This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Huynh Kim Long - Emergency Resuscitation Doctor - Emergency Resuscitation Department - Vinmec Da Nang International General Hospital.Closed chest trauma is the most common type of injury from motor vehicle accidents and is also a major cause of morbidity and mortality in all ages. Types of blunt chest trauma are highly dependent on the intensity of the injury and can range from harmless injuries to potentially life-threatening injuries.
1. Overview of closed chest trauma
Trauma to the chest is a general concept for injuries in the chest area, divided into two large groups: closed chest trauma and chest trauma. For blunt chest trauma, this is the type of injury that does not cause discontinuity of the chest wall.The most common cause of blunt chest trauma is a motor vehicle accident with an incidence of 50–75%. The remaining causes are falls or accidents at work or in daily life. Regardless of the cause, the mechanism of injury is due to the change in speed and pressure of the external force acting on the chest wall, resulting in shear force causing tearing of blood vessels as well as traction and rupture of hollow organs. and snake.
Clinical features of closed chest trauma cases hospitalized are chest pain, hypotension, tachycardia, hypoxia, alveolar hypoechoic in pneumothorax or decreased heart sound in pericardial effusion.
For all patients admitted to the hospital following an accident, the closed chest trauma approach begins with preliminary investigations prior to admission, which may require immediate emergency care on the scene if critical. Accordingly, if the patient is hemodynamically unstable at the hospital, it is necessary to quickly identify life-threatening conditions for timely intervention, including emergency surgery. In addition to the physical examination, the necessary initial tests for rapid diagnostic evaluation are chest x-ray - the initial test for all patients with blunt chest trauma, echocardiography and electrocardiogram, or even computed tomography (CT) scan. computerized class, transesophageal echocardiography, bronchoscopy, angiography. Even if the patient's condition cannot be stabilized, an indication for immediate surgery or exploratory thoracotomy should be made to determine the appropriate clinical picture. Common conditions in blunt chest trauma are presented below.
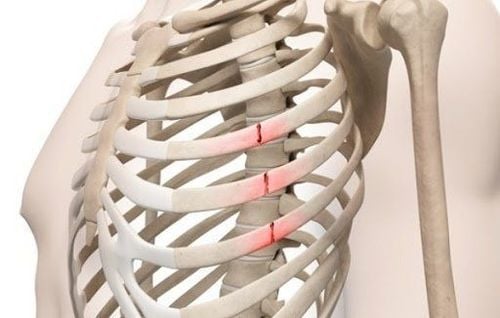
2. Broken rib
The etiology of rib fractures in closed chest trauma is mainly due to severe traumatic forces, fractures on the basis of pre-existing medical conditions or non-accidental trauma such as child abuse.The clinical feature of rib fracture is pain on the chest wall with sharp pain points, and at the same time observed signs of chest wall deformity. If the rib cage has multiple fractures, from more than 3 bones, in 2 or more locations, it will lead to a floating part of the rib wall and soft tissue in the chest wall when breathing, called a mobile rib plaque. At that time, the patient quickly fell into respiratory failure with rapid and shallow breathing or apnea.
The quick diagnosis of rib fracture is by chest X-ray, anteroposterior or lateral position, with signs of fracture, displacement of the rib walls. CT may be indicated if a complicated rib fracture is suspected.
The main complications of rib fracture are pneumothorax, hemothorax, and pulmonary contusion. Especially in the elderly, rib fractures are painful, predisposing the patient to hypoventilation, resulting in atelectasis and/or pneumonia.
3. Nerve injury
Nerve injury in blunt chest trauma is an acute form of injury. In addition to the direct traumatic cause, nerve injury can also be the result of ischemia or compression of the organ or compartment.The clinical feature of acute nerve injury in blunt chest trauma is that the patient has diaphragmatic paralysis. If only one side of the diaphragm is paralyzed, the patient may have no symptoms or only shortness of breath on exertion; On the contrary, if the diaphragm is paralyzed on both sides, it will quickly lead to severe breathing difficulties. The external indirect manifestations of the phrenic nerve injury in the thoracic segment are reduced movement and decreased respiratory rate, unilateral atelectasis. However, a trauma to the phrenic nerve is quickly detected by a chest x-ray showing abnormal diaphragm elevation or mediastinal deviation.
For local nerve injury of the viscera, the patient will present with damage to the corresponding viscera.
4. Heart Injury
Cardiac injury can occur in closed chest trauma with the following conditions:Arrhythmia: palpitations, dizziness, syncope Acute coronary syndrome: chest pain, sweating, dyspnea Hypotension Pressure and tachycardia unresponsive to fluid resuscitation Myocardial concussion and rupture: hypotension, tamponade This is a serious condition and most patients die before reaching the hospital.
