This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Master, Doctor Trinh Thi Thanh Huyen - Obstetrician and Gynecologist - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.Malignant ovarian cysts are a serious disease and account for about 10% of ovarian cysts. The disease is common in women during menopause and progresses rapidly. If not detected and treated promptly, malignant ovarian cysts can be life-threatening.
1. What is a malignant ovarian cyst?
Malignant ovarian cyst, also known as ovarian cancer. This is one of the dangerous gynecological diseases, accounting for about 10% of all ovarian cysts. Ovarian cysts often stick to surrounding organs, increasing the degree of spread of cancer cells. The outer surface of the cyst usually has a rough appearance, the peritoneum has raised nodules. In the nucleus, the cyst is usually partially or completely solid and has buds. Malignant ovarian cysts can appear on the left or right side of the ovary and even on both sides.Malignant ovarian cyst occurs in 4 stages:
Stage 1: Malignant ovarian cyst is limited to one or both ovaries, has not spread to other organs. If detected and treated early, patients have a chance to live over 5 years up to 90%. Stage 2: Cancer cells begin to spread to other nearby organs in the pelvis such as fallopian tubes, uterus,... Stage 3: The malignant ovarian cyst has spread beyond the pelvis and invade the abdominal cavity, even invade organs such as liver, spleen,... Stage 4: This is the final stage, malignant ovarian cyst spreads to parts outside the abdomen such as heart, lungs , brain, ... even metastasize to bones and other organs in the body. Malignant ovarian cyst is one of the gynecological cancers with the highest mortality rate in Vietnam. Each year there are about 1200 cases of malignant ovarian cysts and less than 45% of patients live for an additional 5 years.
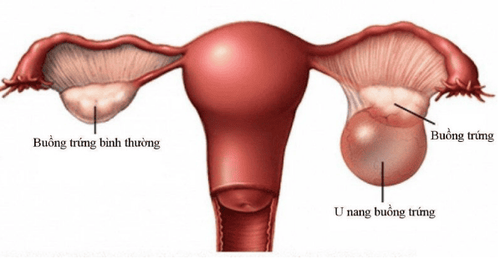
Hình ảnh phân biệt u nang buồng trứng và buồng trứng bình thường
2. Symptoms of malignant ovarian cysts
The majority of ovarian cysts are benign and only about 2% progress to malignant ovarian cysts. The disease often has no obvious symptoms, making it difficult to detect in the early stages. Signs and symptoms of malignant ovarian cysts include:Pelvic pain: dull pain that occurs frequently even without menstruation. The pain may spread to the back and lower thighs. Abnormal urination: due to large tumor pressing on the bladder, causing urination disorders, but not due to drinking a lot of water Determination disorder: due to large ovarian tumor pressing on the rectum, causing defecation disorders, constipation . Abdomen: Ovarian cysts are usually <10cm in size, but malignant cysts progress very quickly and can grow so large that many people mistakenly think they are gaining weight or pregnant. Menstrual disorders: irregular menstruation, often menorrhagia. When malignant ovarian cysts form and grow, the menstrual cycle will be disrupted and intermittent changes occur. Body weakness: The body is tired, the hormones that control metabolism in the digestive tract are destroyed, making the patient feel unappetizing, eating quickly, or vomiting, so it is easy to lose weight. thin and weak. Vaginal burning pain during intercourse, possibly abnormal vaginal bleeding: Malignant ovarian cysts that grow too large can fall behind the uterus causing pain during sex. In addition, malignant cysts caused by endometriosis can also cause pain and bleeding during intercourse because they are located closer to the uterus.
3. Methods of diagnosis and treatment
3.1 Diagnosis To diagnose malignant ovarian cysts, it is necessary to have diagnostic tests by imaging such as: transducer ultrasound or MRI scan,... Through the images obtained from the test results, A malignant cyst may have the following characteristics:Size: The size of a malignant ovarian cyst is usually very large and > 10 cm. Many cases of ovarian cysts are the size of a watermelon or larger. About shape: Malignant ovarian cyst has rough outer shell, many papillae and usually has at least 4 papillae, the more papillae, the higher the risk of ovarian cancer. Features: Hard, solid, malignant ovarian cyst with a septum 2 -3mm thick. Cysts are located in a fixed, non-motile location, usually behind the uterus.

