow.
- Excessive salivation and pain during wide mouth opening.
- Fever.
- Swelling of the jaw.
2.2. Pharyngeal Cancer
Compared to purulent tonsillitis, pharyngeal cancer symptoms are far more insidious. Most symptoms are secondary, arising from nearby organs such as the ear, nose, nervous system, or lymph nodes. Often, symptoms only become apparent in later stages, leading patients to overlook them.
At any stage, the impact of Pharyngeal cancer is significantly greater and far more dangerous, especially in advanced stages when it metastasizes to organs like the brain, bones, or lungs.
Common symptoms of pharyngeal cancer include:
- Headaches: Initially dull and intermittent but progressing to severe pain radiating to both sides.
- Tinnitus: Begins as mild ringing in one ear and later affects both ears, significantly impairing hearing.
- Nasal congestion: Continuous nasal blockage in advanced stages, sometimes accompanied by nosebleeds or bloody mucus discharge.
- Jaw lymph node swelling: Initially small, firm, and movable lymph nodes that later become larger, harder, and fixed to the neck area, with pain upon palpation.
- Cranial nerve palsy: Occurs when cancer spreads to the skull base, disrupting the coordination of related organs.
Pharyngeal cancer also presents with subtle symptoms such as rapid weight loss. However, the most significant distinguishing factor is the persistence of symptoms. If these symptoms persist for more than two weeks, it is advisable to consult a physician for a definitive diagnosis.
In its early stages, pharyngeal cancer symptoms are subtle and challenging to detect. Symptoms typically manifest more clearly in later stages, significantly deteriorating the patient’s quality of life. Early detection through cancer screening at least twice annually is crucial.
3. Treatment for Acute Purulent Tonsillitis and pharyngeal Cancer
Treatment approaches depend on the specific condition and severity. For acute purulent tonsillitis options include medication or surgical removal of the tonsils.
For pharyngeal cancer, treatments often involve radiation therapy or chemotherapy. Radiation is the primary treatment method. Depending on the stage (I, II, III, IV), doctors evaluate the patient’s condition and determine the appropriate treatment. In early-stage pharyngeal cancer, surgery may be an option. However, most cases present at stage III or IV, where surgery is typically not viable, and radiation therapy becomes the preferred treatment. When symptoms raise suspicion, it is essential to seek evaluation at specialized hospitals for necessary tests and examinations.
Both acute purulent tonsillitis and pharyngeal cancer significantly impact health and quality of life. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, regular exercise, and a balanced diet are key to safeguarding your health against these and other illnesses.
The Otolaryngology Department at Vinmec International General Hospital specializes in diagnosing and treating common ENT conditions, such as tonsillitis, sore throat, tinnitus, non-allergic rhinitis, throat cancer, head and neck tumors, and congenital abnormalities in the ENT region, using advanced surgical techniques.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directlyHERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.