This is an automatically translated article.
Article written by Th.S, BS. Ton Nu Tra My, Department of Diagnostic Imaging, Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
Mammography is a non-invasive technique that is widely used in the diagnosis of breast disease. Contrast mammograms help to show clearer images, helping doctors make an accurate diagnosis. So in what cases is this technique indicated, what are the advantages and limitations?
A mammogram is a mammogram with contrast injection to show the mammary ducts. This technique is used mainly in female patients who have obvious discharge or bleeding from the nipple but have normal mammograms (non-contrast mammograms). It is important that the patient does not squeeze the nipple before performing this technique because small amounts of ductal fluid can help diagnose mammary disease.
Tell your doctor about your breast problems, previous surgeries, hormone use (if any) and the possibility that you are pregnant. Leave jewelry at home. You will be asked to wear a hospital gown while performing this technique. Do not use deodorants, powders or lotions under your arms or on your breasts as these can create images and cause an inaccurate diagnosis.
1. What is a mammogram (galactography or ductography)?
Mammography is a technique that uses a low-dose X-ray system combined with the injection of contrast material through the mammary ducts in the nipple area to examine the mammary ducts. In particular, it is necessary to understand that:
Mammography is a non-invasive technique that uses X-rays to survey breast images, helping doctors diagnose breast diseases. This is the oldest and most frequently used medical technique. The breast consists mainly of three main structures: fatty tissue, the lobules (which make milk), and the ducts (which carry milk from the lobes to the nipple). Mammography alone, without the use of contrast material, also known as mammography; Breast ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are the main methods of breast imaging. However, in order to clearly evaluate the milk ducts, it is necessary to use mammography techniques combined with injection of contrast material into the milk ducts in the nipple area.
Chụp ống tuyến vú là kỹ thuật không xâm lấn nhằm giúp khảo sát các ống tuyến vú
2. In what cases is this technique used?
A mammogram (galactography or ductography) is most commonly used in the case of female patients with clear discharge or bleeding from the nipple that cannot be detected by mammography alone. , do not use contrast agent).
Do not have a mammogram in the following situations:
Nipple discharge that is milky, blue, green, or gray is usually not a cause for concern. Discharge from both breasts in women who have not had children may just be a side effect of medication or may be related to a problem with the pituitary gland located in the brain that does not require a mammogram.
3. What to prepare before having a mammogram
The only requirement is not to squeeze the nipple before performing the technique, as in some cases a small amount of fluid in the ducts can determine the cause of the disease. You should inform your doctor about any medications you are taking, any history of allergies (if any), especially any history of allergy to contrast media. In addition, it is important to inform your doctor about any medical conditions you have or have had. Always inform your doctor or x-ray technician about your condition if you are pregnant. Do not use deodorant, powder or lotion under your arms and upper chest on the day of this technique. Simply because these substances can affect the quality of diagnosis. Also, before the test, you should leave all jewelry at home. You will need to change into a hospital gown when performing this technique.
Bệnh nhân dị ứng chất cản quang cần chống chỉ định thực hiện thủ thuật này
4. How does mammography detect abnormalities?
X-rays are a form of radiation like light or radio waves. X-rays pass through most objects, including our bodies. When focusing on the breast, X-rays help record the image of the breast on the film, thereby helping to diagnose breast diseases.
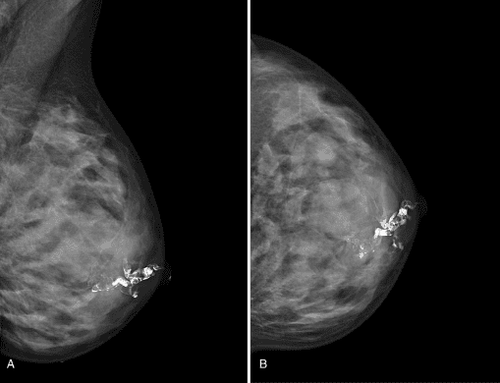
Contrast is injected into the ducts of the nipple area to show the milk ducts on the mammogram. On film, the contrast material in the milk ducts is white. If there is a defect in the lumen of the duct (corresponding to the black area), it means that there is a space-occupying lesion in the duct.
These lesions can be benign or malignant tumors. With the technique of mammography, not only finds abnormalities in the milk ducts, but also locates the abnormalities, guiding the surgeon. In some cases, there is no mass lesion, but only dilatation of the milk ducts, which may be a sign of fibrocystic disease, which can cause bleeding. but in general not to worry.
Tia X trong chụp ống tuyến vú giúp ghi lại hình ảnh vú trên phim và chẩn đoán các bệnh lý về vú.
5. How is this technique performed?
This examination is usually done outpatient.
The patient is in a sitting position, exposing both breasts. The nipple is cleaned, then gently squeeze the nipple to locate the suspected dilated duct, insert a small tube into the dilated duct, and slowly inject the contrast material into the area. Then an X-ray was taken to record the mammary ducts. In some cases, it is necessary to use a warm towel over the breast to help the ducts become more visibly dilated, allowing easier access to the ducts.
During the procedure, you need to stay still during the X-ray to avoid motion blur.
The procedure usually takes from 30 minutes to an hour.
6. What will I experience during and after the mammogram?
Dilation of milk ducts caused by contrast injection sometimes makes you uncomfortable; However, usually you won't feel any pain.
Tiêm thuốc cản quang trong chụp ống tuyến vú thường không gây đau đớn cho người bệnh
7. What are the benefits and risks of a mammogram?
7.1 Benefits
Mammography can find benign or malignant tumors, thereby helping to diagnose and treat early and timely. This technique helps to locate the tumor, guiding the surgeon. Low-dose X-rays usually have no side effects in this technique.
7.2 Risks
There is always a small risk of causing cancer from overexposure to X-ray radiation. However, in this technique the benefits to early diagnosis and treatment far outweigh the risks. It is possible to injure the milk ducts during catheterization or during contrast injection. This is not dangerous because most lesions will heal on their own after a short time. There is a possibility of a breast infection, or mastitis, but it is not common.

Viêm vú là một rủi ro có thể xảy ra khi tiếp xúc với bức xạ tia X
8. What are the limitations of mammograms?
If there is no nipple discharge at the time of the mammogram, the ducts cannot be located and this technique cannot be performed.
In addition, some dilation tubes are quite small, making it impossible to place tubes to inject contrast.
At Vinmec International General Hospital, there is a Breast Cancer Screening Package, which helps customers screen and detect breast cancer early even when there are no symptoms. When registering for the Breast Cancer Screening Package, customers will receive:
Examination and consultation with an oncologist. Breast cancer screening by bilateral breast ultrasound and mammogram. Officially put into operation on January 7, 2012, Vinmec has become a prestigious address in breast cancer screening with:
Team of highly qualified and experienced doctors. Comprehensive professional cooperation with domestic and international hospitals: Singapore, Japan, USA, etc. Comprehensive treatment and care for patients, multi-specialty coordination towards individualizing each patient. Having a full range of specialized facilities to diagnose the disease and stage it before treatment: Endoscopy, CT scan, PET-CT scan, MRI, histopathological diagnosis, gene-cell testing, .. There are full range of mainstream cancer treatment methods: surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, stem cell transplant... To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can You can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
References: Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer, radiologyinfo.org