Hình ảnh u nang buồng trứng trên kết quả siêu âm
Blood test: to check CA antigen levels -125, HE4 in the blood. If CA-125, HE4 antigen levels are higher than normal, it can predict cancer. Biopsy: Biopsy of ovarian cyst cells to diagnose cancer. 3.2 Treatment Methods of treatment for malignant ovarian cysts currently applied include:
3.2.1 Surgery
Surgery is a surgical treatment method and is usually indicated first for patients with ovarian cysts. malignant ovarian cyst. To ensure that the surgery is effective, the patient needs to have some necessary tests before that.
If a malignant ovarian cyst is detected early and appears only on one ovary, the doctor will recommend an open surgery to remove the ovary and fallopian tube, in order to prevent cancer cells from spreading to other ovary. adjacent organs and help preserve the remaining ovary. In the case of ovarian cancer in both ovaries, the entire 2 ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, lymph nodes or part of the fatty tissue must be removed. If malignant ovarian cysts are detected at an early stage, less removal can be done, helping to preserve a woman's chance of fertility.
After surgery, the risk of recurrence of malignant ovarian cysts is very high. Therefore, patients need to continue to perform other treatments such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy, ... to destroy the root cause of cancer cells.
3.2.2 Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a method of removing cancer cells that may be left behind after surgery. Chemotherapy uses specific drugs to kill or inhibit the growth of malignant cells. These drugs will be injected into a vein or injected into the abdominal cavity, depending on the development of the malignant cyst.
The chemotherapy cycle will be divided into different courses and prescribed according to each treatment regimen. The patient will have a certain rest period. Some side effects may be experienced after chemotherapy such as: loss of appetite, nausea, hair loss, weakness,...
Hóa trị được sử dụng trong điều trị u nang buồng trứng ở phụ nữ
Radiation therapy is a method of applying high-energy particles or waves such as: X-rays, Gamma rays, electron beams, protons, ... to bombard and destroy cells. cancer cells. This method is often applied to patients with end-stage malignant ovarian cysts. Radiation therapy is a safe and effective treatment method. However, like many other cancer treatments, radiation therapy can also cause some unwanted side effects such as: fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, dry skin, dermatitis, skin atrophy, bowel disorders,...
In short, malignant ovarian cysts are one of the dangerous gynecological diseases, accounting for about 10% of all ovarian cysts. If not detected and treated promptly, malignant ovarian cysts can be life-threatening. Therefore, it is necessary to have regular gynecological health check-ups. In addition, to prevent malignant ovarian cysts need to be detected and treated when the cyst is still in a benign form. Early treatment of gynecological diseases that are at risk of complications into cysts such as pelvic inflammatory disease, endometriosis,... will help prevent the risk of malignant ovarian cysts.
Cancer inherently does not spare anyone, it is estimated that every year in the world there is a very large proportion of people dying from cancer. In fact, if the cancer can be detected at an early stage, the prognosis for treatment is very high, even if it is completely cured and not recurred. Therefore, cancer screening is essential, especially for high-risk patients.
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has been and continues to be fully equipped with modern diagnostic facilities such as: PET/CT, SPECT/CT, MRI... biology, immunohistochemistry, genetic testing, molecular biology testing, as well as a full range of targeted drugs, the most advanced immunotherapy drugs in cancer treatment. Multimodal cancer treatment from surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, targeted therapy, immunotherapy in cancer treatment, new treatments such as autoimmunotherapy body, heat therapy...
After having an accurate diagnosis of the disease and stage, the patient will be consulted to choose the most appropriate and effective treatment methods. The treatment process is always closely coordinated with many specialties: Diagnostic Imaging, Biochemistry, Immunology, Cardiology, Stem Cell and Gene Technology; Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Department of Endocrinology, Department of Rehabilitation, Department of Psychology, Department of Nutrition... to bring the highest efficiency and comfort to the patient. After undergoing the treatment phase, the patient will also be monitored and re-examined to determine whether the cancer treatment is effective or not.
Especially, now to improve service quality, Vinmec also deploys an Ovarian Cancer Screening Package that can help customers detect ovarian cancer, cystic tumors early before they even have it. symptoms, providing a high prognosis for treatment and a high chance of recovery.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.