This is an automatically translated article.
There are many methods of diagnosing myocardial infarction used today, in which the electrocardiogram is the commonly used method due to its important role in distinguishing the fulminant, acute or stable stage of myocardial infarction. heart attack.
1. Importance of electrocardiogram in myocardial infarction
Electrocardiogram plays a key role in distinguishing the fulminant, acute or stable phase of infarction. In addition, it also helps to localize the area of myocardial infarction.
Image of myocardial infarction on electrocardiogram: ischemic change in electrocardiogram manifested in T wave change, resulting in damaged myocardium, the change of ST segment begins to rise , and finally the Q wave appears showing myocardial necrosis. It is important to distinguish myocardial infarction with Q wave and without Q wave because of different prognostic values. Inferior myocardial infarction, 70-80% of patients with right ventricular myocardial infarction, need further investigation of V3R and V4R.
Criteria in diagnosing acute myocardial infarction on electrocardiogram:
Q wave: at least 30ms wide, up to 0.20mV deep - located in 2 regions of the total lead domains: V1 to V6; D1 and aVL; D2, D3 and aVF; ST-segment elevation or depression in myocardial infarction greater than 0.10 mV - in at least 2 regions of the total number of leads; There is left bundle branch block in the clinical picture; In case of right ventricular myocardial infarction, additional leads V3R to V6R are needed for the purpose of finding changes.
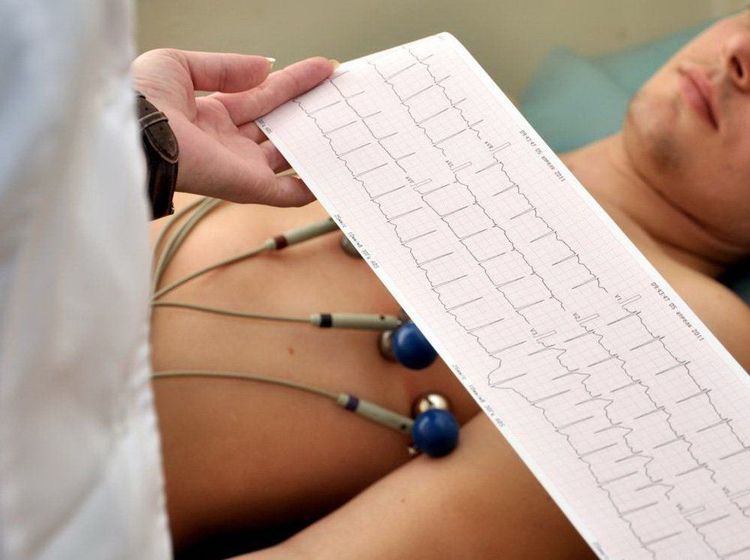
Điện tâm đồ có vai trò chính là phân biệt giai đoạn tối cấp, cấp hay đã ổn định của nhồi máu
2. How is myocardial infarction shown on the electrocardiogram?
2.1 Stages of myocardial infarction ECG Stage 1 - Acute stage: In the first 1, 2 days, arch wave: Possible pathological Q, QT prolongation.
Stage 2 - Subacute stage: From a few days to a few weeks is the most common stage: ST elevation lower, T negative deep, pointed, symmetrical. At the same time, there is a clear pathological Q and a long QT interval.
In these two stages, arrhythmias or atrioventricular block are often present, especially in the type of ventricular septal infarction.
Stage 3 - Chronic phase: From a few months to a few years: ST is electrocoagulated, T can be positive or still negative, and pathological Q is often permanent.
2.2 Types of ECG of myocardial infarction The above signs are not present in all leads equally, but are only evident in the lead where the myocardial infarction electrocardiogram is placed directly above the muscle region. heart attack, so these signs are called direct images.
On the contrary, leads with electrodes placed in the contraradial region of the infarcted area will obtain signs that are contrary to the above signs, which is called indirect imaging.