The best initial diagnosis is by echocardiography and electrocardiogram. However, for a ruptured heart, immediate surgery is required to save the patient.

5. Damage to the aorta
Injury to the aorta in blunt chest trauma, especially in car accidents, is typically located at the isthmus of the aorta, near the division of the left subclavian artery, with a rate of about 70% of cases. Severity ranges from concussion-induced aortic injury to aortic rupture; where the critical nature of aortic rupture can be equated with cardiac rupture.The initial clinical features are often difficult to detect because the patient is asymptomatic or has nonspecific symptoms (eg, chest pain, dyspnea), because of the position of the aorta posterior in the thorax. In case of rupture, the patient will quickly show signs of hemorrhagic shock with tachycardia and hypotension.
Initial examination for aortic injury is also with a chest radiograph showing mediastinal enlargement, tracheal displacement, or hemothorax. In hemodynamically stable patients, clinicians may consider CT and contrast-enhanced CT angiography to achieve greater sensitivity and specificity. In contrast, in hemodynamically unstable patients, transesophageal echocardiography in the operating room is used instead.
6. Pulmonary contusion
Although the lung is classified as a solid organ, but due to its density of empty space due to the filling of air, the lung is still susceptible to contusion in the setting of blunt chest trauma. Any damage to the lungs causes the patient to have chest pain, shortness of breath, tachypnea, tachycardia, hypoxia and hypoxia or acute respiratory failure; may be worse after perfusion because pulmonary edema is more severe.Diagnosis of pulmonary contusion on chest x-ray is diffuse alveolar infiltrates or large opacities in the lung. Computed tomography is indicated if an initial x-ray is not conclusive enough to identify associated lesions.

7. Tracheal Injury
The trachea is a rigid tube covered with cartilage rings. Therefore, the trachea will be very fragile, cracking when trauma to the chest is severe. Clinical features of people with tracheal lesions are dyspnea, hoarseness, subcutaneous pneumothorax and pneumothorax, mediastinum.A chest x-ray showing a discontinuity of the tracheal wall and presence of air in the soft tissues around the neck and mediastinum is a quick sign of tracheal rupture. In addition, bronchoscopy in the operating room is also necessary to help the surgeon easily visualize the injury to stitch and restore the bronchi.
8. Diaphragm rupture
A diaphragmatic rupture, also known as a diaphragmatic injury or tear, is a tear in the surface of the diaphragm that causes a loss of continuity and directly affects breathing. The mechanism of diaphragmatic rupture in blunt chest trauma may be external or penetrating force.The signs and symptoms of a patient with a ruptured diaphragm are chest or abdominal pain, irritation of the cough, decreased breath sounds on the rupture side, and rapid onset of respiratory failure. Also, because the pressure in the abdominal cavity is higher than in the thoracic cavity, rupture of the diaphragm is almost always associated with a herniation of abdominal organs into the chest cavity, known as a traumatic diaphragmatic hernia. closed chest trauma.
Diagnostic techniques for diaphragmatic rupture include X-ray, computed tomography and open laparotomy techniques for both exploration and reconstruction of the diaphragm.
In summary, blunt chest trauma is a significant cause of death frequently in traffic accident patients if not promptly treated appropriately according to each type of injury. Therefore, the quick access and correct classification according to the above types of closed chest trauma not only help guide the appropriate management of the patient but also improve the patient's prognosis in the future.
This is a severe case that can be life-threatening if not diagnosed and treated early. Patients must immediately go to medical facilities for diagnosis and emergency treatment. Vinmec International General Hospital is a prestigious medical address with:
The team of emergency doctors and nurses at the Emergency Department are intensively and professionally trained, able to receive and handle emergency schools. In case of severe chest trauma patients with respiratory failure, life-threatening. There is always coordination with all other specialties such as thoracic trauma, cardiology... quickly. There are modern equipment in diagnosis and treatment. The Emergency Department of Vinmec International General Hospital operates 24/24 on all days of the week, including Saturdays and Sundays as well as holidays of the year. The team of emergency doctors and nurses at the Department are professionally and thoroughly trained, able to receive and handle urgent cases of patients, and always coordinate with all specialties in a timely manner. fast.
With modern equipment and a team of experienced doctors, the Emergency Department has conducted emergency and saved the lives of serious and complicated patients. At the same time, patients at the Emergency Department are always coordinated care by many other specialized specialties (Team Base Care). Therefore, at the Emergency Department, patients will be examined, diagnosed, accurately and quickly, with high reliability and intensive treatment right from the emergency stage to help them quickly get out of the critical stage. dramatic and stable.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.