This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II, Master Nguyen Thi Thu Ha - Head of Department of Medical Examination and Internal Medicine, Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General HospitalVaricella - Zoster virus is the cause of a familiar disease called chickenpox. Let's learn about the disease and see close-up images when infected with Varicella - Zoster chickenpox virus.
1. Varicella - Zoster virus and chickenpox
Chickenpox is a highly contagious disease caused by the Varicella-Zoster virus. Varicella - Zoster virus belongs to the herpes virus family, when first infected (primary Varicella - Zoster virus infection) causes chickenpox.Chickenpox mainly occurs in children (90% of cases are children), but adults can still get chickenpox. Children under 2 years of age are most at risk for chickenpox.
People who are susceptible to chickenpox include:
Have never been infected with Varicella - Zoster virus before, or have never used the Varicella - Zoster virus vaccine. Working in schools or childcare facilities. Live with children. Chickenpox spreads very quickly and is very strong, even just breathing in the dust from the chickenpox blisters or touching the spot where there is dust from the blisters can be infected with the Varicella - Zoster virus. Chickenpox is most contagious 1 to 2 days before the rash appears, until all of the chickenpox blisters have dried and crusted over.
Thủy đậu lan truyền rất nhanh
2. Symptoms of Chickenpox
Symptoms of chickenpox typically appear 10 to 21 days after being exposed to the virus. The first sign that appears is usually a feeling that the body is not feeling well, then the following symptoms will appear:Body pain. Fever. Feeling extremely tired. Feeling easily irritated. Loss of appetite. Headache. Within a day or two, a chickenpox rash will appear. The progression of chickenpox rash consists of three phases:
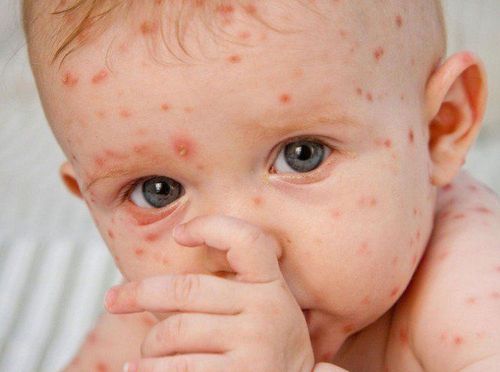
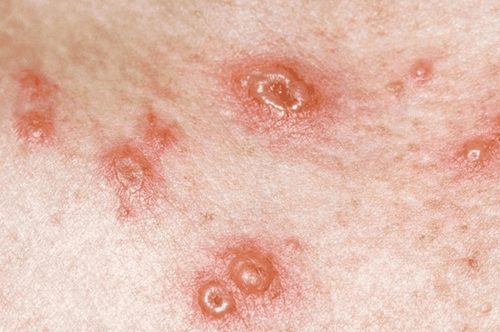
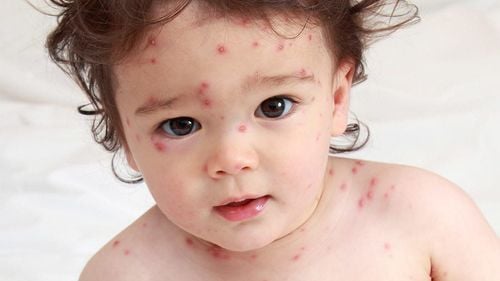
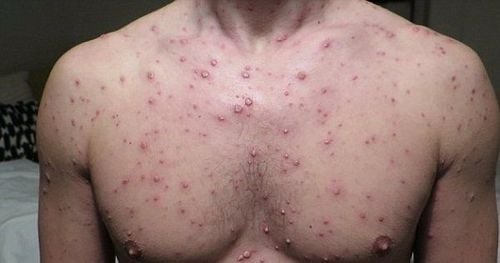
The first phase on the body will appear erythematous, papule-like rash, which appears very quickly and itch, the number can be from 250 to 500 all over the body. In severe cases, a rash can form in the mouth, eyes, anus or genitals. After a few days, these rashes form small fluid-filled blisters (cysts), which persist for about a day before bursting and releasing fluid around them. In the final phase, the blisters that break open dry up, and then scab over. The chickenpox rash with different stages appear simultaneously, alternately, the rash in one site heals, then the rash appears in another, and the possibility of spreading Varicella - Zoster virus only ends when the entire rash is complete. dry and scaly on the body.