Infarction can occur in many different narrow areas of the left ventricle. Depending on the affected area, three main and most common types of infarction are classified, subepicardial and the following signs of stage 2 - subacute:
Anterior septal infarction: That is, in the wall anterior left ventricle and anterior portion of the interventricular septum. Live image: QS wave, ST elevation, negative T - in V2, V3, V4. Sometimes T is low or negative in V5, V6, aVL, and D1 (T1>T3) because the ischemic area spreads to the left wall of the left ventricle. Anterior-lateral infarction: Found in the lateral and anterior wall of the left ventricle. Live imaging: deep and wide Q, ST elevation, deep negative T - in V5, V6, D1, aVL. Indirect imaging: ST depression, very high positive T - in D3 sometimes aVF. Posterior - inferior infarction: Common in the posterior and inferior walls of the left ventricle. Live image: deep, wide Q, ST elevation, deep negative T - in D3, aVF, sometimes even in D2. Indirect imaging: High positive T, possibly pointed, symmetrical, ST depression possible - in V1, V2, V3, V4. Subendocardial infarction, left ventricular: Mainly anterior - lateral wall: ST depression, sometimes T deformed in V5, V6, D1, aVL. Sometimes inferior posterior wall: ST depression at D3, D2, aVF. Myocardial infarction with bundle branch block: In many cases, coronary insufficiency causing infarction also causes a branch of His bundle to be undernourished, causing bundle branch block, the signs of bundle branch block will be combined with other symptoms. primary sign of infarction.
3. Other diagnostic methods
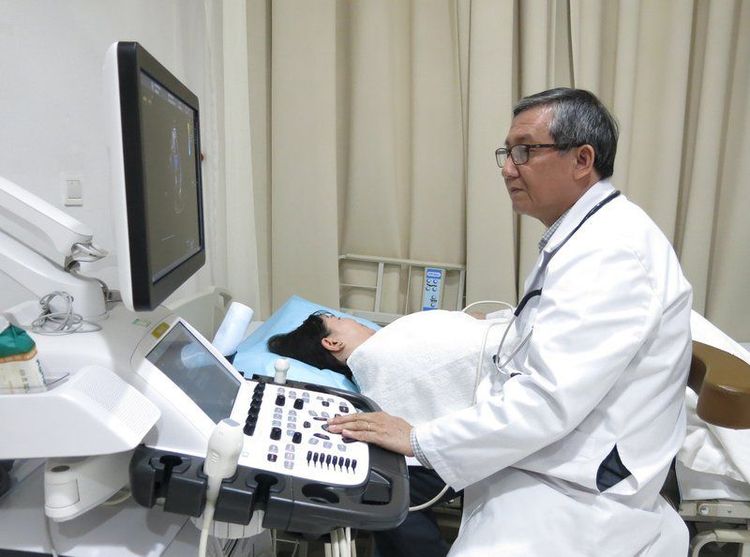

Siêu âm tim mang giá trị chẩn đoán cao trong trường hợp nhồi máu cơ tim không Q hay nhồi máu có bloc nhánh
In addition to diagnosing myocardial infarction on electrocardiogram, electrocardiogram of myocardial infarction, doctors also diagnose the disease by other methods. Specifically:
Serum probiotic test When the heart muscle is deprived of oxygen, the muscle's cell membrane is cracked and its contents are released into the blood. Blood levels of specific substances of the heart muscle: cardiac enzymes and troponins, either type I or T, can be used to diagnose myocardial damage.
It is important to know that sometimes even though a patient is having a heart attack, heart enzyme levels may remain normal for the first few hours. Therefore, while the patient is in the hospital for observation, the ECG and cardiac enzyme levels must be repeated every 6-8 hours to confirm the disease.
Coronary angiography This method will determine which vessels are blocked. This is the surest way to identify, format, and decide on the treatment modality for myocardial infarction. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), a definitive diagnosis of myocardial infarction must have two of the following three criteria:
- Angina for more than 20 minutes
- Change on a series of 2 or 3 ECG measurements a few hours apart
- Heart enzymes increase and then decrease.
Echocardiography Echocardiography has a high diagnostic value in cases of non-Q myocardial infarction or infarction with bundle branch block. The resulting image is often seen as regional motor dysfunction associated with myocardial infarction.
Radiographic exploration of myocardial perfusion This method is not usually applicable in acute cases of myocardial infarction.
In addition to medical examination, screening and diagnosis of myocardial infarction, Vinmec International Hospital also has many effective treatment methods, including fibrinolytic therapy for patients with acute myocardial infarction. level segment.
This is a treatment with a success rate of over 95% of cases. The technique of fibrinolysis for patients with acute myocardial infarction is performed by a team of leading experienced cardiologists at Vinmec, with the support of imaging equipment. modern, ensuring absolute safety for all patients.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.