This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Master, Doctor Huynh Vu Khanh Linh - Doctor of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital
Hysterosalpingography is a process of using X-rays to check the patency of the fallopian tubes and the normal shape of the uterus. This process is usually carried out when a woman has just had a period but before ovulation to rule out pregnancy.
1. How is the hysterosalpingogram and fallopian tube taken?
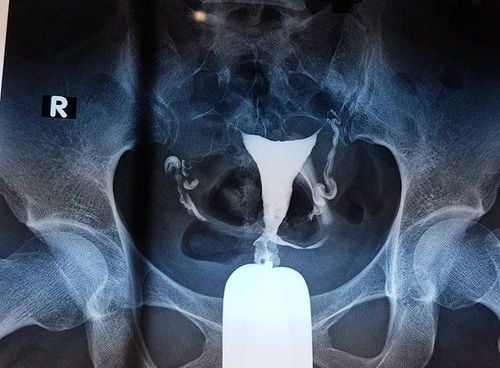
To conduct a hysterosalpingogram (HSG), the patient will be assigned to lie on the imaging chamber. An obstetrician-gynecologist or radiologist will perform a speculum placement, cervical cleaning, and insertion of the cannula into the lumen of the uterus through the cervix. The doctor will then inject a solution containing iodine into the cannula. Contrast will follow the cannula into the uterus, through the fallopian tubes, and into the abdomen if the fallopian tubes are open. HSG also indirectly allows doctors to recognize abnormalities of the uterine cavity. However, it does not help evaluate the ovaries nor diagnose endometriosis. The doctor may also change the position of the patient to take more pictures of the uterus and fallopian tubes. After the scan, the patient can return to normal activities or sometimes the doctor also advises the patient to abstain from sex for a few days.
Sau khi chụp HSG bệnh nhân sinh hoạt bình thường
2. Is the HSG scan uncomfortable?
HSG can cause mild or moderate contractions of the uterus for 5 to 10 minutes. However, there are some that can last up to several hours. These symptoms can be greatly reduced by taking antispasmodics during menstruation. The patient should be accompanied by a family member to assist in leaving after taking the photo.
3. Does HSG increase pregnancy rates?
There is a lot of controversy around whether HSG increases pregnancy rates or not. Some studies have shown a slight increase in pregnancy 3 months after imaging. However, most physicians today only use HSG as a mere diagnostic tool.
HSG có thể làm tăng tỷ lệ mang thai
4. What are the risks and complications of HSG?
HSG is usually quite safe for women. However, a few abnormalities were also noted, accounting for less than 1%. Specifically as follows:
Infection: The most serious is pelvic inflammatory disease. This risk usually occurs when a woman has had tubal inflammation before. In these cases, the infection can damage the 2 fallopian tubes and require removal of them. Patients should contact their doctor immediately if they experience increasing pain and fever 1 to 2 days after the HSG scan. Syncope, lightheadedness: This is a rare condition after the procedure. Radiation exposure: The radiation intensity in HSG is very low, and there is no evidence that an HSG scan will cause illness or affect pregnancy several months later. If pregnancy is suspected, do not take an HSG scan. Allergy to Iodine: This is a rare condition. However, women can be allergic to the iodine contrast agent used in HSG. Patients should inform their doctor about their allergies to iodine, intravenous contrast, to seafood... People with such allergies should have an HSG without iodine contrast. If you experience any redness, itching, or swelling after the procedure, you should contact your doctor right away. Bleeding: Usually occurs 1 to 2 days after the scan. Patients should notify their physician if they experience heavy bleeding after HSG.

Một số ít trường hợp gặp biến chứng sau khi chụp cản quang tử cung
In the case of 2 blocked fallopian tubes, the doctor will advise the patient to do laparoscopic tubal catheterization and genital examination, or immediately do IVF - in vitro fertilization. This is a difficult decision that you should further consult with your doctor.
Laparoscopic genital examination is a method of testing and evaluating the function of the fallopian tubes. In addition, the method of inserting a catheter into the uterus through the vagina, pumping water and gas from the uterus is also applied by many doctors at hospitals. If the fallopian tubes are open, small air bubbles can be seen passing through the ultrasound machine. However, at present, HSG remains the most common choice for preliminary assessment of tubal function.
Vinmec International General Hospital has applied HSG imaging technique in examination and imaging of the uterus and fallopian tubes, detecting many gynecological diseases. HSG imaging technique at Vinmec is carried out methodically and in accordance with standard procedures by a team of highly qualified medical professionals and modern machinery, thus giving accurate results, making a significant contribution to the identification. diagnosis and stage of the disease.
If you have a need for medical examination by modern and highly effective methods at Vinmec, please register here.