This is an automatically translated article.
The pouch that forms along the length of the urethra is called a urethral diverticulum or bladder diverticulum. Patients will feel pain, frequent infections and urinary incontinence when the urine does not flow out completely but remains in the diverticulum. Vaginal diverticulum, although a rare disease, makes the patient very uncomfortable, even at high risk of dangerous complications, including cancer.
1. What is a bladder diverticulum?
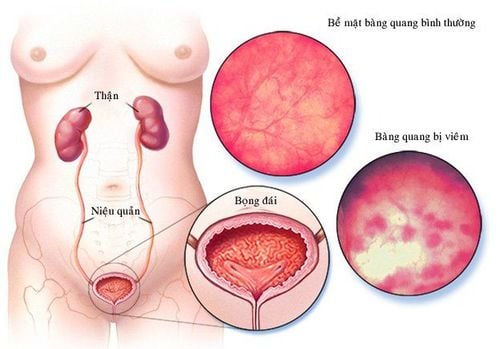
A benign lesion of the bladder wall that manifests as a pouch arising from the wall of the bladder, thin, with only the mucosa and serosa, is called a bladder diverticulum.
Most cases of bladder diverticulum are discovered incidentally or through examination of nonspecific lower urinary tract symptoms such as urinary retention, hematuria, or urinary tract infection. The majority of bladder diverticula are congenital with manifestations as early as infancy. In adults, there are usually no specific symptoms and are quite rare. Bladder diverticulum occurs most often in men and usually only a solitary diverticulum, occurs most in men, is located posteriorly outside the orifice of the ureter.

Túi thừa niệu quản thường xảy ra ở nam giới
2. Symptoms of bladder diverticulum
In the early stages, a bladder diverticulum usually has no specific symptoms, but as its volume increases, symptoms of the disease begin to appear, usually due to local complications from the diverticulum. cause.
Manifestations of bladder diverticula are variable, and the severity of the disease is often unrelated to the diverticulum size. Some common symptoms of this condition include:
Difficulty urinating, pain when urinating (dysuria) Blood in the urine Drip after urinating Leaky urine Recurrent bladder infections Frequent urinary tract infections urinating (UTI) Pain during sex Formation of a mass in the vaginal wall Infected bladder Pain in the pelvic region Urinary disturbances Bladder stones Frequent urination Frequent urination at night Bladder tumors Patient Bladder diverticulum may present with one of the above symptoms or at the same time. These symptoms may not be present continuously.

Bệnh túi thừa bàng quang dễ dẫn tới rối loạn tiểu tiện
3. Causes of bladder diverticulum
Bladder diverticulum causes can be congenital or acquired. Weak bladder wall at the bladder-ureteral junction is the underlying cause of bladder diverticulum. Pelvic trauma during childbirth has also been identified as a causative agent of bladder diverticulum formation. Bladder diverticulum is common in patients with benign prostatic hypertrophy.4. Diagnosis of bladder diverticulum
Several common methods are used to diagnose a bladder diverticulum, including:
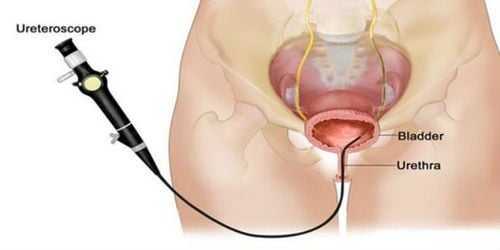
Physical examination: when performing a different examination of the vaginal walls in women, underlying masses may be detected. In addition, pus or urine from the diverticulum will also be removed during the examination. Ultrasound: This is a method that uses sound waves to obtain images of the pelvis. This is considered a common diagnostic method. Cystoscopy: To determine if a bladder diverticulum is present, the doctor will perform a cystoscopy by placing a laparoscope into the bladder to observe. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): this is considered the best diagnostic method today to diagnose bladder diverticulum..
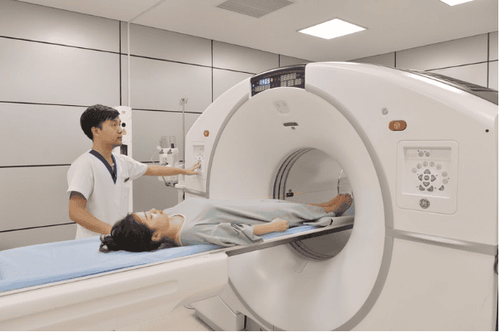
Chẩn đoán túi thừa bàng quang bằng hình ảnh
Intravenous urography An X-ray of the bladder and urinary tract (VCUG). Biopsy if malignancy is suspected To prevent complications caused by bladder diverticulum, it is necessary to pay attention to periodic health monitoring examinations. In addition, to evaluate kidney function, in addition to ultrasound, blood and urine tests can be performed in order to have timely treatment.
5. Complications of bladder diverticulum
The cause of complications in the urinary system is because there is no excuse, so the function of expulsion of urine accumulated in the diverticulum is poor, so each time you urinate, the urine in the diverticulum is not completely empty, so there A certain amount of urine remains.
This process lasts for a long time, causing the diverticulum to become more and more stretched, causing compression of the bladder neck and urethra, leading to complications such as recurrent urinary tract infections, diverticular stones, acute and chronic urinary retention The most dangerous are bladder cancer or premalignant changes.
Water retention in the ureters and kidneys is a common complication, causing impaired urinary tract function as a result of obstruction or reflux. In about 3-5% of cases, there is an increased risk of adenocarcinoma of the lining of the bladder diverticulum.
Early diagnosis and timely treatment of bladder diverticulum are very important, in order to reduce the impact caused by the disease, and at the same time prevent the risk of dangerous complications of the disease.
To register for examination and treatment of common bladder diseases at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.