This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master. BSCK II Phan Thi Minh Huong - Gastroenterologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Da Nang International General Hospital.Pyloric stenosis is a syndrome with the general manifestation of complete obstruction or stagnation in the circulation of food and gastric juice to the duodenum. When signs of pyloric stenosis appear, patients should immediately go to medical facilities or hospitals for early diagnosis and treatment of doctors. Because early diagnosis and treatment will reduce the risk of aggravation of the disease and help you recover quickly.
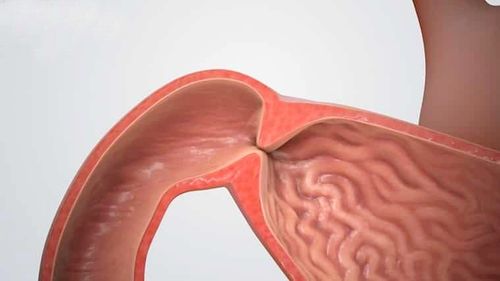
1. Diagnosis of pyloric stenosis of the stomach
1.1. Definite diagnosis Physical signs: abdominal pain in the epigastrium, vomiting of old food, sluggishness, abdominal fullness and indigestion, having to hook the throat to vomit, vomiting is pleasant. Physical symptoms: stomach shake sign (+), Bouveret's sign (+) X-ray symptoms: X-ray of the stomach has seven images showing snowfall, pelvic stomach, three levels, after 6 hours The stomach is still stagnant baryte. 1.2. Differential diagnosis - Cardiac spasm:Expression of choking, choking liquid. X-ray: The upper esophagus is dilated, the lower is narrow like a radish, sock-shaped, without gastric air sacs. Endoscopy showed stagnation of food in the esophagus. The esophagus is dilated, the heart is narrow, the spasm is continuous, but the mucosa is soft. During endoscopy, you must wait for the myocardium to open before inserting the scope into the stomach. - Duodenal stenosis:
Above the ampulla of Vater: symptoms are similar to pyloric stenosis. Under the shadow of Vater: Vomiting profusely, vomiting yellow bile; The whole body collapsed rapidly, X-ray identified the narrow place, on which the duodenum was dilated, endoscopy clearly identified the location of the narrowing and the damage causing the narrowing. Biopsy can determine the type of lesion. - Atrophic gastritis: Diagnosis is based on endoscopy: Antral antral area is atrophied, shrinking; X-ray of the stomach has sevente: has the image of a small, folded antrum.
- Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis : Appears in infants, after a few weeks normally appears profuse vomiting leading to systemic disorders; X-ray: The pylorus is elongated like a thread, above is the dilated stomach.
- High intestinal obstruction: mainly pain, vomiting a lot; X-ray: Air level, water level above the navel.
In addition, it is necessary to distinguish it from some other diseases such as cholecystitis, pancreatic disease, neurological disease...
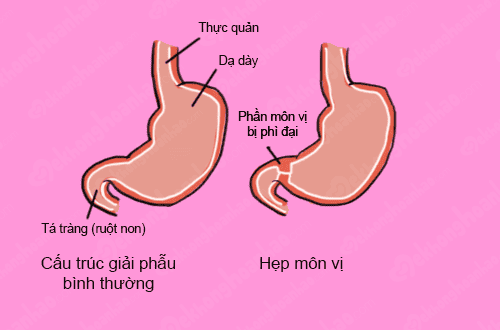
Hẹp môn vị
2. Treatment of gastric pyloric stenosis
Depending on the cause of functional or organic pyloric stenosis, there are different treatment methods. Functional pyloric stenosis requires only medical treatment. Pyloric stenosis due to organic causes often requires surgery. There are two common surgical methods: open surgery and laparoscopic surgery.2.1 Laparoscopy for pyloric dilation Sometimes the pylorus can be dilated without surgery by placing a balloon. In this procedure, the doctor places a tube with a balloon at the tip into the stomach through the mouth. The balloon is then inflated and stretched to open the pylorus. Both children and adults will usually recover well after surgery.
2.2 Open surgery Open surgery is to dissect the pylorus muscle, removing the edematous and thickened pylorus. Hysterotomy or pyloroplasty usually has good results.
3. Steps to perform pyloromyotomy surgery

Sau khi đã xác định được hẹp môn vị thực thể, các bác sĩ sẽ chỉ định phẫu thuật
If the patient comes to the hospital early for gastric bypass surgery, the general condition allows, prepare well. Or the patient is late, weak, and the general condition does not allow it, so gastric bypass surgery is recommended.
Step 1: Before surgery, it is necessary to replenish water, electrolytes and provide energy to the patient. Intravenous nutrition (infusion of protein, blood, fat, booster...) and gastric lavage (using Faucher sonde), especially before surgery.
Step 2: Doctors will perform surgical methods
Gastric bypass, re-establish digestive circulation in the style of Billroth I or Billroth II. If the pyloric stenosis is caused by an ulcer, 2/3 of the stomach should be removed, and for cancer, it is recommended to cut the whole or 3/4, 4/5 of the stomach according to the principle of cancer surgery.
Gastric bypass surgery (resolving pyloric stenosis, but the most common cause of stenosis is the stomach) is indicated for the following cases:
Late stage pyloric stenosis, the elderly, and the exhausted state. Deep duodenal ulcer with no possibility of gastrectomy. Nerveectomy with gastrojejunostomy, antral resection or pyloroplasty: applicable only for pyloric stenosis due to duodenal ulcer, can be X-wire stem resection, classical selective resection, or superselective (currently rarely used).
Doctor Huong has over 30 years of experience in the field of Gastroenterology, in which with nearly 20 years holding the position of Deputy Department, Head of Department of Hue Central Hospital. Currently, he is a Doctor of Gastroenterology - Gastrointestinal Endoscopy - General Internal Medicine Department of Vinmec Da Nang International General Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.