This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Doctor Emergency Department - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
Currently, there are many laboratory methods to help diagnose pleural effusion accurately and easily, even in the case of small pleural effusion, malignant pleural effusion.
1. Clinical signs of disease-oriented significance
To diagnose pleural effusion, it is necessary to rely on clinical and subclinical symptoms.
Below are clinical symptoms that are more accurate in guiding the disease.
Patient has difficulty breathing while lying down. The degree of dyspnea depends on the amount of fluid in the pleural cavity, the amount of pleural fluid increases rapidly, causing acute dyspnea, increasing slowly the patient may adapt to cause mild dyspnea. Fever may or may not be present, if fever is usually a sign of a respiratory infection. Chest pain, low back pain, dull or severe pain, pain increases with deep breathing, coughing or changing position, when lying on the side of the effusion. Patients may have a dry cough or cough with sputum, sometimes coughing up blood. Malignant pleural effusion is often accompanied by: body weakness, emaciation, fatigue, anorexia, often effusion, many patients have difficulty breathing...
2. Diagnostic methods for pleural effusion
To make a definitive diagnosis, it is necessary to rely on the following paraclinical methods:
X-ray of the lungs. CT scan. Supersonic. Pleural effusion: Testing pleural fluid. Chest X-ray is a simple, inexpensive method used first, to detect pleural effusion.
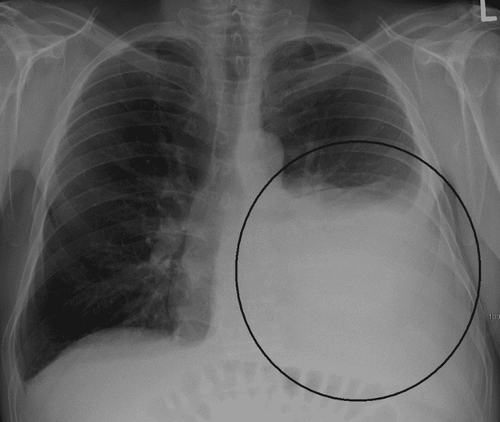
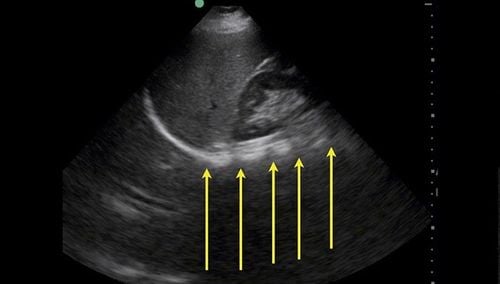
Free pleural effusion: With a small amount, the costophrenic angle is obtuse, the opacity at the base of the lung is more obvious on the lateral lung film. Small localized effusions can be difficult to detect on radiographs. In case of malignant pleural effusion: The pleural effusion on the x-ray film is usually a large number, sometimes the entire lung is blurred, called hemithoracic opacity syndrome, may be accompanied by a tumor. causing compression of trachea, mediastinum or atelectasis. CT scan The technique is very valuable to help diagnose in difficult cases of pleural effusion, especially it can tell us the exact location of the pleural effusion so that it can be probed. Locate tumor, mediastinal lymph nodes in case of malignant pleural effusion. Pleural ultrasound This technique is often used in cases of suspected pleural effusion but clinically and radiographically undetectable. Pleural ultrasound can detect pleural effusion when there is only a few tens of ml of fluid in this space. The fluid image here is a thin layer of fluid interspersed between the parietal and visceral leaves of the pleura. In case of malignant pleural effusion: pleural ultrasound to accurately detect pleural fluid, and abdominal ultrasound to help detect intra-abdominal tumors and metastatic lymph nodes. Aspiration pleural fluid
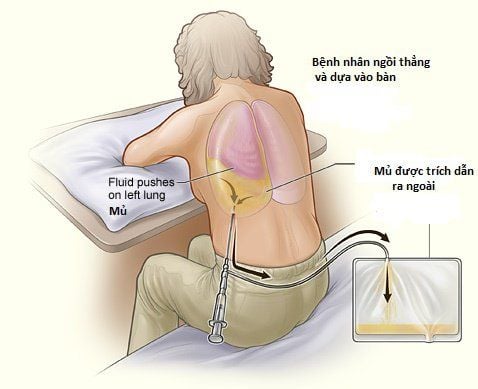
Pleural effusion is the gold standard in diagnosing pleural effusion, pleural aspiration combines diagnosis and symptom relief. Determining the cause of the disease by the nature of pleural fluid:
Color: The fluid has can be lemon yellow, clear fluid, cloudy yellow, pus, brown, blood red, milky white.... Test fluid to find the cause of the disease: Analyze the components of the pleural fluid to determine whether the fluid is permeable or not. secretions, do microbiological tests to determine the microbial cause, test for malignant cells in case of malignant pleural effusion... Combine many different diagnostic methods in diagnosing effusion pleural effusion helps the treating doctor to correctly identify the cause of the pleural effusion, especially early detection of malignant pleural effusions, thereby providing an accurate treatment plan.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.