This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Prof. TS.BS Do Doan Loi - Senior Advisor of Cardiology Center, Vinmec Times City International Hospital; Cardiology support specialist - Vinmec Ha Long International General Hospital.There are two types of lipoproteins in the human body that carry cholesterol to and from cells. One is low-density lipoprotein, or LDL, and the other is high-density lipoprotein, which is HDL. Usually a blood test will be done to quantify these components.
1. LDL - Bad Cholesterol
If the body has elevated LDL , it means there is too much LDL in the blood. This excess LDL, along with several other substances, forms plaque. These plaques build up on the artery walls, this is what we call atherosclerosis.
Coronary artery disease occurs when plaque builds up in the walls of the arteries of the heart, causing the arteries to become increasingly hard and narrow. At this point, blood circulation will be limited or blocked. Because the heart receives oxygen from the blood, this condition causes the heart to not receive enough oxygen. This problem can cause angina pectoris, or when blood flow is completely blocked, a heart attack.
1.1. How to know what LDL level is?
Blood tests that can measure cholesterol, including LDL . When and how often to get tested is recommended by your doctor based on your age, risk factors, and family history.
People under 19 years old:
First test between 9-11 years old. Retest every 5 years. Some children can be tested from 2 years old if there is a family history of high cholesterol, heart attack or stroke People over 20 years old:
Young people should be tested every 5 years. Men aged 45-65 and women 55-65 years old should have their blood lipids tested every 1-2 years.
1.2. Factors that affect the amount of LDL in the blood
Diet: Saturated fat and cholesterol in food increases blood cholesterol levels. Weight: Being overweight tends to increase LDL levels, decrease HDL levels, and raise total cholesterol. Physical activity: Lack of physical activity increases weight and leads to increased cholesterol. Smoking: Smoking lowers HDL levels. Since HDL helps push LDL out of the arteries, a lack of HDL will contribute to high levels of LDL.

Hút thuốc lá làm thiếu hụt HDL sẽ góp phần làm tăng lượng LDL.
Age and gender: As women and men age, cholesterol levels increase. Before menopause, women have lower LDL levels than men of the same age. But after menopause, LDL in women tends to increase. Genes: The genome partly determines the amount of cholesterol the body makes. High cholesterol is often passed on from generation to generation. For example, hereditary hypercholesterolemia is an inherited form of hyperlipidemia. Medications: Certain medications, including steroids, some blood pressure medications, and medications for HIV/AIDS can raise LDL levels. Other health problems: Chronic kidney disease, diabetes, and HIV/AIDS cause high LDL levels. Race: Certain races are increasingly at increased risk for cholesterol. For example, people of African descent tend to have higher levels of LDL and HDL than Caucasians.
1.3. So how much LDL is good?
The lower the LDL, the better, because high LDL increases the risk of coronary heart disease and related problems. The risk-corresponding LDL levels are outlined in the table at the end of the article.1.4. So how to reduce LDL?
Treatment with lifestyle changes
Medical treatment
In cases where lifestyle changes are not enough to reduce the amount of LDL required, medical treatment can be applied. There are many cholesterol-lowering drugs available today, including statins. Each drug works in different ways, and of course, has different side effects. Consult with your doctor to see which medication is right for you. Even while on medication, patients need to continue to make healthier lifestyle changes.
2. HDL-good cholesterol
Experts believe that, HDL cholesterol (high-density lipoprotein) or good cholesterol, acts like a street sweeper, clearing LDL out of arteries and sending it to the liver, where it will be broken down. and expelled from the body. But HDL doesn't remove LDL completely, only one-third to one-quarter of cholesterol in the blood is carried away by HDL.
A healthy level of HDL can protect the body against heart attacks and strokes. Many studies show that low HDL levels increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
2.1. What makes HDL so good?
HDL stands for high density lipoprotein. Each HDL cholesterol particle is a microscopic blob consisting of a rim of lipoproteins surrounding a cholesterol center. HDL cholesterol granules are denser compared to other types of cholesterol particles, so it is called high density.
Cholesterol is not all bad. In fact, cholesterol is an essential fat. It provides stability in every cell of our body.
To move in the blood, cholesterol must be transported by helper molecules called lipoproteins. Each lipoprotein has its own cholesterol profile and each behaves differently with the cholesterol it carries.
Experts believe that HDL cholesterol can work in many helpful ways that tend to reduce the risk of heart disease:
HDL cholesterol picks up and removes LDL - the bad cholesterol. HDL reduces, reuses, and recycles LDL cholesterol by transporting it to the liver, where it can be reprocessed. HDL cholesterol acts as a maintenance team for the inner walls (endothelial) of blood vessels. Damage to the inner walls is the first step in the process of atherosclerosis, which causes heart attacks and strokes. HDL scrubs the wall clean and keeps it healthy.
2.2. What to do if HDL is low?
In the case of low HDL, the patient will take several steps to increase HDL levels and reduce the risk of heart disease as follows:
Exercise: Physical activity helps increase HDL levels. Do moderate exercises for at least 30 minutes most days of the week.

Tập các bài tập trung bình ít nhất 30 phút hầu hết các ngày trong tuần giúp tăng lượng HDL
Quit smoking, because smoking lowers HDL, when you stop smoking, the amount of HDL can increase. Maintain a healthy weight: Besides improving HDL levels, preventing obesity reduces the risk of cardiovascular diseases and many other health problems. Choose good fats: Monounsaturated and Polyunsaturated fats. These can be found in plants, nuts, and fish such as salmon or tuna. And like anything when it comes to eating, divide it up into small portions. Just a small amount of fat contains a lot of calories. Below is a cholesterol table, outlining HDL and LDL levels and the risks and benefits of each.
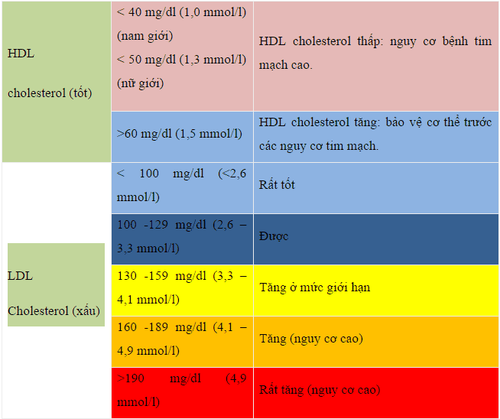
Bảng cholesterol.
The clinic brings together experienced specialists and doctors. Experience, great reputation in the field of medical treatment, surgery, interventional cardiac catheterization and application of advanced techniques in the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
In particular, the clinic has modern equipment, on par with the most prestigious hospitals in the world such as:
2D and 3D ultrasound machines supporting transthoracic and esophageal ultrasound. Systemic stress electrocardiogram (running mat, bicycle) and stress echocardiography. Cathlab room for interventional cardiology. The Hybrid Cardiovascular Surgery Room is equipped with a DSA scanner, an anesthetic machine with integrated hemodynamic monitoring software.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Articles by source: Mayoclinic, medlineplus, webmd, heart