This is an automatically translated article.
Season change is a favorable time for bacteria and viruses to develop and cause respiratory diseases, including acute pharyngitis. The disease does not affect much to health, however, if treated late, dangerous complications such as glomerulonephritis and rheumatic heart disease may occur, especially in young children.
1. What is pharyngitis?
The pharynx includes the pharynx and larynx. The pharynx contains many blood vessels, pharyngeal muscles, tonsils, and vocal cords.
Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the mucosa and submucosa in the pharynx. Acute pharyngitis is an acute inflammation of the nasal mucosa - pharynx - mouth, often accompanied by tonsillitis, sinusitis, rhinitis, in rare cases combined with tonsillitis at the bottom of the mouth. Because of this combination frequently, acute pharyngitis is also called acute pharyngitis - tonsillitis. The disease can also occur at the same time with other respiratory infections such as flu and measles.
The disease is encountered in both adults and children, in which mainly children due to weaker resistance, often appear in autumn - winter when the weather changes. The disease usually begins with a viral infection. The combination of viral toxins, the body's resistance, and commensal bacteria available in the oropharynx (streptococcal, pneumococcal) causes superinfection.
Pharyngitis is spread through secretions in the nose, throat and mouth such as saliva, droplets through communication, runny nose.
2. Diagnosis of acute pharyngitis
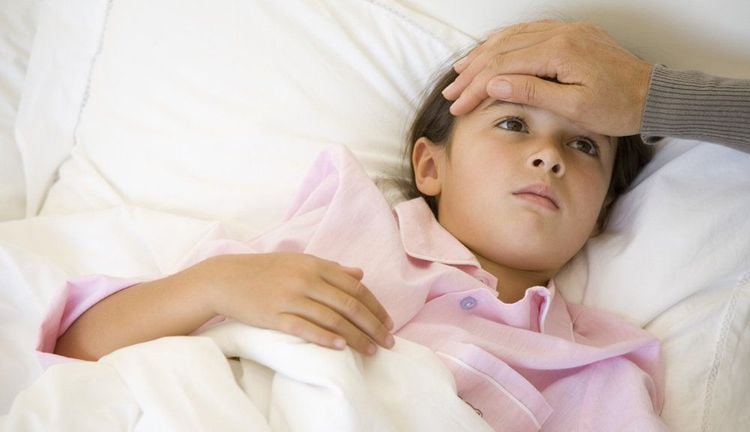

Bệnh nhân viêm họng cấp có biểu hiện sốt, nhiệt độ từ 38 - 39 độ C
2.1 Find signs of illness through examination Patients with acute pharyngitis have a fever, temperature from 38 - 39 degrees Celsius, sometimes as high as 40 degrees Celsius, common in young children, chills, headache, fatigue, and poor appetite. , body aches and pains, difficult to work. Mandibular angle lymph nodes are prominent, mobile, and painful to palpation.
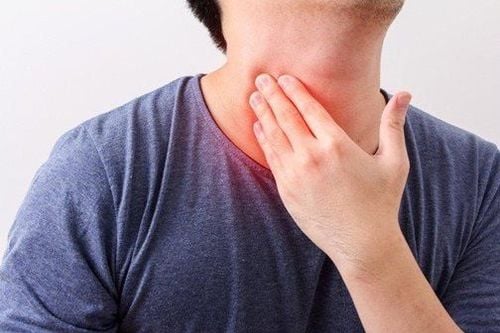
Throat pain, especially when swallowing, even just swallowing liquids. When the patient swallows, coughs or talks, sometimes there is a sharp pain in the ear. The patient has a cough that is intermittent, at first a dry cough, then a cough with sputum, often with stuffy nose, runny nose, at first in mucus, then cloudy. Voice is gradually lost or has a slight hoarseness that makes communication difficult.
Observing the nasopharynx, the throat mucosa is red, with secretions. Lymphatic organization in the back wall of the pharynx is red, with prominent capillaries. The two palatine tonsils are enlarged, sometimes with white dots of pus or a white coating on the surface of the tonsils. Congested nasal mucosa, mucus secretion. The angled lymph nodes are mildly swollen and painful when pressed.
