This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Dinh Thanh Ha - Obstetrician and Gynecologist - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Vinmec Nha Trang International HospitalCervical ectropion, cervical cancer, ... are common diseases of the cervix and can cause many dangerous complications, affecting reproductive health, even causing infertility in women. Therefore, women should actively learn about these diseases to be able to prevent and minimize the consequences caused by the disease.
1. Cervical ectropion and cervical ectropion
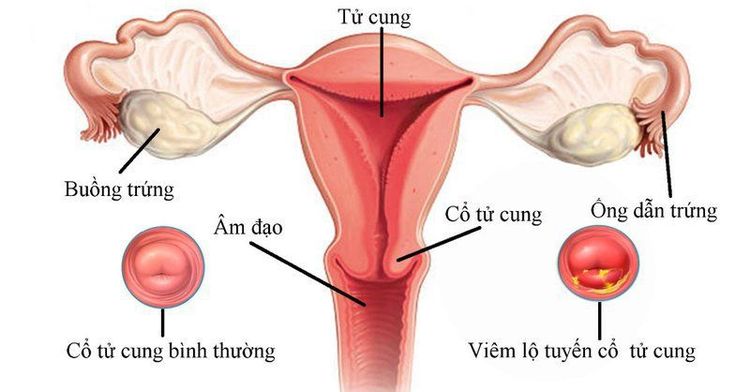
1.1 Cervical ectropion Cervical ectropion is a benign lesion in the cervix, caused by glandular cells located in the cervical canal growing outward, invading the outer surface of the cervix, exuding fluid as when in the cervix. Therefore, patients often have increased vaginal discharge, smelly discharge, itching, ... easily leading to infection (cervical ectropion).Cervical ectropion is often asymptomatic. Patients are mainly discovered during gynecological examination. Some women have congenital cervical ectropion. However, this condition can also occur due to the use of oral contraceptives or in women during pregnancy or due to improper vaginal hygiene, strong sexual activity that damages the uterus, abortion. many times,... The level of danger of cervical ectropion depends on the wide or narrow area of the route.
1.2 Cervical ectropion Cervical ectropion is a warning phenomenon of inflammation in the glands. When the cervix is exposed to the mucosa, the glands are easily infected by fungi, bacteria, parasites, ... The disease is common in married women, who have experienced childbirth or have been pregnant. have had sex for many years.
Causes of disease
Failure to clean the intimate area: creating conditions for pathogenic bacteria to grow and attack. They will quickly penetrate, move to the cervix and cause inflammation here; The hormone estrogen spikes: promotes a disturbance of the protective environment in the sex organs, causing the glands to become exposed and inflamed; Abortion does not ensure sterility: causes the cervix of women to be eroded and infected; Unsafe sex: increases the risk of cervical ectropion due to sexually transmitted diseases such as syphilis, gonorrhea, genital warts...; Gynecological procedures: Gynecological procedures such as abortion, IUD insertion, fibroid surgery, etc. wear down the cervix, increasing the risk of thyroiditis. Disease symptoms
Vaginal discharge appears much, has a strong odor, turns yellow, sticky, foamy, sometimes mixed with blood; The skin outside the vagina is red and swollen, itchy, and even ulcerated; Pain in the waist, pelvic region, menstrual pain, later the pain spreads to the ligaments, affecting marital life and may lead to infertility; Cystitis spreads to the three corners of the bladder, irritates the bladder, leading to frequent urination, frequent urination, pain when urinating; Bleeding during sex, there is a burning sensation because the surface of the cervix is inflamed and becomes rougher, more vulnerable; Fatigue, inflexibility and inactivity; Irregular menstrual cycle: late period, prolonged menstrual period or dark black menstrual blood,... Treatment
The gland itself is a benign lesion but in the process it invades the surface of the neck. In the uterus, the cells lining the outside of the cervix can respond proliferatively to repel this invasion, giving rise to lesions that can lead to cervical cancer. In addition, prolapse with prolonged cervicitis also makes the cervix large and elongated, easily mistaken for uterine prolapse. Therefore, early treatment is essential. Treatment methods include:
Medical: Using vaginal suppositories for mild infections. The patient should make the drug in the evening, before going to bed and strictly follow the doctor's prescription; Surgery: Electrocautery or laser to destroy the inflamed area and the cells that cause the gland.