Most cases of chickenpox are mild and will go away on their own. However, if any of the following symptoms appear, see a doctor immediately:
The chickenpox rash has spread to one or both eyes. The rash becomes red, or painful (a sign that the rash may have become infected). Dizzy. Shortness of breath. Vomit. Stiff neck. Difficulty moving. Fever of 390C or higher. Close-up image when infected with chickenpox virus Varicella - Zoster:
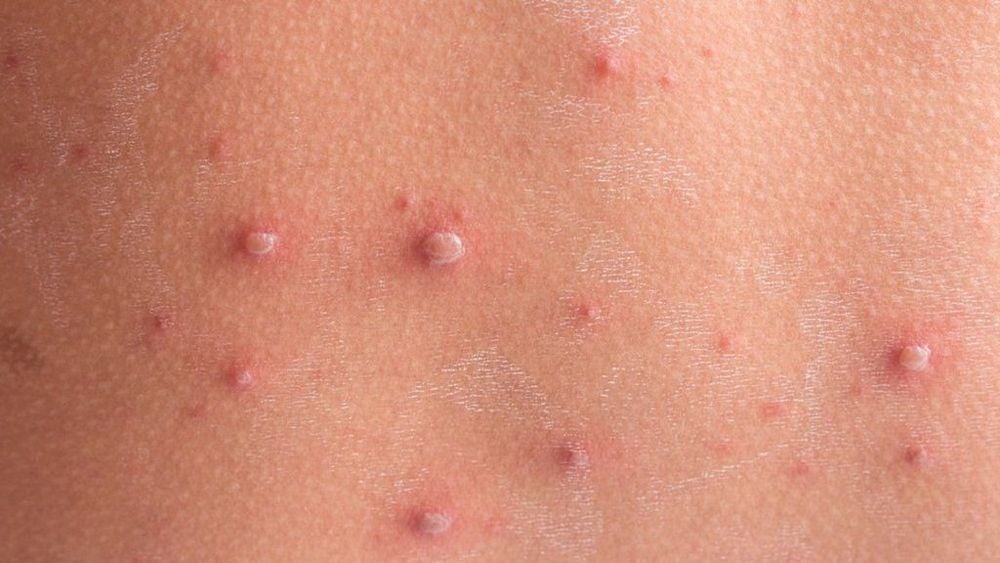
Thủy đậu
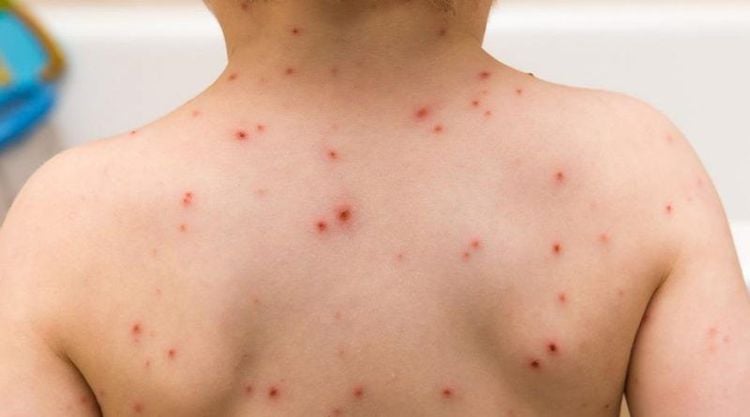
Thủy đậu
3. Complications of chickenpox
Chickenpox is usually a mild and benign illness. In rare cases the disease can be serious and cause complications including:Infections of the skin, soft tissues, bones, joints or sepsis. Loss of water. Pneumonia. Encephalitis caused by the Varicella-Zoster virus. Toxic shock syndrome. Reye's syndrome in children and adolescents with aspirin use during chickenpox. Dead. Those at higher risk of complications from chickenpox include:
Newborns and infants whose mothers have never had chickenpox or have never received the Varicella - Zoster virus vaccine. Teenagers and adults. Pregnant women who have never had chickenpox before. Smokers. People with weakened immune systems due to medications (such as chemotherapy) or medical conditions (such as cancer, HIV, etc.). People who are using steroid medicine for treatment (such as for asthma). Pregnant women with chickenpox can cause a number of complications such as low birth weight, limb abnormalities,... These complications can occur when a pregnant woman has chickenpox in early pregnancy. period. When a mother gets chickenpox in the last week before giving birth or in the first days after giving birth, the baby faces a higher risk of serious and potentially life-threatening infections.
4. Chickenpox Prevention
Using the Varicella - Zoster virus vaccine is the best way to prevent chickenpox . The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that if the vaccine is used correctly and at the recommended dose, it will provide complete protection up to 98%. Although it is not possible to guarantee complete protection for all cases, vaccination can still reduce the severity of the disease in those who are still infected.Vaccine - the chickenpox virus vaccine should be given in two doses, one dose when the child is between the ages of 12 and 15 months, the second dose when the child is between the ages of 4 and 6. Children 7 to 12 years old who have never been vaccinated should receive 2 doses at least 3 months apart. Children 13 years of age and older and adults who have never received the vaccine should receive 2 full doses at least 4 weeks apart.
Contraindications to the use of varicella vaccine include:
Pregnant women. People who are immunocompromised due to illness or medication. People who are allergic to gelatin or the antibiotic neomycin. The varicella vaccine, if used correctly, is completely safe and highly effective in preventing the disease.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: webmd.com