This is an automatically translated article.
Bronchiectasis is an irreversible dilation of part of the bronchial tree, making it difficult to bring phlegm and mucus from the lower respiratory tract to the upper respiratory tract and creating conditions for the growth of inflammatory bacteria. The diagnosis of bronchiectasis depends a lot on imaging tools, especially chest computed tomography, which helps to show the area and severity of bronchiectasis as well as clues about the cause of the disease. .
1. Causes of bronchiectasis
In fact, up to 40% of cases of bronchiectasis of unknown cause are also known as “primary bronchiectasis”. Others may have four main causes:
Hereditary diseases such as cystic fibrosis and primary ciliary dyskinesia Immune problems that decrease the body's ability to fight infections History of infection past lung infection Problems with swallowing or aspiration causing food or liquid to enter the lungs
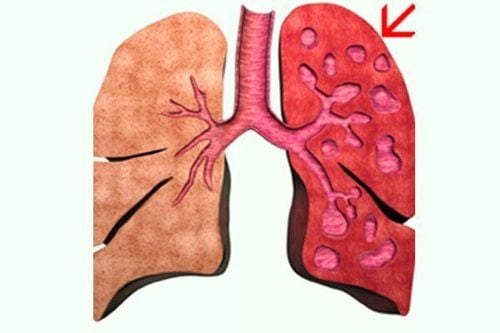
Có đến 40% các trường hợp giãn phế quản không rõ nguyên nhân
2. How does bronchiectasis manifest?
Patients with bronchiectasis have systemic symptoms depending on the extent, cause and complications of the disease, which can be anemia or weight loss. The specific symptoms of bronchiectasis are as follows:
Profuse sputum production (500-1000ml/24h), purulent sputum, sometimes foul-smelling due to anaerobic bacteria. During an exacerbation, it is often accompanied by fever and increased sputum production Coughing up blood repeatedly and lasting for many years Shortness of breath is a manifestation of respiratory failure Chest pain is an early symptom of lung infection in the bronchiectasis In addition, when examining the doctor, the following symptoms can also be detected:
Auscultation of the lungs has moist rales, bronchial rales in the affected areas. calculate cupped fingernails, drumstick fingers

Ho ra máu tái phát nhiều lần và kéo dài trong nhiều năm là một trong những biểu hiện giãn phế quản
3. Computed tomography image of bronchiectasis
The definitive diagnosis of bronchiectasis relies heavily on imaging because respiratory symptoms are relatively difficult to distinguish from diseases with similar manifestations. Computed tomography (CT scan) of the chest is the gold standard in the diagnosis of bronchiectasis. This method will show the image of the affected area and the severity of the disease, the indicators of the cause of the disease. The images of bronchiectasis lesions on CT can be:
The inner diameter of the bronchi is larger than the accompanying artery The bronchi are less than 1 cm from the chest wall pleura The bronchi are close to the mediastinal pleura Thickened bronchial wall There are also other imaging methods that complement computed tomography in the diagnosis of bronchiectasis such as:
X-ray of the lungs: For images of tubular opacities representing the bronchi filled with mucus, the bronchial walls form parallel lines, the volume of the lobes is reduced, and the light foci are small like honeycombs Contrast bronchogram: Cylindrical, sac-shaped dilated bronchi, rosacea Bronchoscopy: Can detect foreign bodies, folded, narrowed bronchi or sites of bleeding, and bronchial aspirate for bacteria An electrocardiogram can also be indicated. Designed for early detection of congestive heart failure Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience With experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured that they will be examined and treated for bronchiectasis at the Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
MORE
Diagnosis and treatment of bronchiectasis Management of bronchiectasis in adults Common causes of bronchiectasis