2. Cervical nabothian cyst
Cervical nabothian cysts are small, mucus-filled cysts that form on the surface of the cervix. Nabothian cyst is a benign lesion, usually 2 to 10 mm in size, formed by an overgrowth of squamous epithelial cells, covering the glandular epithelium at the border of the cervical junction. Depending on the time and extent of development, nabothian cysts can be small or large (the size of a grain of rice, a pea or larger).Nabothian cysts are white or yellow, very smooth. Usually, when a woman has nabothian cyst, there are no specific symptoms, often only discovering the disease when going to a gynecologist. Vaginal bleeding also occurs after sex, but it's very rare.
In general, nabothian cysts are not life-threatening but can affect a woman's sex life and fertility. Nabothian cysts are small and few, most of which are self-resolving and do not require treatment. However, if the cyst grows too large, it can burst on its own, causing infection, a very dangerous uterine infection. Therefore, in many cases, the doctor will poke the fluid out to avoid the risk of the cyst spontaneously bursting and causing infection.
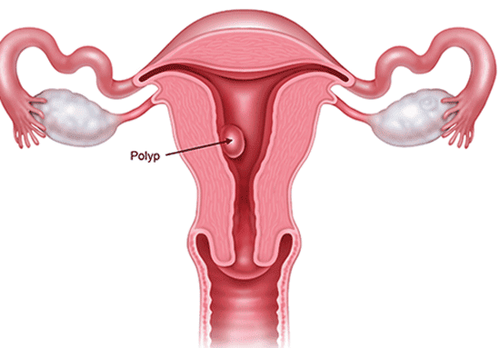
3. Cervical polyp
Cervical polyps are small, long growths that usually arise from the outer or inner cervix and spread outside the cervix. Polyps are formed by enlarged proliferative glands, surrounded by a stromal mass, and most polyps are benign. If you have polyps, usually you only have 1, 2, and at most 3 polyps on your cervix. The size of polyps can be very small or very large. Cervical polyps do not have obvious symptoms, usually only discovered when a woman has a gynecological examination. 99% of cervical polyps are benign and 1% will have neoplastic changes leading to cervical cancer. Cervical polyps are unlikely to regrow.3.1 Disease symptoms Vaginal bleeding; There is white, yellow mucus; Abnormally heavy menstrual cycles; Bleeding after sex, between periods, after douching, after menopause. 3.2 Causes of the disease Until now, the cause of cervical polyps has not been clearly identified. Some theories suggest that the cause of the disease is:
Increased estrogen levels; Vascular occlusion; Cervicitis, vaginitis or chronic uterine disease. The subjects at high risk of disease are:
Women aged 40 - 50 who have more than 1 child; Pregnant women (due to increased estrogen hormone); Patients with cervical infection. 3.3 Treatment Usually, doctors will not remove cervical polyps unless they are causing uncomfortable symptoms. The procedure to remove cervical polyps is simple, can be done in the clinic and does not require pain medication. Methods to remove cervical polyps include:
Twisting polyps at the base; Attach surgical wire around the base of the polyp and cut it off; Use clamps to remove polyps; Destruction of the base of the polyp with liquid nitrogen, electrocautery (including the use of a hot electric needle) and laser surgery. 3.4 Prevention and control of cervical polyps Regular cervical examination to detect early polyp growth; Use cotton underwear for good air circulation, preventing excessive heat and humidity in the genitals; Use condoms during sex; Periodic health check and regular PAP check .

