This is an automatically translated article.
Pressure ulcers on the skin and subcutaneous tissue often appear in the elderly, people with sedentary disease or inactivity. The disease needs to be prevented and treated early to avoid anemia and tissue necrosis.
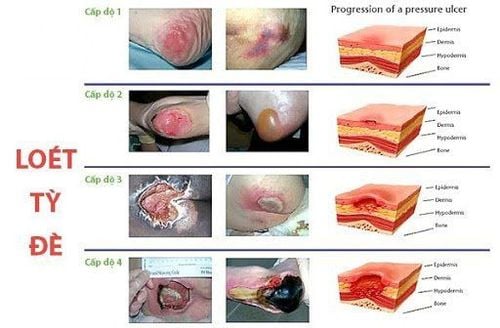
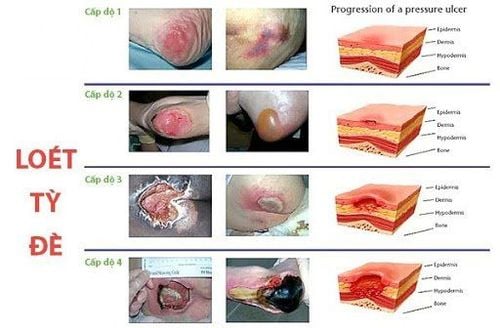
1. Developmental stages of pressure ulcers
Pressure ulcers in the elderly are divided into 4 stages, increasing according to the degree of damage and difficulty of treatment. 4 stages of development of pressure ulcers include:
1.1 Stage 1: Injury to the epidermis and dermis Features: The skin is intact, not lost, with a light red color. Unable to whiten in a localized area usually on a bony convex.
People with dark skin may not be able to see whitening, skin color may be different from surrounding areas.
When palpated, the pressure sores at this stage are hard and warmer or colder than the surrounding skin. The patient feels pain.
Các cấp độ ứng với từng giai đoạn của loét do tì đè
1.2 Stage 2: Injury to the epidermis, dermis and subcutaneous layer Characteristics: Partial loss of the dermis, manifesting as a shallow open ulcer with a pinkish red bottom, no scabs, shallow ulcer bottom, dry, no necrotic tissue (dead cells are milky white).
This area of skin may also present as a blister, containing intact serum or open, broken.
1.3 Stage 3: Injury to the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous fat layer Features: Loss of tissue in the entire skin layer, subcutaneous fat can be seen but no tendons, bones or muscles are visible. A scab may be present, but the lost tissue may not be filled.
May include tunnels as red holes.
1.4 Stage 4: Injury penetrates deep into muscle tendon Features: Loss of all skin and subcutaneous tissue, exposing tendon or muscle. There may be a yellow scab due to opaque necrosis or eschar at the base of the wound.
Often appear tunnels or red holes.
2.Other criteria for evaluating pressure ulcers

Tổn thương loét sâu có vùng khu trú da đổi màu đỏ nâu
In addition, evaluation for pressure ulcers may not fall under the above stages such as:
2.1 Suspected deep tissue injury Localized area of skin red-brown or dark purple discoloration, or blisters filled with blood. It is caused by damage to the internal soft tissue, which is subjected to compression or sliding forces.
Suspected areas of deep tissue injury may be hard, soft, mushy, painful, and unusually hot or cold compared to adjacent tissue areas.
2.2 Unclassified Here, pressure sores have total tissue loss, in which the base of the ulcer is covered with gray, red-brown, green, yellow, or brown scabs that are layers of dead or necrotic cells. death. There may be red-brown, black, or brown eschar at the base of the wound or no visible ulcer depth.
3. What to do when you have a pressure ulcer?
For stage 1 and 2 pressure ulcers, conservative wound care is usually non-surgical.
If pressure ulcer lesions are stage 3 and 4, surgical intervention (eg, pedicled skin graft) may be considered. Some lesions must be treated conservatively if the patient has other comorbidities.
Our folk have many ways to use natural medicinal herbs to treat, reduce pressure sores, and avoid infection. In particular, today's medicine recognizes, the use of honey in quickly clearing infection in wounds caused by pressure ulcers is effective. In addition, some evidence suggests that honey also helps promote self-healing, effective antibacterial against certain types of bacteria and fungi.
In addition to honey, folk people also use papaya and sugar to care for pressure ulcers.
4. How to treat pressure ulcers?

Thuốc Sulfadiazine sử dụng điều trị loét tì đè
There are many methods of treating pressure ulcers, which can be applied individually or in combination, depending on the condition of the disease.
4.1 Support your health by: Pain relief, care for urinary incontinence, proper cleaning of the ulcer and surrounding tissues. In addition, ensure adequate nutrition (calories, vitamins, proteins, trace elements).
4.2 Reduce pressure by: Lie with your head 30 degrees, help change lying position every 2 hours, can exercise if possible. The use of beds and special booster seats can reduce pressure and maintain it below 32 mmHg.
4.3 Care of the ulcer By:
Removal of necrotic tissue: by ablation, whirlpool pump, Povidone-Iodine, or Protein-degrading enzyme. Wound cleaning fluid: can be physiological saline, acetic acid (0.5%), diluted Povidone-Iodine or Sodium Hypochlorite (2.5%). Bandaging the ulcer: with stage 2 or more severe ulcers, gel can be used to prevent contamination and remove necrotic tissue. Antibiotics: Using antibiotic creams such as Sulfadiazine inhibits DNA and changes in cell membranes. There are also a number of other ulcer care methods such as: Hyperbaric oxygen, Negative pressure therapy, Electrotherapy, growth factors,...
Vinmec International General Hospital is not only famous for its high expertise. but also fully equipped with the most modern and advanced medical equipment in Vietnam. In particular, the examination and treatment procedures at Vinmec are carried out by a team of highly qualified and well-trained medical doctors, which will bring high treatment efficiency.
To register for medical examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.