This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Le Nguyen Hong Tram - Gastroenterologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Nha Trang International General HospitalLiver failure occurs when large parts of the liver are so damaged that it cannot repair itself and function properly again. There are two types of liver failure: acute (rapid liver failure) and chronic (gradual liver damage).
1. Symptoms of liver disease
Impaired liver function is difficult to diagnose early because the symptoms will be similar to other liver diseases, namely:
Nausea; Loss of appetite; Tired; Diarrhea. But as liver failure progresses, symptoms gradually become more severe and require immediate treatment, including:
Jaundice ; Easy bleeding; Swelling, bloating; Mental disorders (called hepatic encephalopathy); Frequently sleepy.
Trắc nghiệm: Làm thế nào để bảo vệ lá gan khỏe mạnh?
Làm test trắc nghiệm kiểm tra hiểu biết về gan có thể giúp bạn nhận thức rõ vai trò quan trọng của gan, từ đó có các biện pháp bảo vệ gan để phòng ngừa bệnh tật.2. Causes of liver failure
2.1. Acute Liver failure is when the liver stops working within a few days or weeks. Most patients had no previous liver disease or unusual symptoms. Causes include:
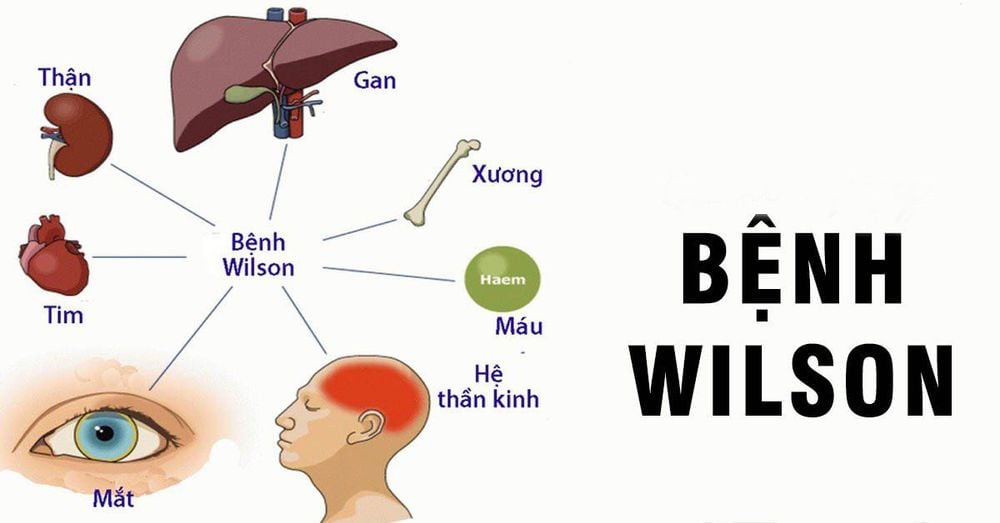
Acetaminophen overdose: Large doses can damage the liver or lead to impaired liver function; Hepatitis A, B and E viruses, Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus and herpes simplex virus: Liver damage or cirrhosis; Reactions to certain prescription drugs and herbs: Drugs that can kill cells in the liver or damage the tubes between the liver and bile; Eating toxic wild mushrooms: Amanita phalloides mushrooms - also known as death caps, contain toxins that damage liver cells and lead to liver failure within a few days; Autoimmune hepatitis : Similar to viral hepatitis, this disease also attacks the liver and can lead to acute deterioration in liver function; Wilson's disease: An inherited disease that prevents the body's function of eliminating copper, causing copper to accumulate and damage the liver;
Acute fatty liver in pregnancy: This condition is quite rare, when excess fat accumulates in the liver and damages the liver; Septic shock: Excessive infection in the body will damage the liver or cause it to stop working; Budd Chiari syndrome: A rare disease that narrows and blocks blood vessels in the liver; Industrial toxins: Many chemicals such as carbon tetrachloride, detergents and degreasers on metal surfaces, etc. can damage the liver's detoxification function.