4. Cervicitis
Cervicitis is a common gynecological disease. In Vietnam, up to 33% of women have cervicitis, in which up to 40% of cases have severe complications, turning into cervical ulcers and increasing the risk of cervical cancer. Cervicitis is a swelling, inflammation, and sores in the cervix caused by a bacterial, fungal or parasitic infection. Cervicitis can increase and cause endometritis and pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). The disease is divided into two categories: acute and chronic. Acute cervicitis that recurs many times or is not detected, timely treatment can lead to chronic cervicitis.4.1 Cervicitis symptoms Most women with cervicitis have no symptoms. The disease is usually only discovered during routine check-ups or when the patient is seen for another related illness. Others, patients may have the following symptoms:
Unusual discharge: yellow, milky or light gray; Abnormal vaginal bleeding: Bleeding after sex or between periods; Vaginal pain, itching; Burning pain during sex; Pain when urinating; Heaviness in the pelvis. 4.2 Causes Cervicitis can be caused by any infection, the most common of which are chlamydia and gonorrhea, with chlamydia accounting for about 40% of cases. Other causes include Trichomonas vaginalis, herpes simplex virus, and Mycoplasmaroductionium. Cervicitis can also be idiopathic without a specific cause found
4.3 Risk factors Unprotected sex: Not using condoms (increased risk of sexually transmitted infections and viruses) sex), too rough sex (causing damage to the cervix, creating conditions for infection to develop), marital activities with partners suffering from social diseases such as syphilis, gonorrhea, genital warts , genital warts; Vaginitis: If not treated promptly, it will create opportunities for parasites, fungi, bacteria to attack the cervix and cause inflammation, even increasing the risk of cervical cancer; Allergies: Using feminine hygiene solutions, condoms, lubricants of unknown origin or improperly used to cause genital allergies and lead to cervicitis; Abortion: Women with a history of abortion have a higher risk of cervicitis, especially in cases of unsafe abortion or poor postoperative care; Sex too early, too much: Women who have sex at a young age, get pregnant early when the reproductive organs are not fully developed, or have intercourse continuously with high frequency, have many different partners in a time,... susceptible to gynecological diseases in general, cervicitis in particular; Poor personal hygiene: Wearing clothes for a long time, wearing tight pants, using douches too deep into the vulva, not cleaning the genitals clean before and after sex, ... increases the risk of cervicitis; Abnormally prolonged menstrual cycle: Menstrual cycles of more than 7 days cause menorrhagia, heavy bleeding, keeping the cervix open, creating conditions for bacteria and fungi to penetrate and cause cervicitis. bow.

Use of drugs: Depending on the cause of the disease, the doctor will prescribe the appropriate drug. For patients with cervicitis caused by sexually transmitted diseases, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics. In the case of cervicitis caused by a virus, the doctor will prescribe antiviral drugs; Laser Therapy: Using high-intensity laser to burn and destroy abnormal tissue; Electrocautery (thermotherapy): Using a heating rod to burn infected cells inside the cervix; Cryosurgery (freezing therapy): Indicated for cases of persistent cervicitis. This procedure uses extreme cold to destroy abnormal cells. The instrument used is a cryogenic rod containing liquid nitrogen. Cryosurgery is virtually painless, but the patient can experience cramping, bleeding, infection, and scarring. 4.5 Prevention Always use protective measures such as condoms, IUDs, etc. and use them correctly; Live in monogamy, limit the number of sexual partners; Clean the vulva properly before and after intercourse, change tampons at the right time during menstruation, choose the right underwear material and change underwear regularly; Avoid abortion. In the case of forced abortion, women should choose a reputable medical facility to minimize complications and avoid affecting their reproductive function in the future; Have sex in moderation and in moderation.
