This is an automatically translated article.
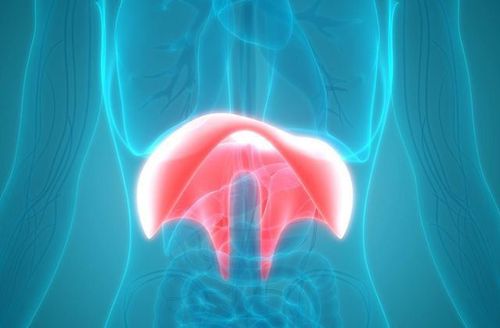
The article was consulted professionally with Master, Doctor Nguyen Thai Binh - Gastroenterologist - General Surgery Department - Vinmec Ha Long International General Hospital.The diaphragm is a large, flat, dome-shaped muscle that separates the rib cage from the abdomen. The diaphragm also plays an important role in the respiratory system. Small diaphragmatic hernias are usually not cause for concern. Many people don't even know they have a diaphragmatic hernia when they have no symptoms.
1. What is a diaphragmatic spasm?
The diaphragm is a flat, wide, dome-shaped muscle that forms a tendon wall - the muscle that separates the rib cage and the abdomen. The diaphragm plays an important role in the human respiratory system.
When the diaphragm contracts, the diaphragm will move down, the ribcage expands, the pressure in the chest decreases, air is inhaled. It will then shift back up during exhalation, causing the lungs to run out of air.
Sometimes people can feel pain or discomfort in the diaphragm, although in some cases the pain can come from another body area nearby, it is called a diaphragmatic spasm.
2. What causes diaphragm spasm?
2.1 Injury Strong impacts or procedures can damage the diaphragm. The pain in this case can be intermittent or continuous.
Certain types of trauma can cause a diaphragmatic tear. This is a serious condition called diaphragmatic rupture, and a CT scan or thoracoscopy can diagnose it.
Symptoms include: Abdominal pain, shortness of breath, chest or shoulder pain, cough, heart palpitations, nausea, vomiting.
2.2 Musculoskeletal problems When you have injuries, twisting movements or strenuous coughing will strain the intercostal muscles, causing pain similar to diaphragm pain. Diaphragmatic pain is similar to pain from a broken bone.
Broken ribs or broken bones tend to heal on their own within 6 weeks, but the following treatments can alleviate symptoms during this time:
Rest

Avoid vigorous activity Apply cold Apply common pain reliever Inject local anesthetic around the nerves near the ribs Practice regular breathing 2.3 High intensity activity When you try to breathe every time you do heavy activity, it will make the diaphragm spasms, resulting in severe pain or tenderness.
This interferes with breathing. Many people find themselves unable to inhale fully and comfortably. Symptoms will worsen if activity continues.
If diaphragmatic pain occurs during exercise, it is best to take a break until the spasm dissipates. A proper warm-up routine can prevent this type of pain.
2.4 Diaphragm hernia A diaphragmatic hernia occurs when the upper part of the stomach is pushed back up into the chest through an opening at the base of the diaphragm. The opening (called the esophageal opening) allows the esophagus to pass through the diaphragm to connect with the stomach.
Smaller diaphragmatic hernias are usually not cause for concern. Many people don't even know they have a diaphragmatic hernia when they have no symptoms. However, larger diaphragmatic hernias can cause symptoms such as:
Gastroesophageal reflux; Black or bloody stools; Chest or stomach pain; Heartburn, reflux of food into the mouth; Nausea, vomiting; Hiccup. 2.5 Pleurisy Pleurisy is an inflammation of the pleura, the tissue covering the inside of the chest cavity that surrounds the lungs.
Inflamed pleura causes severe chest pain when breathing, along with shortness of breath. In many cases pleurisy is also the cause of cough and fever. Sometimes the pain can radiate to the shoulder and to the back.
Treatment includes medication to control pain and treat underlying medical conditions. Related conditions that may require treatment include infections, autoimmune disorders, and sickle cell disease.
2.6 Bronchitis Bronchitis is inflammation of the lining of the bronchial tubes – the system that transports air in and out of the lungs. Bronchitis can be acute or chronic.
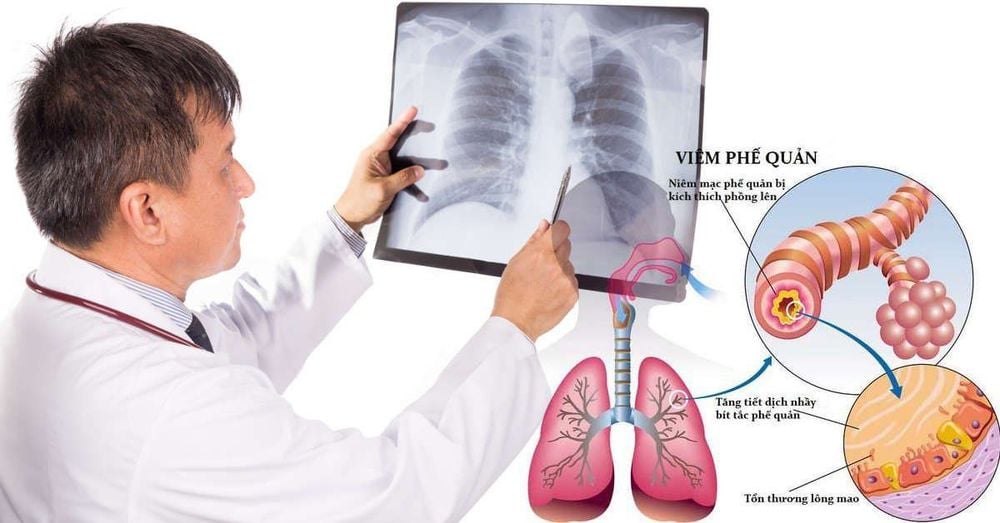
Bronchitis causing chest pain is often confused with diaphragmatic pain. Other symptoms may include: Chills, cough, fatigue, fever, shortness of breath, thick colored sputum
Acute bronchitis usually develops from a cold and will clear up on its own within a week or more. Cough medicines and pain relievers can ease symptoms until the infection clears up.
Chronic bronchitis requires medical attention. Treatment options include inhalers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and pulmonary rehabilitation to help people breathe easier.
2.7 Pneumonia Pneumonia is an infection that causes inflammation of the air sacs (alveoli) in the lungs. The cause can be bacteria, viruses or fungi. Symptoms of pneumonia include: shortness of breath, chest tightness, cough with sputum or pus, and high fever.
Some cases of pneumonia can be life-threatening, especially in young children, the elderly and people with other health problems.
Treatment is aimed at curing the infection and preventing complications. Treatment options include antibiotics, cough suppressants, and pain relievers. Some cases may require hospitalization.
Patients with suspected signs of diaphragmatic dysfunction should go to the hospital as soon as possible to avoid the situation where the weakness of the diaphragm progresses to paralysis of the diaphragm, then the treatment will be very difficult and affect the patient. greatly affect the patient's quality of life. Vinmec International General Hospital has good experts and the most modern equipment. Please contact us for the most timely advice, examination and treatment to avoid affecting your health.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.