This is an automatically translated article.
Early craniosynostosis in children (also known as craniocervical stenosis) is a relatively rare anomaly, an average of 6 children out of every 10,000 children. This is a relatively dangerous malformation that, if not treated promptly, can affect the child's life in the future.
1. What is early craniosynostosis in children?
Early craniosynostosis in children (also known as craniocervical stenosis), scientifically known as Craniosynostosis, is a birth defect in children resulting from a condition where the cranial sutures fuse together prematurely (premature closure of the skull). ) from the fetus. According to some studies, craniofacial joints in children with malformations will interlock between the ages of 2-4 and become fused after 20 years of age. The characteristic presentation of children with craniocervical stenosis is an abnormal face and head shape.
For some special cases, the growth of the skull bones is restricted, leading to increased pressure on the skull, thereby causing headaches, vision problems or slowness develope.
The main mechanism of early craniosynostosis in children is due to disease of the skull bones (also known as primary craniosynostosis) or due to brain disease leading to failure to develop, leading to the condition of the joints. premature closure of the skull (secondary craniosynostosis).
For primary craniosynostosis, the child often has skull deformity. Depending on the craniosynostosis, the skull will grow in a way that compensates for that shortfall, resulting in the baby's head being distorted in a certain direction.
Some common cases of primary cranial ankylosing spondylitis are medial longitudinal fusion (boat-shaped head deformity), accounting for 60% of all cases due to primary cranial ankylosing spondylitis; In addition, there is ankylosing spondylitis (20%), causing the child's head to be distorted and flattened to the sides; metopic ankylosing spondylitis (triangular head defect) accounts for 10%... It should be noted that these malformations can be accompanied by a number of other malformations in the maxillofacial region, extremities, and upper respiratory tract causing complex and difficult to treat pathological syndromes.
Secondary craniosynostosis often causes microcephaly in children.

Trắc nghiệm: các chỉ số cần chú ý về sự phát triển thể chất của trẻ
Chiều cao, cân nặng của bé ở từng giai đoạn nên là bao nhiêu là bình thường, bao nhiêu là bất thường? Cùng ThS.BS Ma Văn Thấm điểm lại xem bạn đã nắm được các chỉ số phát triển thể chất của bé chưa nhé!The following content is prepared under supervision of Thạc sĩ, Bác sĩ y khoa, Ma Văn Thấm , Nhi , Phòng khám Đa khoa Quốc tế Vinmec Dương Đông(Phú Quốc)
2. Some symptoms of children with early craniosynostosis
Characteristic manifestations of early craniosynostosis is the deformation of the skull in many different forms: boat-shaped head, triangular head, flattened head, small head... In addition, it can be observed. Observe the uneven development of 2 eyebrows in children, often one side is flattened and the other side is lower, making the eyes bulge.
In some cases, the child's nasal bones are found to be deviated to one side or the frontal bones are overdeveloped, causing the appearance of 2 protruding forehead mounds.
3. Is early craniosynostosis in children dangerous?
First of all, early craniosynostosis in children if not treated will cause serious aesthetic loss, the longer the child gets older, the more it will cause feelings of inferiority, psychological disturbance, and difficulty in integrating into society. festival. In addition, cranial ankylosing spondylitis, if not treated promptly, will affect brain development and increase intracranial pressure.
4. Methods of early diagnosis of craniosynostosis in children
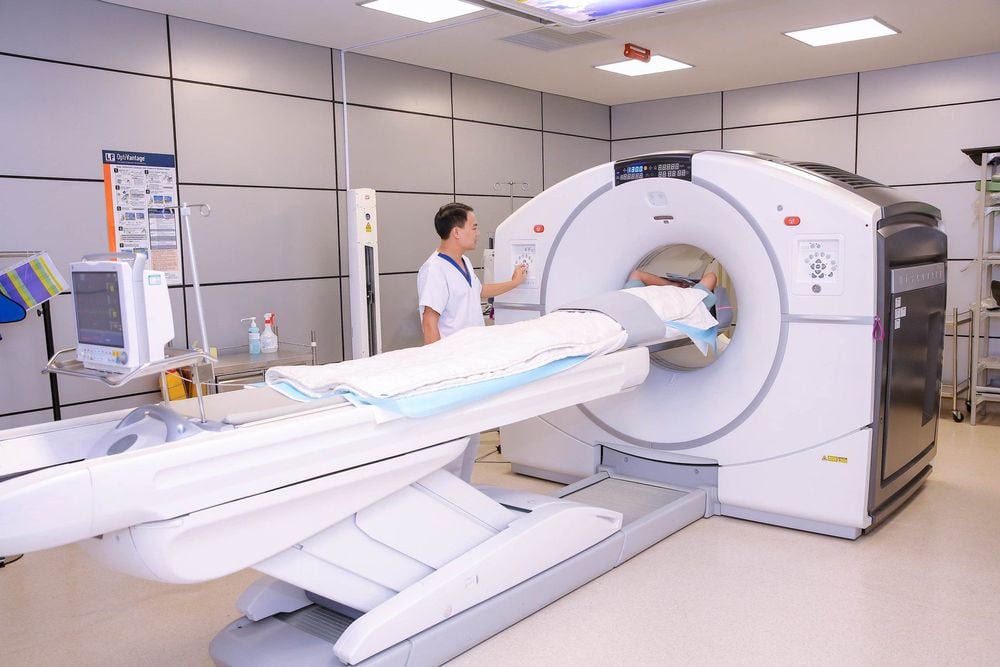
Early craniosynostosis in children is usually diagnosed through multi-slice computed tomography and 3D skull reconstruction (CT Multi-slice 3D) which helps to locate the fused skull joints and the skull deformation. In some special cases, a CT or MRI scan of the brain will be required to provide additional information for surgical treatment.
5. Treatment methods for early craniosynostosis in children
Currently, the main treatment method is to perform surgery to remove the sticky joints, reshape the skull, completely eliminate the compression to create space for the brain to develop.
Some studies show that the best age for children to have surgery is from 3-8 months old, because at this time the baby's skull bones are still thin, malleable and not deformed much. Early surgery is beneficial, both increasing bone growth and helping brain development.
In the case of surgery after 12 months, the surgery will be more difficult and most have to reconstruct the entire skull and this is relatively complicated. It can be considered as a major surgery and often requires blood transfusions when performed.
Surgical treatment of craniosynostosis in children is currently applying 2 methods: classical surgery and endoscopic surgery.
Classic surgery is done in 3-7 hours depending on the specific case, may require blood transfusion and hospital stay for 3-7 days.
Laparoscopic surgery is less invasive, but only applied in certain cases. The advantage of laparoscopic surgery is that the patient experiences less blood loss and swelling. The average surgery takes 1 hour and most patients can show up the next day. This method gives the best results when the baby is between the ages of 3-6 months.
Pediatrics department at Vinmec International General Hospital is the address for receiving and examining diseases that infants and young children are susceptible to: viral fever, bacterial fever, otitis media, pneumonia in children, .... With modern equipment, sterile space, minimizing the impact as well as the risk of disease spread. Along with that is the dedication from the doctors with professional experience with pediatric patients, making the examination no longer a concern of the parents.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.