2.2. Chronic impaired liver function is liver damage that builds up over time and causes the liver to stop working. Common causes include:
Hepatitis B : Causes the liver to become swollen and unable to function properly; Hepatitis C : Long-term disease can lead to cirrhosis; Alcohol abuse: Over time also leads to cirrhosis; Hemochromatosis: This genetic disorder causes the body to absorb and store too much iron. Iron builds up in the liver and causes cirrhosis. Other conditions that can also lead to chronic liver failure are:
Hepatitis A : Consuming food or water contaminated with the virus, or being in close contact with an infected person can make you infected. Hepatitis A usually goes away on its own after a short time; Autoimmune hepatitis : The body's immune system mistakenly attacks the liver and causes inflammation;
Cirrhosis: Drinking alcohol for a long time or having scars in the liver will make it difficult for the liver, even unable to function properly; Primary sclerosing cholangitis: Gradual damage to the bile ducts, mainly appearing in young men; Increased oxalateuria: When the kidneys are not able to remove calcium oxalate crystals through the urine, it also affects liver detoxification over time; Wilson's disease: A rare genetic disease that causes people to store too much copper in the brain and liver; Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency: This inherited condition can lead to lung or liver disease; Liver cancer: People with long-term hepatitis B or C often lead to cancer; Liver adenoma: Benign tumor appearing on a healthy liver, common in women aged 20 - 44 years; Fatty liver disease: Excess fat cells can accumulate on the liver, which is common in people who are overweight, obese or have high cholesterol. While alcohol-related fatty liver disease occurs in heavy drinkers; Alcoholic hepatitis : Hepatitis caused by heavy drinking or long-term alcohol abuse; Alagille syndrome: An inherited disorder that causes a person to have a smaller number of bile ducts in the liver than usual; Primary cholangitis: Over time, primary biliary cirrhosis destroys the small bile ducts in the liver; Galactic metabolism disorder: Patients cannot use galactose - a type of sugar found in many foods, causing a lot of accumulation in the body and damage to liver detoxification;

Lysosomal acid lipid deficiency (LAL-D): This genetic condition prevents the body from producing the enzyme lysosomal acid lipase (LAL) - which breaks down fat and cholesterol in cells. As a result, fat stays in the liver and causes impaired liver function.
3. Stages of liver disease
Stage 1: Inflammation In the early stages, the liver becomes inflamed and may cause pain or no symptoms.Stage 2: Fibrosis/scarring If left untreated, scarring of the liver can result. Scar tissue that builds up in the liver blocks blood flow, making it work harder for the liver to work properly.
Stage 3: Cirrhosis Scar tissue grows more and more, overwhelming most of the healthy liver cells. The liver cannot function properly, or even stops working.
Stage 4 (late): Liver failure The liver may become swollen, internal bleeding, loss of kidney function, fluid in the abdomen, as well as accompanying lung problems. Liver transplantation is the only treatment at this stage.
If not treated promptly, impaired liver function can lead to complications such as:
Brain edema: Liver failure often causes fluid accumulation. In addition to the abdomen, fluid can also enter the brain and increase pressure; Difficulty clotting: The liver plays a large role in helping the blood to clot. When the liver stops working, you run the risk of uncontrollable bleeding; Infections: End-stage liver disease can make you more susceptible to infections, leading to pneumonia and UTIs; Kidney failure: Liver failure can change the way the kidneys work and lead to impaired kidney function.
4. Diagnosis and treatment of liver failure
4.1. Tests Commonly used tests to diagnose liver failure as well as liver diseases include:
Blood tests: Help your doctor see how well your liver is working. Your blood clotting time may be measured, because in acute liver failure the blood will clot more slowly than usual; Imaging tests: Help the doctor see the condition of the liver and find the cause of the problem. Includes ultrasound, computed tomography of the abdomen (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); Biopsy: The doctor removes a small piece of liver tissue and looks at it in a lab. A jugular liver biopsy is a special procedure in which your doctor inserts a needle into a vein in your neck.
4.2. Treatment Acetylcysteine can reverse acute liver failure caused by acetaminophen overdose provided it is taken immediately. There are also drugs that detoxify fungi or other chemicals.
Supportive care If liver function declines due to the virus, the hospital will treat the patient's symptoms until the virus stops working. In these cases, the liver will sometimes recover on its own.
Liver transplant If liver failure is caused by long-term damage, the first step in treatment is to preserve and restore the part of the liver that is still functional. In case of progression to impaired liver function, the patient is required to have a liver transplant with a high success rate.
5. Prevent liver failure
The best way to prevent impaired liver function is to limit the risk of cirrhosis or hepatitis. Doctors recommend people:
Get vaccinated to prevent hepatitis A and B; Adhere to a reasonable diet; Maintain a healthy, moderate weight; Do not drink too much alcohol, avoid drinking alcohol while taking acetaminophen; Maintain personal hygiene, wash hands thoroughly and often; Do not share personal items, such as toothbrushes and razors; If you plan to get a tattoo or body piercing, choose a facility that is hygienic and that all equipment is sterile; Safe sex with condoms; Do not share needles with anyone. In conclusion, impaired liver function is a life-threatening condition that requires urgent medical attention. Usually, liver diseases occur gradually over many years, reaching a final stage called impaired liver function. But there is also a rarer condition - called acute liver failure, which happens quickly in just 48 hours and is difficult to detect in the first place.

Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has Hepatobiliary Screening packages, which help detect Hepatitis Virus at an early stage even when there are no symptoms. In addition, the comprehensive hepatobiliary screening package helps customers:
Evaluate the liver's ability to work through liver enzyme tests; Evaluation of bile function; vascular nutrition; Early screening for liver cancer; Perform tests such as Total blood cell analysis, blood clotting ability, screening for hepatitis B, C Assessment of hepatobiliary status through ultrasound images and diseases that are at risk of affecting liver disease/treating liver disease. more severe liver disease In-depth analysis of parameters to evaluate hepatobiliary function through laboratory and subclinical tests; the risk of affecting the liver and early screening for hepatobiliary cancer
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: Webmd.com