This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Doctor Department of Emergency Resuscitation - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
To diagnose acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema can be based on symptoms: the patient has difficulty breathing, must sit, blue skin, sweating, cold extremities, worried face...
1. What is acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema?
Acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema is excessive extravasation of pulmonary capillaries into the interstitial and alveolar tissues.
There are many causes leading to acute cardiac pulmonary edema including:
Left atrial obstruction: Mitral stenosis, left atrial mucinous tumor, left atrial thrombosis, congenital 3 atrioventricular chambers; Left heart failure: Left ventricular systolic dysfunction, left ventricular diastolic dysfunction; Left ventricular volume overload leads to left ventricular systolic dysfunction and non-adherence to treatment and diet. Excessive transmission. Acute aortic regurgitation causes left ventricular volume overload; Obstruction of left ventricular outflow tract: Due to aortic stenosis, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, hypertension increases peripheral resistance against the contractile force of the left ventricle. It is also a form of left ventricular outflow tract obstruction.
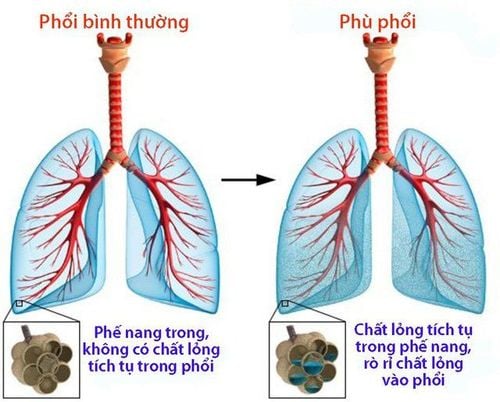
2. Diagnosis of acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema
Clinical symptoms: The patient has difficulty breathing, must sit (if the patient can sit), pulls the accessory respiratory muscles, blue skin, sweating, cold extremities, anxious face (feeling of suffocation, lack of air), the jugular vein floats in the supine position with the head elevated 45 degrees, moist rales, possibly with rales throughout the 2 lung fields (especially the rising pattern from the bottom to the top); Accompanying symptoms may be: Leg edema, ascites, apex deviated from and below the V intercostal space, left midclavicular line, wide apex, cardiac murmur, heart rate is usually rapid, with irregular body; History: Cardiovascular disease history can be recorded; X-ray: Interstitial edema, alveolar edema, typically diffuse edema from the hilum to the periphery (butterfly shape); Electrocardiogram: There may be signs of ischemic heart disease, myocardial infarction, enlarged heart chambers, arrhythmia... Echocardiogram: Usually performed when the patient is fine, except for some Urgent cases such as suspected mechanical complications of acute myocardial infarction include ligament rupture, mitral valve prolapse, interventricular septum, left ventricular free wall perforation. Diagnosing the cause of heart disease plays an important role in the radical treatment, helping to limit or prevent the recurrence of acute pulmonary edema.
3. Treatment of acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema
3.1 Emergency treatment of acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema Oxygen: Ensure blood oxygenation.
Mechanical ventilation:
Non-invasive: If relatively mild, patient cooperates well; Invasive mechanical ventilation: In case of refractory hypoxia, obvious respiratory muscle fatigue, the patient cannot cooperate well, and CO2 pressure increases in the blood. Drug use:
Vasodilator: Nitroglycerin intravenous infusion; Loop diuretics; Drugs that increase myocardial contractility: Used in cases of clinically reduced cardiac output; Vasoconstrictor: Used when accompanied by hypotension, concomitant cardiogenic shock; Morphin: Helps reduce pulmonary congestion, patients reduce anxiety; Consider placing a retrograde aortic balloon pump in case of concomitant cardiogenic shock, acute myocardial infarction, refractory pulmonary edema... Monitoring: Electrocardiogram, oxygen saturation through continuous pulse on monitor.
Blood pressure: Invasive arterial blood pressure monitoring when hemodynamic instability, using vasopressors.
Treatment of co-morbidities: Hypertension, diabetes, pneumonia...
3.2 Treating the cause of heart disease Depending on the specific cause of heart disease, the doctor can have a treatment method. suitable.
The above are methods of diagnosis and treatment of acute cardiac pulmonary edema. Patients with acute pulmonary edema can go to Vinmec International General Hospital for examination and treatment. Vinmec has a team of specialized respiratory medicine doctors with rich expertise and experience in the examination and treatment of diseases related to the respiratory system, capable of synchronously and effectively deploying diagnostic and therapeutic methods. the most advanced, with the support of a system of modern technical equipment according to international standards.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.