This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Cao Thanh Tam - Cardiologist - Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Ventricular tachycardia is a type of cardiac arrhythmia. To diagnose ventricular tachycardia, doctors need to base on the patient's clinical symptoms and perform subclinical diagnostic methods such as echocardiography, electrocardiogram.
1. Diagnosis of ventricular tachycardia based on symptoms
Ventricular tachycardia is a type of arrhythmia in cardiovascular disease, when there are ≥ 3 consecutive ventricular beats with a rate of ≥ 120 beats/min. Symptoms of ventricular tachycardia may be monomorphic or polymorphic and may or may not be persistent:Monomorphic ventricular tachycardia: mechanism due to an exogenous drive or a solitary re-entry loop, complex shape The QRS set on the electrocardiogram is uniform and monomorphic. Varicose ventricular tachycardia: due to multiple peripheral foci or multiple re-entry loops, the rhythms are different, leading to the QRS complex on the electrocardiogram being irregular in shape and frequency. Unstable ventricular tachycardia: duration <30 seconds Prolonged ventricular tachycardia: duration ≥ 30 seconds or earlier discontinued due to hemodynamic loss. For cases of prolonged ventricular tachycardia, there will always be symptoms, clinical manifestations in patients are palpitations, hemodynamic instability or hemodynamic disturbances, even sudden death. Because the ventricles are primarily responsible for pumping blood around the body, ventricular arrhythmias cause symptoms compared with other arrhythmias. Ventricular tachycardia if not diagnosed and treated early can progress to ventricular fibrillation and cause cardiac arrest.
MORE: Supraventricular tachycardia

2. Diagnosis of ventricular tachycardia based on echocardiography
Echocardiography is an easily performed laboratory diagnostic method that contributes to the diagnosis of several causes of ventricular tachycardia. Echocardiography can help visualize tachycardia and cardiac structures in concomitant cardiac conditions. Diseases causing ventricular arrhythmias such as:Coronary artery disease Heart failure Congenital heart disease, genetic disorders Autonomic disorder Primary ventricular arrhythmia Cardiomyopathy: dilated, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, Right ventricular dysplasia Electrolyte disturbances, poisoning,... These are also risk factors leading to prolonged supraventricular tachycardia. Therefore, patients are often performed additional echocardiography in the diagnosis of ventricular tachycardia.
3. Diagnosis of ventricular tachycardia based on ECG
Diagnosis of ventricular tachycardia by the subclinical method that is electrocardiogram, this method is easy to perform, fast and gives accurate results. On the electrocardiogram, the QRS complex is dilated with atrioventricular dissociation, the QRS complex does not have a typical bundle branch block pattern. Prolonged ventricular tachycardia is an emergency rhythm situation because it can change to ventricular fibrillation causing sudden death.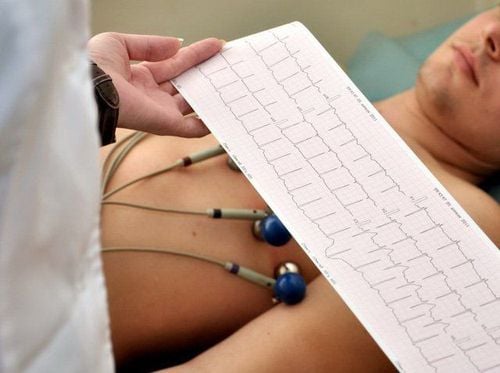
The frequency is erratic 140-200 beats/min and the rhythm is usually irregular. The QRS complex is often enlarged and distorted, QRS > 0.12 sec. There is often dissociation between the P wave and the QRS, the frequency of the P wave is usually lower than that of the QRS. Captured and mixed QRS strokes Seen in more than 33% of cases of ventricular tachycardia Fastest sure diagnosis Seen in bradycardia (<160 beats/min) QRS: Right bundle branch block >120ms Left bundle branch block >140ms Right bundle branch block with left axis suggestive of ventricular tachycardia Left bundle branch block with excessive left axis is rare in paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia with aberrant conduction. According to Wellens: QRS >140ms is the main indicator of ventricular tachycardia QRS 120-140ms only 50% chance of ventricular tachycardia Besides, it is necessary to differentiate with supraventricular tachycardia with bundle branch block or conduction through accessory pathways. However, because some patients with ventricular tachycardia are well tolerated, it is easy to confuse and lead to erroneous conclusions that dilated QRS tachycardia is a tachycardia of supraventricular origin. Misdiagnosis can aggravate the condition when using some supraventricular tachycardia drugs in patients with ventricular tachycardia and lead to hemodynamic disturbances, even death.
In summary, ventricular tachycardia is a cardiac arrhythmia and is definitively diagnosed based on clinical manifestations such as a rhythm of more than 3 consecutive ventricular beats and accompanying hemodynamic disturbances. In addition, the doctor will prescribe subclinical diagnostic methods and especially electrocardiogram. Sustained ventricular tachycardia is a medical emergency that, if not, can lead to death. Therefore, patients with cardiovascular disease need periodic health check-ups for timely diagnosis and treatment.

The whole process of examination, diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases is carried out by a team of doctors with many years of experience and expertise in the profession. Therefore, customers can be completely assured when choosing Vinmec as the address to examine and screen for early cardiovascular diseases.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.