This is an automatically translated article.
The kidney is an organ located deep in the peritoneum, with a brittle parenchyma, so it is easy to break due to injury, but with good perfusion and nourishment, it is easy to heal scars and restore function. Closed kidney injury accounts for 80-85% of kidney injury cases with symptoms that should be noted for early detection and prompt treatment.
1. What is a closed kidney injury?
Closed kidney injury is a condition in which the kidney is damaged but the abdominal or back wall is not punctured, the most common causes are traffic accidents, falls, sports accidents and assaults. In particular, a traffic accident or a high fall can tear the renal artery or completely cut it. After kidney injury, there are symptoms of hematuria, shock, the risk of damage to the large blood vessels of the kidney is very high (about 20%)
2. Is kidney contusion dangerous or not?
Renal contusion is used to refer to grade 1 kidney injury, when the damaged kidney tissue is broken, the kidney is intact with hematoma under the capsule and around the kidney. This is the most common injury in kidney injury, in addition, kidney damage is also divided into the following levels.
Grade 2: Rupture of the capsule of the kidney tissue under 1cm, does not affect the calyx, renal pelvis and part of the kidney. renal medulla and is located in a small, mild lesion that occurs in 85% of cases of kidney injury Grade 3: Rupture of renal tissue greater than 1 cm Grade 4: Large rupture penetrates the calyx, renal pelvis causing urine leakage and damage Injury to the small vessels is classified as grade 4 Grade 5: fragmented renal rupture and major renal vascular injury. Grade 3-5 is known as severe major kidney injury, seen in 15% of cases of blunt renal trauma. Renal artery injury will include blockage or tear of the renal artery or one of its accessory branches. Usually occurs in less than 1% of blunt renal trauma. Note that the kidney cannot recover after 1 hour of complete blood loss and the diagnosis of renal vascular injury is difficult.
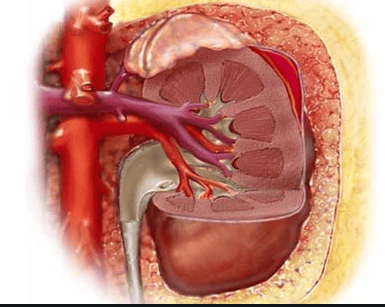
Dập thận nặng gây tắc hoặc rách động mạch thận
3. How is closed kidney injury diagnosed?
Diagnosis of occult kidney injury should be based on both the mechanism of injury, the patient's clinical features, and supportive tests.
Systemic symptoms:
Symptoms of shock are seen in 40-50% of kidney injury cases, especially in cases of combined lesions Infectious syndrome: occurs when the patient is late, leading to superinfection with perirenal blood clots Local symptoms:
Macroscopic or microscopic total hematuria: seen in 90-95% of cases, it should be noted that the degree of hematuria is not commensurate with the extent of the lesion. Pathophysiology Post-traumatic lumbar pain: common in all cases, but is usually nonspecific and sometimes occurs after renal colic Pain Lumbar rib: the progression of this symptom Valuable in assessing prognosis. In addition, there may be symptoms of combined organ damage such as blunt chest trauma (pneumothorax, hemothorax), blunt abdominal trauma (trauma ruptured liver, spleen). ), perforation of hollow viscera or injuries to limbs, skull

Người bệnh chấn thương thận kín sẽ thường xuyên xuất hiện các cơn đau quặn thận
Subclinical symptoms:
Blood count: red blood cells and hemoglobin decrease, especially in cases of moderate and severe lesions, white blood cells often increase Urine test: red blood cells, white blood cells increase, protein Positive urinary tract X-ray of the kidney: diffuse opacities in the injured kidney, the lumbosacral margin is erased perirenal function Ultrasound: images of parenchymal fissures and accumulations of fluid in the renal fossa CT scanner: is the best test in diagnosing closed kidney injury, giving clear images of renal parenchymal lesions and deposits perirenal fluid Renal angiogram: show the location and extent of damage, especially the renal vascular branches
Chụp vi tính cắt lớp cho phép chẩn đoán những tổn thương liên quan đến chấn thương thận kín
4. Treatment of closed kidney injury
The patient will be treated conservatively in the following cases:
No shock or shock quickly recovers after treatment The condition of hematuria, tension in the lumbar region gradually stabilizes over time Indications Surgical treatment when:
Ribular ridges exceed mid-white line Patient has persistent fever that does not recover despite active treatment Hematuria, renal prolapse, pain worsening over time Suspicion Suspected injury to abdominal organs Complications of renal fossa abscess Patients should be examined and treated at reputable hospitals to minimize complications after closed kidney injury. Vinmec International General Hospital is a high-quality medical unit in Vietnam, with a team of well-trained, specialized doctors at home and abroad, with high qualifications and experience.
Modern medical equipment, imported in the US, Japan, the Netherlands... supports the most effective diagnosis and treatment of diseases. Treatment techniques at Vinmec are regularly and continuously updated, keeping up with new trends of world health, providing the most effective treatment regimens.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact the nationwide Vinmec Health System Hotline, or register online HERE.