2.2 Diagnostic tests for acute pharyngitis Disease symptoms of acute pharyngitis are characteristic and easy to observe, so often without testing, the disease can be accurately diagnosed. However, in severe cases, testing plays an important role in determining the exact cause and severity of the disease.
Blood count test: In the early stage, the white blood cells in the blood do not increase, but in the stage of superinfection, the neutrophils are elevated. Bacterial throat swab: This test is used to identify the type of bacteria that is causing the disease. From there, the treatment is based on the antibiogram to be more effective. The disease is diagnosed based on the following clinical manifestations:
Sudden onset of fever, body aches and pains, sore throat, may have a dry cough or cough with sputum, Red throat mucosa, swollen tonsils with pus dots white Examination of lymph nodes at the angle of the jaw, moving, painful pressure The disease also needs to be differentially diagnosed with foreign bodies in the airways, inflammation of the oral mucosa and inflammatory diseases in the throat caused by other causes such as pharyngitis, pharyngitis, pharyngitis, pharyngitis, throat syphilis.
3. Treatment of acute pharyngitis
In the absence of testing for viral or bacterial pathogens, all cases of acute pharyngitis in patients over 3 years of age should be treated as acute strep throat. Including the following treatments:
Beta-lactam antibiotics or some other antibiotic groups: Amoxicillin, cephalexin, erythromycin, clarythromycin
Peniciline V orally 50-100 UI/kg for children, 3 million UI for adults, divided into 3 times a day, treatment lasts for 10 days. Slow penicillin type Benzathin-Peniciline G dose 600,000 UI for children < 30 kg and 1.2 million UI for children > 30 kg and 2.4 million UI for adults. 1st generation cephalosporin, or Peniciline A (Amoxicilline) for 10 days. In case of allergy to Peniciline, it is possible to replace the Macrolide group such as Rulide, Zithromax, Dynabac, or Josacine for 5-7 days. Treatment of symptoms with anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic drugs: Paracetamol, aspirin. Limit use to patients with gastritis - duodenal ulcer.
Local treatment with throat ointment, gargle, throat aerosol
Test to determine the cause for treatment
Increase the body's resistance by adding trace elements, vitamins, especially vitamin C and B1 and vitamins.

Điều trị các triệu chứng bằng thuốc giảm viêm, giảm đau, hạ sốt
4. Prognosis and complications
If the treatment is effective, the disease will be cured after 3-5 days. In case of streptococcal superinfection, the disease will last longer. If antibiotic treatment is not effective, it will leave complications such as:
Local complications: Inflammation, abscess around the tonsils; posterior wall abscess, lateral pharyngeal wall; complications of acute rhinosinusitis ; pharyngitis gangrene. Proximal complications: laryngitis - bronchiolitis, pneumonia, acute otitis media, acute sinusitis. Distant complications: glomerulonephritis, arthritis, pericarditis, streptococcal toxic shock, sepsis.
5. How to prevent acute pharyngitis?
Cold season is approaching, parents need to protect themselves and protect children from respiratory diseases including acute pharyngitis by the following ways:
Avoid direct contact with people who are suffering from inflammatory diseases upper respiratory tract Quit smoking and alcohol, avoid eating salty, raw, fermented foods Improve living standards to increase body resistance, create a clean, pollution-free environment Good labor protection, anti-dust , anti-heat, good oral hygiene Active treatment of diseases of the nose and sinuses, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, VA patients with chronic diseases For young children, it is necessary to keep the oropharynx warm when the weather turns cold, do not let children Soaking in the rain, playing in the sun, washing hands often with soap, eating and drinking, creating a clean and cool living environment for children. Flu vaccination for children to create active immunity to protect against the attack of viruses and bacteria that cause disease. Otolaryngology - Vinmec International General Hospital specializes in examining and treating common ENT diseases such as: tonsillitis, sore throat, tinnitus, non-allergic rhinitis, throat cancer; tumors of the head, face and neck, congenital malformations of the ear, nose and throat area by common surgical methods.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.