5. Cervical cancer
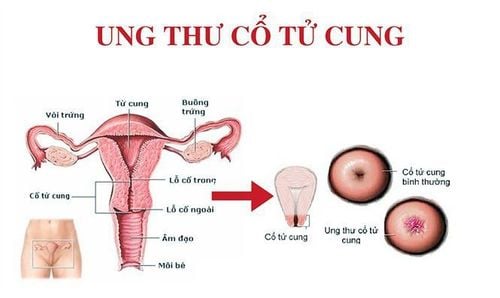
5.1 Cervical Cancer Symptoms Irregular Vaginal Bleeding: Vaginal bleeding on days other than menstrual cycle; Abnormal vaginal discharge: Vaginal discharge is abnormal, has a strange color such as yellow, green like pus or blood, has an unpleasant smell,... Irregular menstrual cycle: Cervical cancer It also affects development, ovulation and hormone balance in the body. As a result, the menstrual cycle is irregular, menstruation is prolonged or menstrual blood is dark in color; Change in urination habits: Frequent urination, urgency to urinate; Pelvic pain: Occurs when cancer cells have spread to the pelvis, causing pelvic pain that is not related to menstruation, pain during sex or pain when urinating; Anemia: In cervical cancer patients, the number of healthy red blood cells is reduced, which is replaced by white blood cells to fight cancer, leading to anemia. Manifestations of anemia are fatigue, lack of energy, unexplained weight loss and loss of appetite; Other symptoms: Pain or bleeding after sex; back pain, pain that radiates down the leg and causes swelling in the leg; 5.2 Causes of cervical cancer Studies have shown that up to 99.7% of cervical cancers are caused by HPV virus through sexual activity. Two strains of the HPV virus, HPV 16 and HPV 18, account for about 70% of cervical cancer cases.
Factors that increase the risk of cervical cancer include:
HPV infection: Due to sex with many people; Smoking: Secondhand smoke contains many chemicals that can be harmful to the body. Women who smoke are twice as likely to develop cervical cancer as non-smokers; Immunosuppression: Taking medications or having diseases that affect the immune system (eg HIV/AIDS) can increase the risk of HPV infection and lead to cervical cancer; Chlamydia infection: The risk of cervical cancer is higher in people with Chlamydia; Other causes: Eating less fruit and vegetables, being overweight, using birth control pills for a long time, using an IUD, having multiple pregnancies (more than 3 times), getting pregnant for the first time under 17 , difficult living circumstances, family history, ... are all factors that increase the risk of cervical cancer. 5.3 Treatment of cervical cancer There are 3 main methods of cervical cancer treatment: surgery, radiation therapy and chemotherapy. Specifically:
Surgery: The doctor removes the tumor, including cervicectomy (removing the cervix, surrounding tissue and upper part of the vagina but keeping the uterus), hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) removal of the cervix and uterus, possibly both ovaries and fallopian tubes depending on the stage of cancer) and pelvic segment (removal of the cervix, vagina, uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, and bladder) optic and rectal); Radiation therapy: A method of irradiating the body with radiation, performed alone or in combination with surgery in the treatment of cervical cancer in the early stages. When cancer has progressed to a later stage, radiation therapy can be combined with chemotherapy to reduce bleeding and uncomfortable symptoms for the patient; Chemotherapy: A method of injecting anti-cancer drugs into the body through an intravenous line, chemotherapy alone or combined with radiation therapy to treat cervical cancer. In cases where cervical cancer is found at an advanced stage, the doctor will use chemotherapy to prevent the cancer from spreading. 5.4 Measures to prevent cervical cancer Regularly do a PAP test as prescribed by your doctor to detect and treat cervical cancer in time; The HPV vaccine is recommended for women ages 9-26, preferably 11 to 12 years old, regardless of whether they have had sex or not. The vaccine is most effective when given before having sex for the first time. Practice safe sex by using condoms and limiting the number of sexual partners to avoid getting HPV.

Currently, at the Vinmec International General Hospital system, the basic gynecological examination and screening package is being applied.
With a team of medical - doctors who are leading experts, highly qualified, dedicated and wholeheartedly for the benefit of patients. Comprehensive and professional medical examination, consultation and treatment services. The system of modern equipment, supports effective diagnosis and treatment. Modern, civilized, luxurious and sterile medical examination and treatment space. Fully guarantee the safety and privacy of customers. Modern, efficient and effective model for managing, sharing and connecting information online.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.